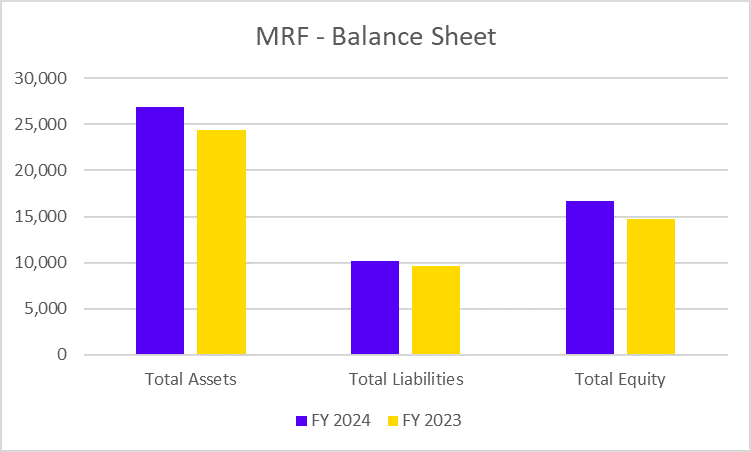
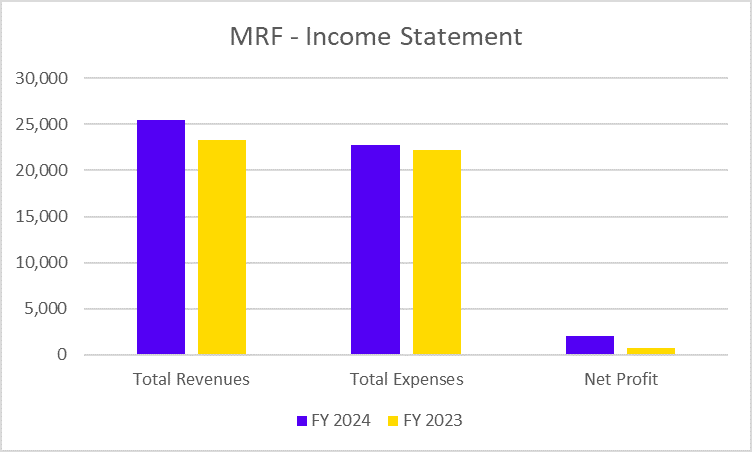
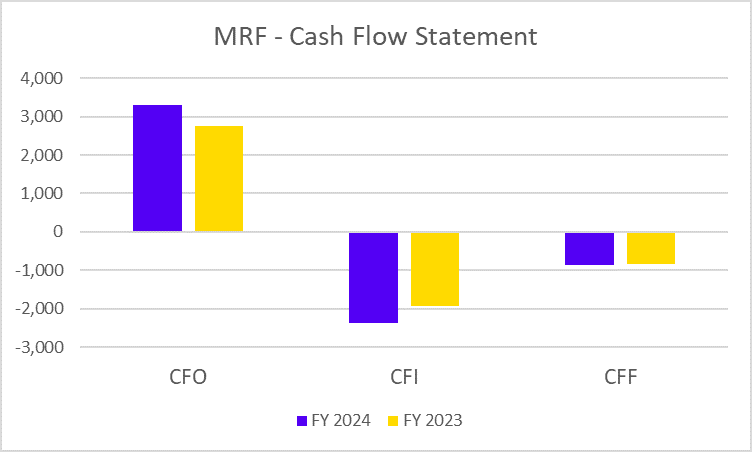
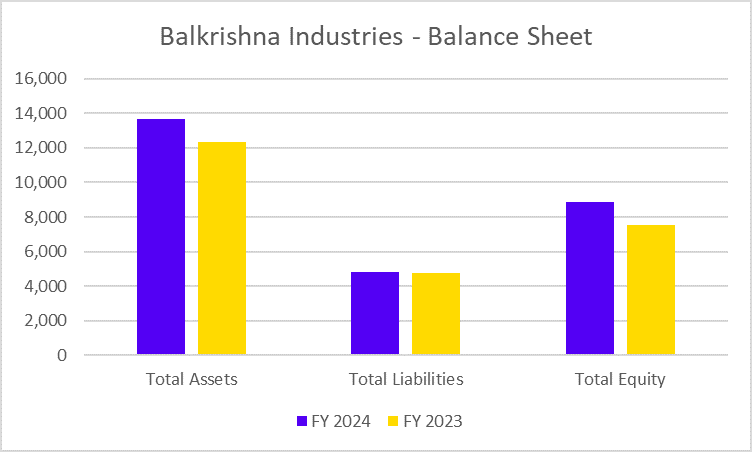
Did you know you can grow wealth while staying true to your Islamic values? Shariah-compliant mutual funds provide investors with the solution who seek the balance between ethics and investments.
In this blog, we will explore the key features, benefits, risks, etc. of Shariah-compliant mutual funds.
Overview Shariah-Compliant Mutual Funds
Sharia-compliant mutual funds are a form of investment vehicle curated for investors who want to align their investments with Islamic principles. These funds follow the guidelines of Sharia law, which forbids activities such as interest-based earnings, gambling, and investing in sin industries like alcohol and tobacco.
What is Shariah Law?
Shariah law is a religious law in the Islamic culture. It is not a set of fixed rules but divine guidance for Muslims to lead an ethical and moral life. It is derived from two sources:
Quran – the holy book of Islam.
Hadith – teachings and practices attributed to Prophet Muhammad.
The main objective of this law is to guide Muslims in every aspect of life, including religious practices, social interactions, and business & financial dealings.
Features of Shariah-compliant Mutual Funds
- These mutual funds invest only in companies that follow Islamic law. They prefer investing in companies with lower debt levels and ethical business practices.
- Interest income is prohibited (Riba), i.e., investment in companies that deal with interest-bearing instruments are not allowed including traditional banks and financial institutions.
- A board consisting of Islamic scholars supervises these funds to ensure that the investments comply with the Shariah law and check the fund’s investments and strategies to ensure they follow Islamic principles.
- These funds use profit-sharing structures instead of earning interest, which means that the investors share the profits or losses of the companies in which they have invested.
- Transactions with excessive uncertainty or speculation are not permitted. This includes derivatives and speculative trading.
- Investments can sometimes generate income from activities that do not comply with the Sharia law. However, such income is donated to the charity.
Shariah Indices of Shariah-Compliant Mutual Funds
The Shariah Indices are designed to offer investors Shariah-compliant investment solutions. In India, both the leading exchanges, i.e., NSE and BSE have their own Sharia Indices.
Shariah-compliant BSE Indices:
1. BSE Tasis Shariah 50 Index: It is the first Shariah compliant equity index in India constructed using the strict guidelines and local expertise of India-based Shariah advisory board. The index consists of the 50 largest and most liquid Shariah compliant stocks within the BSE 500 universe.
Shariah-compliant NSE Indices:
NSE Indices Limited calculates three Shariah indices: Nifty 50 Shariah, Nifty 500 Shariah, and Nifty Shariah 25.
1. Nifty Shariah 25: It represents 25 Shariah compliant stocks selected based on higher free-float market capitalization and aggregate traded turnover.
2. Nifty 500 Shariah: In this, constituents of the Nifty 500 index are screened for Shariah compliance. The compliant stocks form the Nifty 500 Shariah index.
3. Nifty 50 Shariah: In this index, the constituents of the Nifty 50 index are screened for Shariah compliance. The compliant stocks form the Nifty 50 Shariah index.
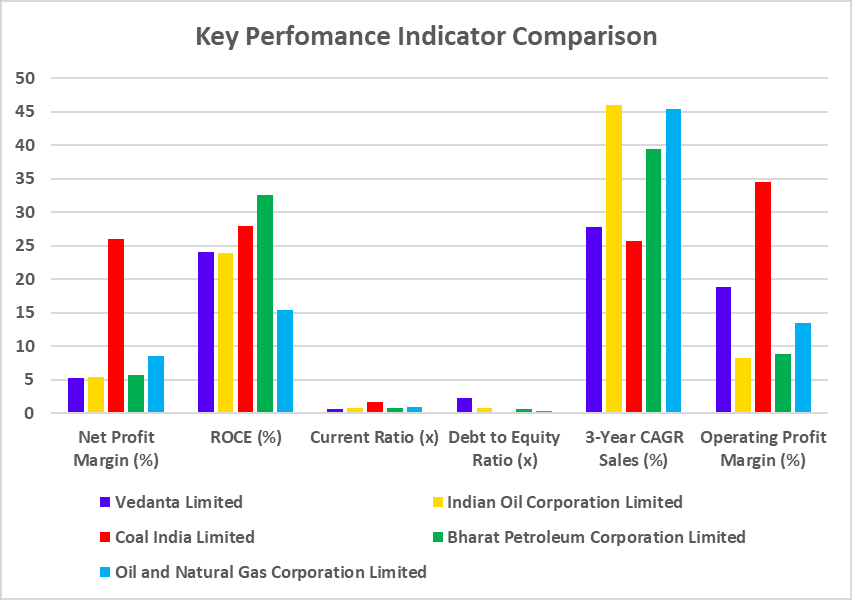
The top constituents of Nifty 50 Shariah by weightage are as follows:
| Company’s Name | Weight (%) |
|---|---|
| Tata Consultancy Services Ltd. | 20.54 |
| Hindustan Unilever Ltd. | 15.21 |
| Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd | 8.51 |
| HCL Technologies Ltd. | 6.45 |
| Asian Paints Ltd. | 5.73 |
| UltraTech Cement Ltd | 5.31 |
| Coal India Ltd. | 4.68 |
| Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd. | 4.58 |
| Nestle India Ltd. | 4.22 |
Read Also: How to Check Mutual Fund Status with Folio Number?
Shariah-compliant Funds in India
Tata Ethical Fund
This is the mutual fund offered by Tata Mutual Fund in India. It invests in equity and equity-related instruments of companies that comply with Islamic investment guidelines and is meant for medium to long-term investors.
Nippon India ETF Shariah Bees
It is an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) that helps investors to invest in Shariah-compliant fund. It mirrors the Nifty 50 Shariah Index.
Taurus Ethical Fund
It is a Shariah-compliant mutual fund launched by Taurus Mutual Fund in April 2009. Investors looking for investment opportunities that comply with Shariah norms can invest in this fund with a medium to long term investment horizon.
Tax Implications of Shariah-Compliant Mutual Funds

Shariah-compliant mutual funds are subject to the same tax regulations as conventional mutual funds, i.e., their gains are taxed according to the existing tax laws. These funds invest majorly in equity and equity related instruments. As per current taxation law in India, if a mutual fund has at least 65% investments in equity then it will carry equity taxation.
And for that, STCG and LTCG will apply if the holding period is less than a year and LTCG if the holding period exceeds one year.
- Short-term Capital Gains (STCG) – If holding period is less than a year, then STCG will apply @15% on gains without any indexation benefit.
- Long-term Capital Gains (LTCG) – If the holding period exceeds one year, then LTCG will apply @10% on gains. Also, there is no LTCG tax till the income of INR 1 lakh.
Key Points to Consider
When analysing Shariah-compliant mutual funds, it is necessary to consider multiple factors. Below mentioned are some of the factors:
- Companies involved in activities prohibited by the Shariah law are excluded. For example, alcohol, tobacco, gambling, etc. are prohibited.
- The law discourages excessive debt financing. Hence, the company’s debt should be limited in relation to its equity.
- Investors must ensure that only a minimal portion of a company’s income is derived from the restricted activities mentioned in points one and two.
- Shariah law mandates that compliant funds must emphasize ethical business practices and social responsibility alongside financial performance.
Benefits of Shariah-Compliant Funds
- These funds let investors invest in companies that function according to Islamic ethical guidelines. Investors of Shariah compliant mutual funds can grow wealth while staying true to your Islamic values.
- With a major focus on lower debt levels, Shariah-compliant mutual funds can offer long-term growth to investors.
- The screening process assures investors that their money is being managed according to Islamic principles.
Risks involved in Shariah Compliant Funds

- These funds have fewer companies to invest in than traditional funds because the screening process eventually limits diversification and exposure to high-growth sectors.
- A smaller investment universe can lead to overall lower returns if the excluded sectors perform better than the overall market.
- Shariah-compliant funds focus more on specific sectors that follow Shariah law during the screening process. This increases the concentration risk for the fund if those sectors witness a significant downfall.
Conclusion
To sum it up, Sharia-compliant mutual funds assist you in growing your wealth in line with the Islamic values. While these funds are a great way to participate in the financial markets ethically, they also come with specific risks and considerations.
It is crucial to understand the screening process, as well as the benefits and risks involved before investing in these funds.
| S.NO. | Check Out These Interesting Posts You Might Enjoy! |
|---|---|
| 1 | What Is An IPO Mutual Fund? Should You Invest? |
| 2 | Mutual Fund Taxation – How Mutual Funds Are Taxed? |
| 3 | Is Your Mutual Fund Investment Safe? |
| 4 | What is an Open-Ended Mutual Fund & How to Invest in it? |
| 5 | How to Cancel Mutual Fund SIP? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Sharia-compliant mutual fund?
Sharia-compliant mutual fund invests in companies that follow Islamic principles and prevent things like interest, alcohol, and gambling.
Why should I invest in Sharia-compliant funds?
One can invest in such funds because they align investments with Islamic values and promote ethical business practices.
What lead to the evolution of Shariah-compliant mutual funds?
The idea likely arose in the mid of 1960s as Muslim communities in regions like Southeast Asia sought financial instruments that followed Islamic principles and the evolution is not attributed to a single person.
What is TASIS?
Taqwaa Advisory and Shariah Investment Solutions, or TASIS is India’s Shariah advisory institution in the field of Finance. Their advisory board boasts internationally renowned Shariah scholars.
What is Shariah law?
It is a religious law in the Islamic culture and serves as a divine guidance for Muslims to lead an ethical and moral life. It is derived from the Quran and Hadith.