Imagine being able to buy stocks worth more than the capital you currently hold! MTF is a facility that you can use to magnify your returns using little capital. Consider it as a short-term loan from your stockbroker, where you as an investor will have to pay a small proportion of the total investment amount and the broker helps cover the rest.
However, it is necessary to find brokers that offer MTF at reasonable interest rates as interest charged on the amount availed via MTF can reduce investment returns. In this blog, we will give you a list of brokers that provide MTF at lowest interest rates.
Understanding Margin Trading Facility (MTF)
MTF is a service offered by brokers through which they lend money to investors or traders and charge interest in return. This interest rate associated with the loan taken via MTF is known as MTF interest rate and brokers usually charge a daily fee on the amount funded.
It is crucial to select the broker that offers MTF at a low interest rate as it can impact your profit as well as the losses, if you keep the position open for weeks or months. Low MTF interest rates help reduce trading costs; thereby increasing profitability. Now lets look at the top 10 brokers with the lowest MTF rates in India.
Top 10 Brokers Offering the Lowest MTF Interest Rates in India (Comparison Table)
| Broker | MTF Interest Rates | Per Day charges per Lakh |
|---|---|---|
| Pocketful | Starts from 0.0164% per day (5.99% p.a.) for amounts up to ₹1,00,000, varies based on funded amount. | ₹16.4 |
| Zerodha | 0.04% per day (14.6% p.a.) | ₹40 |
| ICICI Direct | 0.026% to 0.049% per day (9.69% to 17.99% p.a), varies based on brokerage plans | ₹26 to ₹49 |
| Groww | 0.041% per day (14.95% p.a.) | ₹41 |
| Kotak Securities | 0.026% per day (9.75% p.a.), varies based on brokerage plans | ₹26 |
| mStock | MTF interest rates are slab based Above ₹5 crores : 0.0192% per day Above ₹25 lakh to ₹5 crore : 0.0274% per day Up to ₹25 lakh : 0.0411% per day | ₹41 |
| Paytm Money | 0.026% to 0.041% per day (9.75% to 14.99% p.a.) – varies based on slab | ₹26 |
| 5paisa | 0.045% per day (16.425% p.a.) | ₹45 |
| Dhan | 0.034% to 0.045% per day (12.49% to 16.49% p.a.) varies based on Gross Holdings | ₹34 |
| Angel One | 0.041% per day (14.99% p.a.) | ₹41 |
| Alice Blue | 0.049% per day (18% p.a.) on the funded amount. | ₹49 |
| Arihant Capital | 0.05% per day (18% p.a.) on outstanding debit for MTF positions. | ₹50 |
| Mirae Asset Sharekhan | Up to 18% p.a. interest on MTF facility balance (standard rate) per terms. | ₹49 |
| HDFC Securities | 12% p.a. interest for their “Buy Stocks Pay Later / MTF” offering. | ₹33 |
| Lemonn | 0.0273% per day (10.95% p.a.) interest rate. | ₹30 |
Overview of Top 10 Brokers with the Lowest MTF Rates in India
1. Pocketful
Pocketful is an emerging stock broking firm and is a subsidiary of Pace Stock Broking Services. It is a growing and well trusted platform which provides a modern trading experience to the users. It has been developed by professionals with more than 27 years of experience and offers free equity delivery and zero account opening fees, making it the best option for both traders and investors.
MTF Interest Rate: Currently, they are offering the lowest MTF interest rate in the stock market, starting at just 5.99% p.a. which means per day rate of 0.0164% on borrowed funds up to ₹1,00,000. For funded amounts between ₹1,00,001 and ₹25,00,000, the MTF interest rate is 14.60% p.a. (0.040% per day) and for funded amounts above ₹25,00,000, the MTF interest rate is 16% p.a (0.0438% per day)
Check Out – Stocks Available for MTF
2. Zerodha
It is one of the largest discount brokers in India, which charges low brokerage and consists of an advanced trading platform called Kite. Many traders in India begin their stock market journey with Zerodha, which has revolutionized online investing through its easy-to-use platforms.
MTF Interest Rate: Unlike Pocketful, Zerodha charges a daily interest of 0.04% on borrowed funds, i.e. an annual interest rate of 14.6%.
3. ICICI Direct
It is one of the best suited platforms for investors looking for a 3-in-1 account as it provides demat, trading and banking services to the customers. Backed by ICICI Bank it provides secure and comprehensive financial services.
MTF Interest Rate: Borrowing costs or MTF interest rates vary depending upon the brokerage plan. The brokerage plan can cost as low as 9.69% per annum for some plans, while other plans can charge up to 17.99% per annum.
4. Groww
Groww has a user friendly trading app with exceptional user interface, making trading easier for beginners as well as the advanced traders. It has a vast customer base and offers real time market data, advanced charts for you to make informed trading decisions.
MTF Interest Rate: An annual charge of 14.95% per annum is charged that roughly translates to 0.41% per day charge on the funded amount.
5. Kotak Securities
A prominent market player which has been around for many years, backed by the Kotak Mahindra Group. Investors often pick them for their in-depth research reports and personalized advisory services. The platform feels easy-to-use whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned trader.
MTF Interest Rate: Under the Trade Free Pro plan, margin funds cost roughly 9.75% per year, which makes them appealing to anyone who wants to borrow money without giving up too much in interest.
6. mStock
m.Stock is a next-generation stockbroking platform backed by Mirae Asset Financial Group, bringing global financial expertise to Indian investors. Trusted by 22 lakh+ users, it offers a secure and powerful trading ecosystem with equities, IPOs, mutual funds, F&O and ETFs available through advanced web and mobile platforms. Known for competitive pricing and cutting-edge tools, m.Stock has quickly become a leading name in India’s discount brokerage space.
MTF Interest Rate: m.Stock follows a slab based system with 0.0411% per day up to ₹25 lakh, 0.0274% per day for ₹25 lakh to ₹5 crore, and 0.0192% per day above ₹5 crore.
7. Paytm Money
A digital platform to invest and trade, that is an integrated part of the wider Paytm ecosystem. New users like one-click mutual fund purchase and the chat-support built right into the app. Serious investors appreciate seamless trading and investing.
MTF Interest Rate: The broker recently switched to a slab based system, on book sizes up to 1 lakh, the rate is about 9.75% p.a. Borrowings between 1 lakh to 25 lakh range usually see a 14.99% per annum. However, if book size is above 25 lakh, then again the rate will come down to 9.75% p.a.
8. 5paisa
It is a budget-friendly stock broker that lets you trade cost-effectively but still offers a lot of features. It is perfect for active traders who want to keep costs down while putting in orders all day.
MTF Interest Rate: When it comes to Margin Trading Facility (MTF) money, the daily interest charge is 0.045% which roughly translates to 16.425%. It is slightly on the higher side and when you compare this with the Pocketful MTF rate, the difference is huge.
9. Dhan
It is a brokerage platform built using the latest technologies, integrated with advanced tools for traders. This trading ecosystem includes : Dhan mobile app, the web dashboard, and even integration with TradingView for an ultimate trading experience.
MTF Interest Rate: Interest on borrowed capital (MTF) is in 5 brackets. It starts at 12.49% a year, or nearly 0.034% per day, for an amount funded up to ₹5 lakh. From 5 Lakh to 10 Lakh, the interest rate is 13.49% p.a. The rate rises up as the funded amount increases. The highest rate is for the amount funded above 50 Lakh which is 16.49% p.a.
10. Angel One
Angel One has been around long enough to win the trust of traders, yet remains relevant due to continuous technical upgrades. The platform provides an easy to use mobile app and levies standard brokerage charges. On its platforms, one can easily hop between research reports, charts, and executed trades.
MTF Interest Rate: The daily interest charged is around 0.041% which constitutes to 14.99% in a year, which is pretty much on par with the market but definitely much higher than what is offered at Pocketful.
11. Alice Blue
Alice Blue is a popular brokerage known for its user-friendly platform ANT and competitive brokerage plans. It offers MTF to traders with a simple interface and real-time data.
MTF Interest Rate: Charges a daily interest of 0.049% on borrowed funds, i.e., an annual interest rate of 18%.
12. Arihant Capital
Arihant Capital is a full-service Indian broker with a wide range of services including its trading platform “ArihantPlus”. For its Margin Trading Facility (MTF) product, they allow clients to purchase approved stocks by paying a margin (typically around 22-40% depending on the stock) and borrowing the rest.
MTF Interest Rate: They charge interest at 0.05% per day on the outstanding borrowed amount (which translates to 18% p.a.) for MTF positions.
13. Mirae Asset Sharekhan
Mirae Asset Sharekhan is one of India’s leading brokers with a strong presence in retail and institutional trading, offering an intuitive platform for new and experienced traders.
MTF Interest Rate: Charges up to 0.0493% per day on borrowed funds, i.e., an annual interest rate of 18% (upper benchmark).
14. HDFC Securities
HDFC Securities provides a trusted trading platform with research-backed recommendations and multiple investment products, catering to both beginners and seasoned investors.
MTF Interest Rate: Charges a daily interest of 0.0329% on borrowed funds, i.e., an annual interest rate of 12%.
15. Lemon
Lemonn is a growing discount broker offering low brokerage and a simple, fast trading platform for retail traders entering the Indian markets.
MTF Interest Rate: Charges a daily interest of 0.0273% on borrowed funds, i.e., an annual interest rate of 10.95%.
Importance of Low MTF Interest Rates
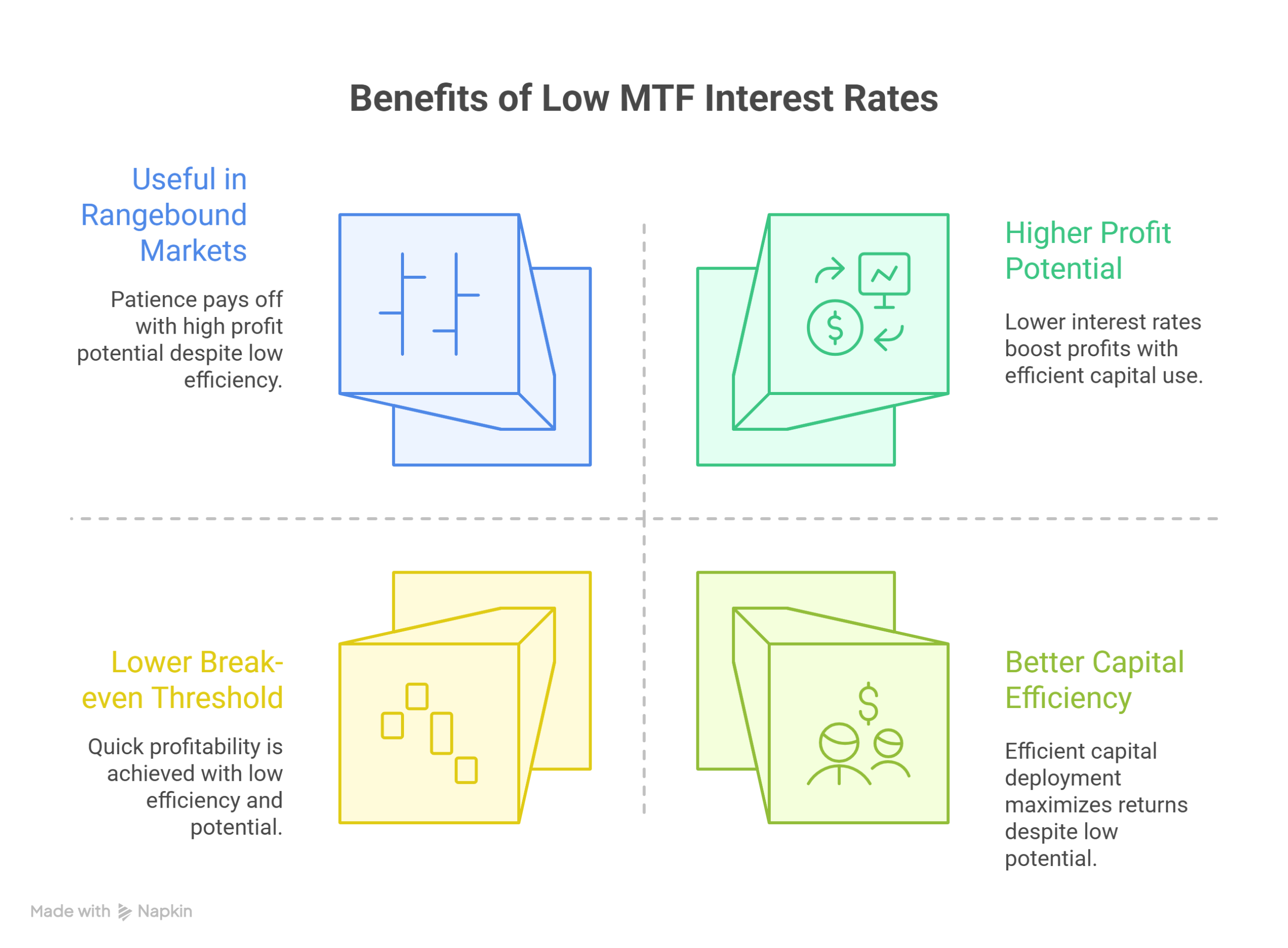
Borrowing money in the stock market through Margin Trading Facility (MTF) can benefit traders with higher profits. And borrowing money with the lowest interest rate in the market is icing on the cake. Some of the key benefits of using MTF with low interest rate are:
- Higher Profit Potential: Lower MTF interest rates can significantly boost your profits as lower interest rates help an investor reduce costs.
- Useful in Rangebound Markets: Stock prices can remain rangebound for a long period before moving in your predicted direction. When the cost to borrow is cheap, you aren’t worried about borrowing costs and can patiently wait to realize profits.
- Better Capital Efficiency: With reduced borrowing costs, traders can deploy capital more efficiently across multiple trades without worrying about high interest payments eating into returns.
- Lower Break-even Threshold: A lower interest rate reduces the minimum price movement needed to cover costs, allowing traders to achieve profitability faster even with small price swings.
MTF: When to Tap the Borrowing Button, When to Hold Back?
Margin Trading Facility (MTF) lets you borrow funds so that you can increase your buying power. That extra firepower can pay off big, yet the same leverage can flip on you faster than you expect. Here are some of the drawbacks:
- Risky for Beginners: MTF is not recommended for those new to the stock market. If you have just started trading , it is better to trade only with the money you have. Start with the basics and skip the borrowed cash aka MTF for now. Borrowing makes sense only after you have a good grasp of the risks that tag along.
- Volatile Stocks: Using borrowed money to invest in highly volatile or high beta stocks is risky. These are stocks whose prices can swing dramatically both up and down. A sudden price drop could force you to sell at a significant loss, making it difficult for you to repay your MTF loan. Remember when using any kind of leverage, higher potential profits also mean higher potential losses.
- Avoid MTF when you’re Uncertain: It is wise not to borrow if you are not fully confident in a company’s future performance, such as its future growth prospect or the success of a new product. In these situations, it’s often better to be patient and wait for more clarity. Also, one can buy using their own funds in such situations instead of using MTF.
- Plan to hold for Long term: Margin trading facility, or MTF, probably isn’t your friend if you are a long term investor and want to hold stocks for years. The daily borrowing charges can pile up and reduce your gains.
Use our Margin Trading Facility Calculator
Conclusion
As we all know leverage is like a double-edged sword, the funds borrowed using Margin Trading Facility (MTF) are no different. If used wisely, it has the potential to enhance your returns significantly, whereas if used carelessly can cause you huge losses. However, it is always recommended to select the broker that offers MTF at lowest rates.
Choosing a broker with the lowest MTF fee is crucial as a tiny difference in MTF interest rates can result in big savings down the road. Pocketful offers you MTF at lowest interest rate in the market, starting at just 5.99% p.a. You can open a demat account with Pocketful for free with zero AMC.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which broker offers the lowest MTF interest rate in India?
Pocketful currently offers the lowest MTF interest rate starting at 5.99% p.a.
Which broker has the lowest MTF charges per day?
Pocketful has one of the lowest daily MTF costs at 0.0164% per day for up to ₹1 lakh funding.
What is a good MTF interest rate for traders?
A good rate is between 6%–10% p.a. Anything above 14–18% significantly increases cost.
How is MTF interest calculated and billed?
Most stock brokers calculate the MTF charges on a daily basis, which adds up until the position is closed. However, the MTF charges are deducted on a weekly basis usually.
What are the main costs associated with MTF besides the interest rate?
Apart from brokerage charges, it is important to check pledge and unpledge charges as the securities bought using MTF are automatically pledged and then unpledged when sold. Also, if your balance dips too low, some brokers automatically liquidate your position and may hit you with margin call penalties.
For how long can I hold shares bought using MTF?
Most brokers in India allow you to hold shares for an unlimited time period.
How Do I Pay Back the MTF Loan?
Repaying your MTF loan is an easy process. When you sell the shares that were bought using MTF, the broker deducts what you owe-plus any interest charges and then deposits the leftover cash into your trading account.
What should the traders do if there is a margin call?
Traders must deposit cash into their trading account quickly as most brokers give you less than a full day to fulfill the margin requirements. If delayed, the broker can start selling your stocks to cover the shortfall along with margin call penalty.