India’s IT industry has made a strong presence globally, with HCL Technologies and Infosys being the two major players. Infosys today offers its services in 56 countries and its brand value is expected to exceed $16 billion in 2025, making it among the top 3 IT service brands in the world. HCLTech, on the other hand, is active in 60 countries and has more than 200 delivery centers.
In this blog, we will compare various aspects of “HCL vs Infosys” to help investors, analysts, and students understand the position of these companies.
Company Overview: HCL Technologies
HCL Technologies, popularly known as HCLTech, is one of the top IT companies in India. It was started in 1976 by Shiv Nadar and his team. Earlier this company was hardware focused, but in the 90s it entered the software and IT services sector. Today HCLTech is working in more than 60 countries of the world and has 200+ delivery centers and 150 innovation labs. Its clients come from sectors like banking, healthcare, auto, telecom and retail. The chairperson of the company is Roshni Nadar Malhotra and the CEO is C. Vijayakumar, who is leading the global growth of HCL.
Business model
HCL Tech’s business model is quite diverse and this company provides a variety of services in different sectors. It has three main business verticals:
- IT and Business Services (ITBS): This includes application development, cloud, digital processing and infrastructure services.
- Engineering and R&D Services (ERS): Technology solutions ranging from product design to manufacturing.
- HCL Software: Operates solutions acquired from IBM such as AppScan, BigFix and Notes/Domino.
In terms of revenue, the company earns from fixed-price and time-based contracts, as well as sells its products on a subscription model. HCL’s focus is on value-driven and client-need-based service delivery, making it trusted by customers around the world.
Read Also: HCL Technologies Case Study: Financials, KPIs, And SWOT Analysis
Company Overview: Infosys
Infosys was started in 1981 by Narayan Murthy and his team with a capital of just ₹ 10,000, and today it is counted among the most trusted IT companies in India. The company is operating in more than 56 countries and its brand value has crossed $ 16 billion in 2025. Infosys is recognized globally for its digital transformation, AI and cloud solutions.
Its clients include Fortune 500 companies, and it provides technology services in sectors such as BFSI, healthcare, manufacturing, and retail. The CEO and MD of Infosys is Salil Parekh, under whose leadership the company is constantly moving towards innovation and growth.
Business Model
The business model of Infosys is client-centric and technology-driven. The company earns revenue from four main areas:
- Digital Services: Which includes cloud, data analytics, and AI based solutions.
- Consulting and Outsourcing: Provides services to clients from end-to-end business strategy to IT implementation.
- Enterprise Applications: Solutions on platforms like SAP, Oracle.
- Managed Services: Long-term support of infrastructure and applications.
Infosys’ model is scalable and globally competitive, in which the ‘Global Delivery Model’ plays a major role. This model helps the company to provide high-quality services at low cost.
Read Also: Infosys Case Study: Business Model and SWOT Analysis
Who is Better: HCL Technologies Or Infosys?
In 2025, both HCLTech and Infosys have shown significant progress in their respective fields.
- Financial performance : Talking about financial performance, Infosys’ total revenue was around ₹ 1.66 lakh crore, which is far ahead of HCLTech’s around ₹ 1.19 lakh crore. Also, Infosys’ net profit and operating margin are also better than HCLTech, which reflects the company’s operational efficiency and profitability.
- Strategic focus : In terms of strategic focus, HCLTech has secured large contracts in cloud migration and AI services, giving it a strong market presence among large enterprise clients. At the same time, Infosys has emphasized on AI-based new products and language model development, thereby playing a leading role in digital transformation.
- Global Presence : The global presence of both the companies is almost the same, both are operating in about 60 countries. But Infosys has been slightly better in adding new clients, which has diversified its revenue streams and customer base.
- Future plans : Both companies have prioritized balanced growth in their future plans. HCLTech is planning further expansion in the cloud and AI sector, while Infosys is focusing on improving operating margins and responsible use of AI.
Overall, both companies are strong in their respective domains of expertise and are making significant contributions to the IT industry. Saying who is better depends entirely on the investor’s risk profile and analysis of the company’s fundamentals. It is essential for investors to conduct a thorough analysis of both the companies along with management’s track record in delivering results before investing.
Comparative Analysis: HCL Technologies Vs Infosys
| Particulars | HCL Technologies | Infosys |
|---|---|---|
| Current Price (₹) | 1,740 | 1,623 |
| Market Cap (₹ Crores) | 4,72,151 | 6,74,187 |
| 52-W High (₹) | 2,012 | 2,007 |
| 52-W Low (₹) | 1,303 | 1,307 |
| FII Holdings as of March 2025 | 19.14% | 29.4% |
| DII Holdings (as of March 2025) | 15.48% | 34.46% |
| Book Value (₹) | 257 | 231 |
| PE Ratio | 27.1 | 25.4 |
Financial Statements Analysis
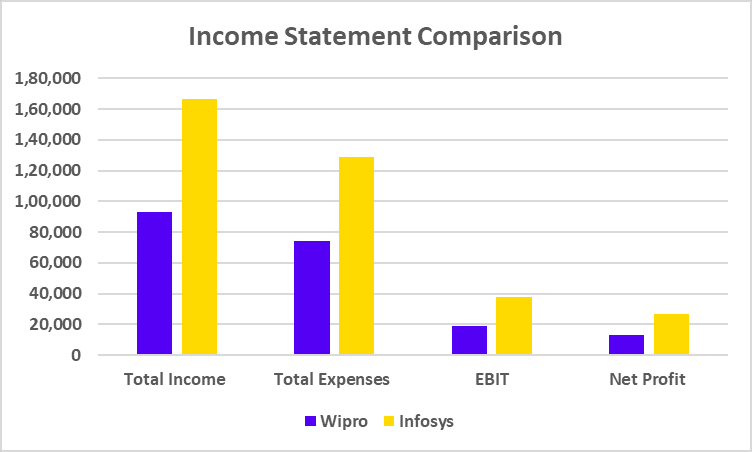
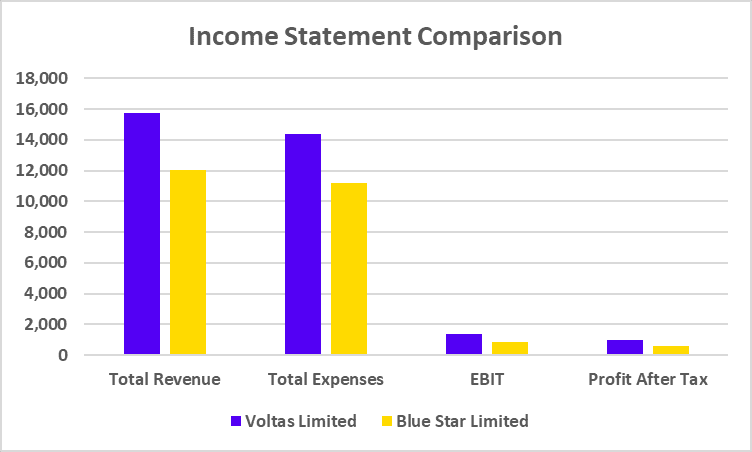
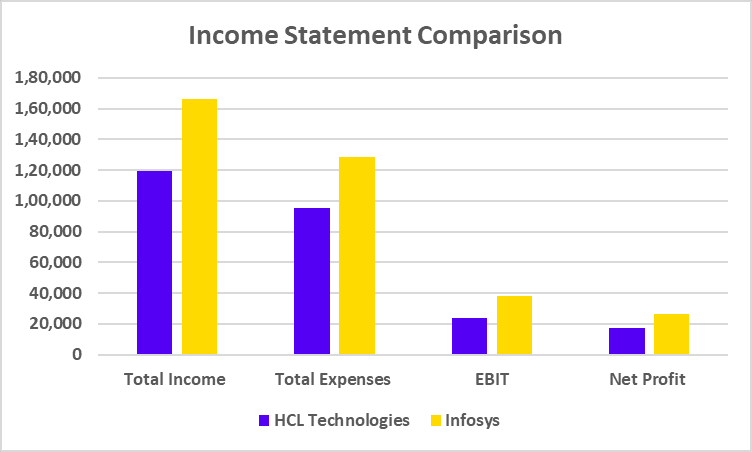
Income Statement Comparison
| Particulars | HCL Technologies | Infosys |
|---|---|---|
| Total Income | 1,19,540 | 1,66,590 |
| Total Expenses | 95,635 | 1,28,566 |
| EBIT | 23,905 | 38,024 |
| Net Profit | 17,399 | 26,750 |
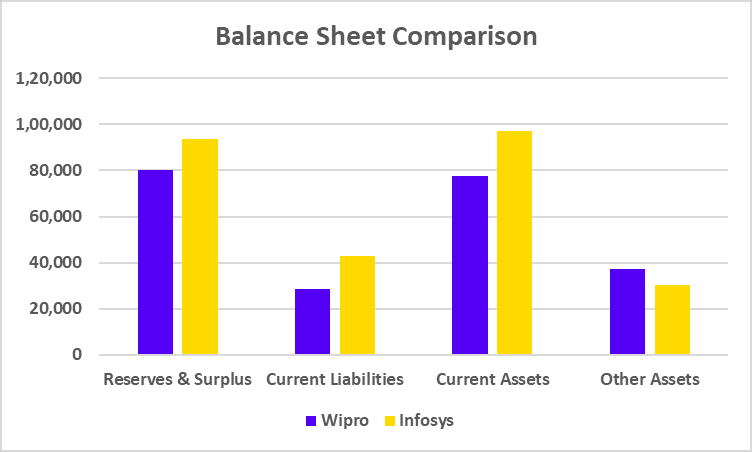
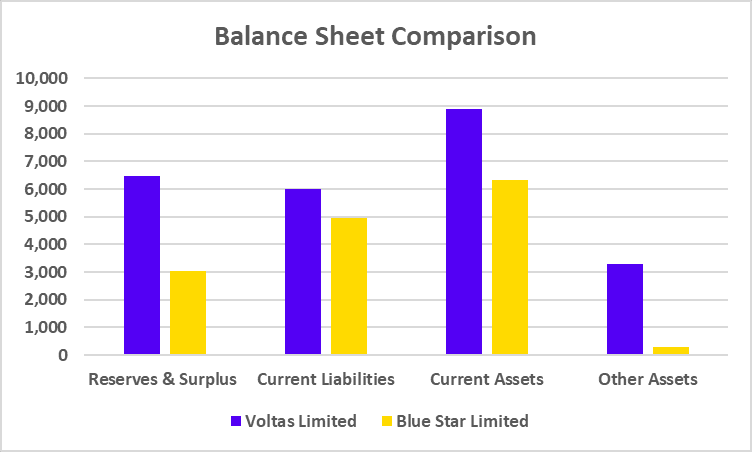
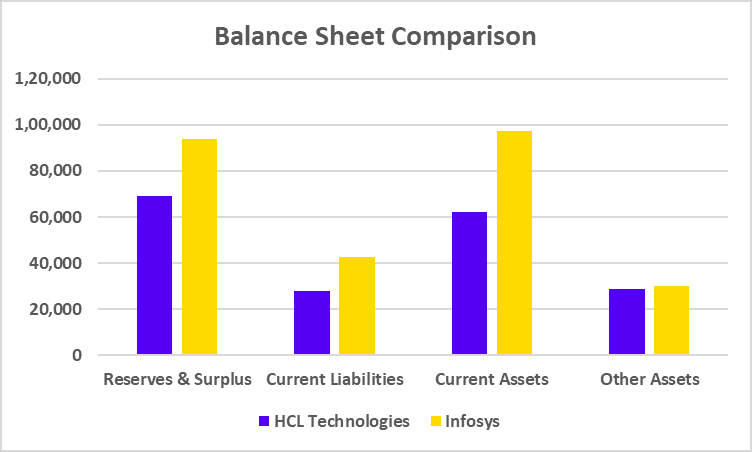
Balance Sheet Comparison
| Particulars | HCL Technologies | Infosys |
|---|---|---|
| Reserves & Surplus | 69,112 | 93,745 |
| Current Liabilities | 28,039 | 42,850 |
| Current Assets | 62,109 | 97,099 |
| Other Assets | 28,960 | 30,135 |
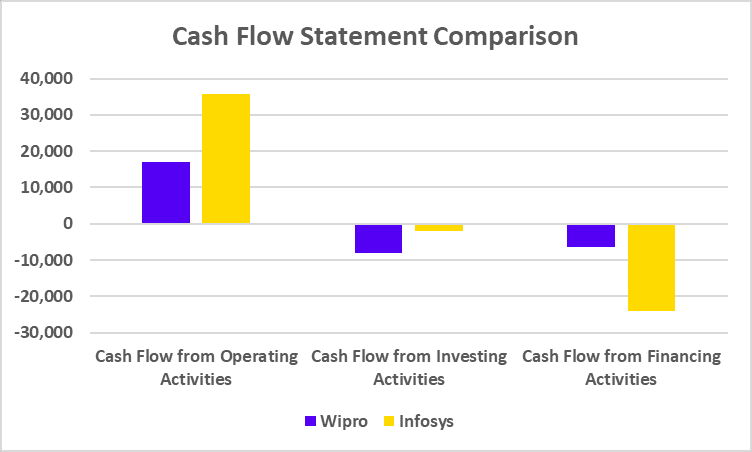
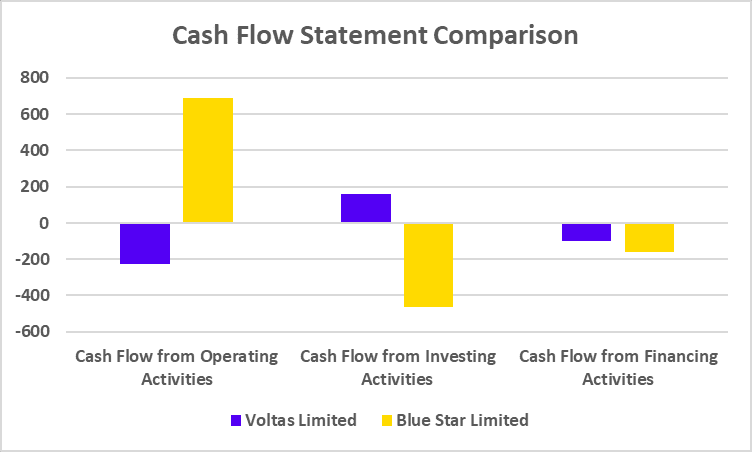
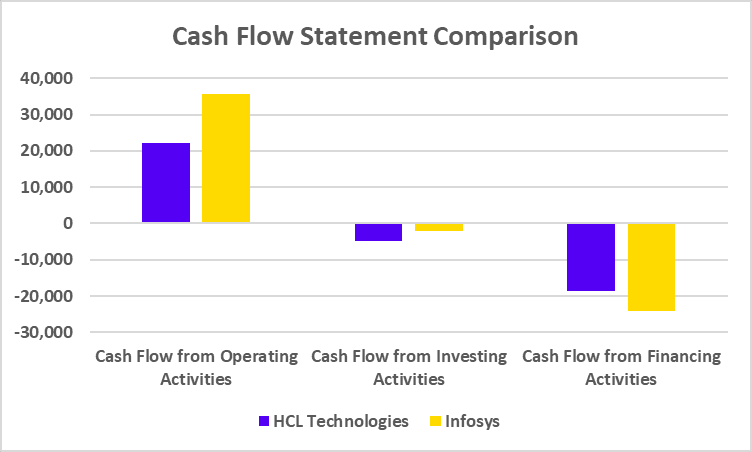
Cash Flow Statement Comparison
| Particulars | HCL Technologies | Infosys |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow from Operating Activities | 22,261 | 35,694 |
| Cash Flow from Investing Activities | -4,914 | -1,946 |
| Cash Flow from Financing Activities | -18,561 | -24,161 |
Key Performance Ratios (KPIs)
| Particulars | HCL Technologies | Infosys |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Profit Margin (%) | 20.42 | 23.32 |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | 14.86 | 16.41 |
| ROE (%) | 24.96 | 27.87 |
| ROCE (%) | 30.84 | 35.85 |
| Debt to Equity (x) | 0.03 | 0.00 |
Read Also: Infosys vs TCS: A Comparative Analysis of IT Giants
Future plans of HCL Technologies
The future plans of HCL Technologies are mentioned below;
- Investing and scaling in Generative AI : HCLTech has further strengthened its AI strategy in FY25. The company has launched platforms such as “AI Force” and “Enterprise AI Foundry”, which optimize the entire lifecycle of software development and product engineering. In the first quarter of FY25, HCLTech has signed 12 new AI-integrated deals, many of which involve developing AI solutions.
- Global expansion and partnerships : The company has further expanded its partnership with Google Cloud, under which 25,000 engineers will be trained on Google Gemini. In addition, HCLTech plans to set up a new AI/Cloud lab in Singapore, which will contribute to AI innovation and talent development in collaboration with local institutions.
- Employee skilling and training : By the end of FY25, HCLTech aims to train 50,000 employees in generative AI. For this, the company is using platforms such as “AI Force” and “AI Foundry”, which will enable employees to develop and implement AI-based solutions.
- Acquisitions and strategic partnerships : HCLTech plans acquisitions to strengthen its portfolio in regions such as Japan and Europe. The company is focused on semiconductor, automotive and platform-based businesses, which can provide stable revenue streams.
Read Also: SAIL Vs Tata Steel: Which is Better?
Future plans of Infosys
The future plans of Infosys are mentioned below;
- Investments in Generative AI and Cloud Services: Infosys forecasts its revenue growth for FY25 to be between 3% and 4%, reflecting the growing demand for AI and cloud services. The company is currently working on over 225 generative AI projects, and has integrated GenAI components across all of its service lines.
- Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions : Infosys has partnered with companies such as “Citizens Financial Group” and “Telstra”, enabling it to drive AI-driven transformation in the financial services and telecommunications sectors. In addition, the company has acquired “InSemi”, a German R&D company, strengthening its chip-to-cloud strategy.
- Employee Skilling and Training : Infosys has made significant investments to train its employees in GenAI, and its employees have already built over 3 million lines of code using large language models. The company aims to enable its employees to develop and implement AI-powered solutions.
- Responsible AI and Ethics : Infosys has launched the “Responsible AI Toolkit”, which helps ensure the ethical use of AI. This toolkit is helpful in identifying and addressing security risks, privacy violations, biased results, and other related issues.
Conclusion
Both HCLTech and Infosys are major players in the Indian IT sector, which have gained a strong foothold in the market on the basis of their respective strengths and strategies. While Infosys focuses more on digital innovation and operational excellence, HCLTech emphasizes on cloud services and large enterprise contracts. Both have displayed strong financial performance, but their future growth plans are different. Therefore, investment decisions should not be made only on the basis of financial metrics, but keeping in mind the company’s future plans, your individual goals and risk tolerance. It is advised to consult a financial advisor before investing.
| S.NO. | Check Out These Interesting Posts You Might Enjoy! |
|---|---|
| 1 | JK Tyre Vs CEAT: Which is Better? |
| 2 | XIRR Vs CAGR: Investment Return Metrics |
| 3 | ITC vs HUL: Comparison of India’s FMCG Giants |
| 4 | IndiGo vs SpiceJet: Which is Better? |
| 5 | Tata Motors Vs Ashok Leyland: Which is Better? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main difference between HCLTech and Infosys?
HCLTech focuses more on cloud and enterprise services, while Infosys leads in digital innovation and operational excellence.
Which company has better financial performance in 2025?
Infosys revenue and profit margins are better than that of HCLTech.
Are both companies expanding globally?
Yes, both companies are operating in around 60 countries and adding new clients.
Which company is investing more in AI and cloud services?
Both companies are investing in AI and cloud, but HCLTech has recently been more active in securing contracts related to cloud services.
Should I invest in HCLTech or Infosys?
The investment decision depends on your investment strategy and risk tolerance as both companies are strong players in the IT sector.