In the ever-evolving world of rapid delivery services, Zepto is a notable case as it has solved two major problems, i.e. convenience and speed. The company’s commitment to 10-minute delivery services has made it a key player in the quick commerce segment.
In this blog, we will cover the marketing strategy, business model, financials of Zepto, and a holistic SWOT analysis of Zepto. This will enable us to analyze the future growth prospects of Zepto.
Zepto: An Overview
Zepto was launched in July 2021 by Aadit Palicha and Kaivalya Vohra with the aim to deliver groceries in less than 10 minutes to its customers. Their claim of ten minutes grocery delivery has led to a surge in demand by users in the urban areas. The founders of Zepto are Stanford University dropouts who chose to launch Zepto in 2021 after securing funding from Contrary, a San Francisco-based venture capital firm.
Initially, the business was branded as KiranaKart and its business model relied on partnership with local kirana stores for grocery delivery. However, the business didn’t perform as expected, which led to a complete overhaul of the business model. The business was rebranded as Zepto, which focused on building ‘dark stores’ across the country to fulfill orders. This shift in business model helped them deliver groceries in under 10 minutes.

In 2022, Zepto launched Cafe, its coffee and ready-to-eat food delivery division focused on the demands of the urban population. The company also launched Bloom and Harvest Hero for farmers for better farm management and delivery of related products.
This case study will make you familiar with the innovative strategy, efficient business model, marketing tactics, finances, and SWOT analysis of Zepto.
Zepto Business Model Approach
Quick Commerce
Zepto employs innovative quick commerce strategies to provide 10-minute delivery of groceries and essential items, leveraging strategically placed ‘dark stores.’ These dark stores, which serve as mini-warehouses, are stocked with frequently purchased items and located in proximity to high customer populations.
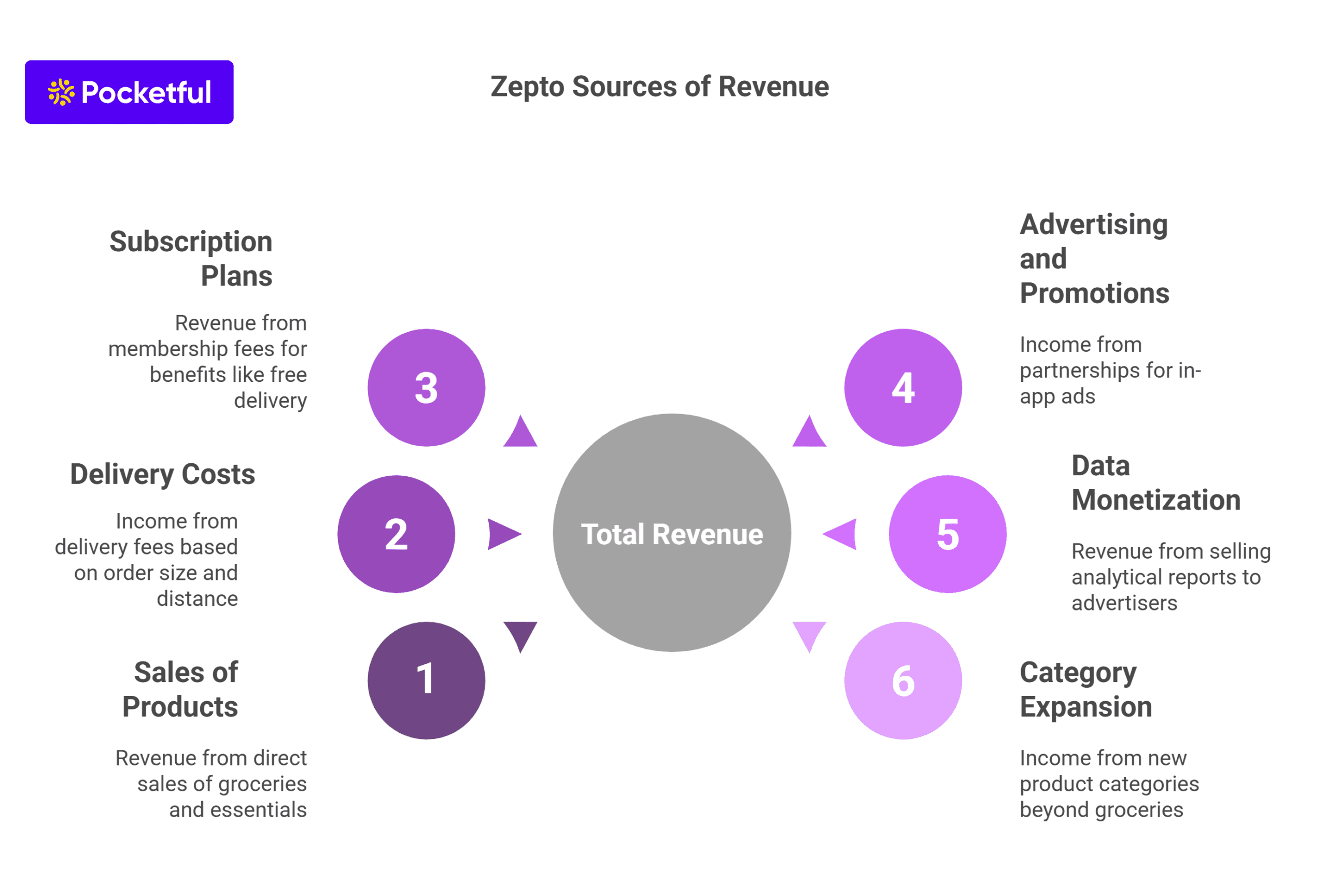
Zepto Sources of Revenue
The sources of revenue for Zepto are tailored around a variety of products as follows:
- Sales of Products – Groceries and daily essentials, which are sold directly to the buyers.
- Delivery Costs – Collection of varied delivery fees according to the size of the order and the distance.
- Subscription Plans – Charging membership fees where payments are made for plans that allow benefits such as free and cheap delivery along with other exclusive promotional offers.
- Advertising and Promotions: Partnering with businesses for in-app advertising and promotional tiles.
- Data Monetization: Using client information to offer analytical reports to advertisers and suppliers.
- Category Expansion: Identifying new areas other than grocery items for additional income.
Marketing Strategy of Zepto
The marketing strategy of Zepto is characterized by the themes mentioned below:
1. Speed and Convenience
Zepto’s core value proposition lies in its 10 minute delivery promise, which it highlights prominently in all marketing and branding materials. Urban consumers such as Gen Z & millennials form the majority of Zepto’s customer base due to their busy life schedules and urgency to get the products, which is addressed through the 10 minute delivery model.
Zepto uses this unique selling proposition (USP) everywhere including: online and offline ads, billboards, app store description, and social media. For advertising, the platform makes sure to offer convenience through accurate geolocation tracking, real time stock controls, micro-warehouses (dark stores), and much more.
2. Targeted Advertising
Zepto utilizes targeted advertising by launching marketing campaigns on social media apps such as Instagram, YouTube, Google Ads, and OTT platforms, driven by data related to urban millennials and Gen Z viewership habits. These campaigns combine elements of advertising and influencer marketing, especially with food and lifestyle influencers popular among youthful consumers.
The company also makes use of geotargeting capabilities to run ads relevant to the geographical location of the user. Moreover, Zepto’s advertisements demonstrate practical situations, such as running out of milk before the afternoon tea, depicting how it can help alleviate everyday problems quickly.
3. Referral Programs
Zepto’s referral programs are examples of virality-driven growth tactics designed to increase market share. Users gain discounts, free deliveries, or credits in exchange for inviting new participants through these self referral programs. Its effectiveness stems from a two sided reward system where both the referrer and the referee benefit from the referral program.
Time-sensitive referral rewards are displayed on the app interface, which lets customers earn 25% off on the next order (max ₹200) or a total of ₹2,000 for 10 successful referrals. This approach focuses on customer acquisition, engagement, and retention simultaneously.
4. Locally Targeted Campaigns
Recognizing how different neighborhoods have distinct consumer behavior, Zepto designs its marketing campaigns with a hyperlocal strategy. For instance, Zepto markets and focuses on region-specific and festival-specific products during local festivities like Ganesh Chaturthi in Mumbai or Pongal in Chennai with discounts. Colloquial language is strategically placed in the marketing messages to make the impact deeper.
Regional preferences shape customized smartphone push notifications, vendor advertising, and city-specific regional delights, which helps in making Zepto the go-to quick commerce app.
5. Collaborations
Deals with popular FMCG brands, D2C start-ups, and seasonal vendors are made by Zepto for new product launches, discounts, and limited-time offers. Added variety and low pricing increases the customer base of Zepto and those brands.
For example, a known beverages company could exclusively launch new flavor products on Zepto with 10-minute delivery. Launching on Zepto gives the new brand instant credibility and a customer base. Claiming they are not just a delivery service, but a platform that provides exclusive access and product browse for instant delivery helps the company’s image. These sponsorships are further advertised through social media for increased exposure.
Financial Analysis of Zepto
The financials of Zepto demonstrate how quickly the company is growing and the issues that come with trying to scale a quick-commerce business. Some of the key metrics related to Zepto’s valuation are listed below:
- The total funding raised was over $1.95 billion over 10 funding rounds as of 21 April 2025.
- The estimated valuation is around $5 Billion in 2025.
- Some of the key investors include Y Combinator, Nexus Venture Partners, Glade Brook Capital, and General Catalyst.
A detailed financial metrics is shown below :
| Financial Metrics | FY24 | FY23 | FY 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Revenue | ₹ 4,455 cr. | ₹ 2,026 cr. | ₹ 142 cr. |
| Total Expense | ₹ 5,747 cr. | ₹ 3,350 cr. | ₹ 532 cr. |
| Net loss | ₹ 1,249 cr. | ₹ 1,272 cr. | ₹ 390 cr. |
| Loss as % of Revenue | -28% | -63% | -275% |
SWOT Analysis of Zepto
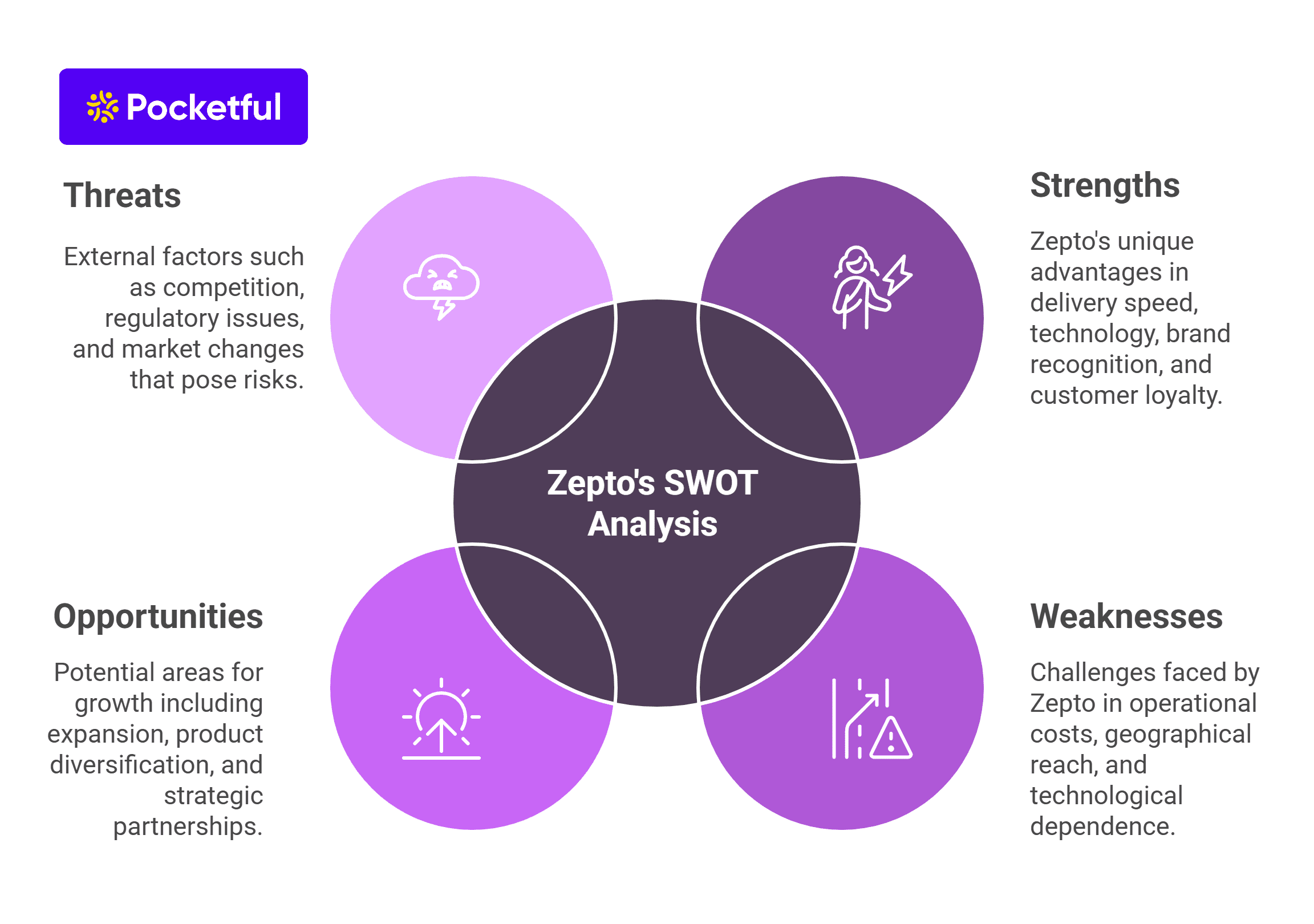
Strengths
- Ultra fast delivery: The quickest delivery in the market, Zepto’s 10 minute delivery, stands unmatched.
- Tech driven operations: AI and data analytics improve efficiency of inventory management and delivery.
- Strong brand recognition: Gaining brand recognition at a virtually unprecedented speed in urban India.
- High customer loyalty: Customers increasing orders and repeated purchases indicate loyalty towards the brand.
Weaknesses
- High operational costs: Harboring dark stores and the complete delivery value chain is expensive.
- Limited Geographical outreach: Primary exposure to metropolitan cities and very few expansion in tier 1 and 2 cities.
- Dependence on technology: In the event of shutdowns or technology glitches in the application, products may take longer than expected to get delivered.
Opportunities
- Geographical expansion: Moving into Tier 2 and 3 cities to widen the customer base.
- Diverse product offerings: Apart from groceries, the company can add electronics, personal care products, and other products with a higher price tag to improve its profit margins.
- Strategic Expansion with Local Businesses: Local vendors and brands can be collaborated with to provide customers with better products and reduced logistics.
- International Expansion: Venturing into the spaces outside India to increase its customer base.
Threats
- Intense Competition: Competing with players like Blinkit, Swiggy Instamart, and BigBasket is proving to be extremely challenging.
- Regulatory Issues: Possible scrutiny of pricing policies as well as labor practices.
- Sustainability Issues: The environmental ramifications of quick deliveries and excess packaging waste.
- Changes in the market: Changes in customer preferences may lower the need for ultra-fast deliveries.
Read Also: Blinkit Case Study: Business Model, Financials, and SWOT Analysis
Challenges Faced by Zepto
Like every other firm, Zepto has its set of challenges, from operational expenditures to competition. Here’s a snapshot of some of them:
1. High Operational and Logistics Costs
- Keeping Dark Stores Operational: Maintaining dark stores is not cost effective as most of the grocery items have a low shelf life and require refrigeration facilities.
- Staffing During High Demand Hours: Marketers, retail associates, and shelf fillers charge high salaries.
- Rental and Other Overheads: Rental and other overheads in urban areas, such as advertising, restocking, utilities, etc. increases the overall costs.
- Fleet Management: It is challenging to maintain a strong fleet of delivery partners as high attrition rates among freelance delivery staff is common.
2. Low Profit Margin
- Steep Discounts: Heavy cash rewards result in greater losses as the amount spent per customer reduces.
- Low order value: For orders above ₹199, the customer gets free delivery even with a low order value, leading to less revenue per order.
- Perishable Goods: Perishable goods like bread, vegetables and meat products generally require refrigeration and are at higher risk of going unsold.
3. Limited Reach
- Metropolitan cities: Only operative in major metro cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and Chennai.
- Limited accessibility to Tier 2 and 3 cities: These cities lack developed infrastructure, have minimal internet usage and also the consumer behaviour in these regions is different.
4. Intense Competition
Direct competition to Zepto includes Blinkit, Swiggy Instamart, BigBasket Now, Amazon Fresh, Reliance JioMart etc. These companies have a large customer base, established infrastructure, and significant financial resources.
5. Regulatory and Legal Risks
Compliance with social laws and legal frameworks poses risks due to strict controls placed on gig workers. In India, there is a rising focus on policies regarding labor benefits, compliance with wage laws and food safety laws requiring companies to operate within strict guidelines of FSSAI; these legal measures add complexity in operational processes.
6. Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Excessive fuel consumption during fast deliveries leads to increased CO2 emissions. Moreover, reliance on single-use plastics and cardboards results in wastage and environmental pollution. The adoption of eco-friendly materials and changing of operational structure in order to adopt new techniques result in an increase in expenses.
7. The Risks of Downtime and Dependency on Technology
Order complete! Zepto’s entire model relies on inventory tracking in real-time, AI demand forecasting, and route optimization. Every system failure, data breach, or app failure will result in order delays, cancellations and reputational damages.
8. Retaining Customers in a Discount-Centric Market
The user retention is accomplished primarily using coupons and discounts as customer behaviour is such that users can be easily swayed to a competing app if discounts are paused or cut.
Read Also: Blinkit vs Zepto: Which is Better?
Conclusion
Zepto has emerged as a game-changer in India’s quick-commerce industry, offering unmatched 10-minute grocery deliveries through its tech-enabled dark store network. With a sharp focus on speed, convenience, and customer experience, it has built strong brand recognition among urban consumers. While it faces challenges like high costs, limited reach, and stiff competition, its innovative business model, effective marketing strategies, and strong investor backing positions it well for future expansion. Zepto holds strong potential for long-term growth in the evolving commerce landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Zepto and how does it function?
Zepto is a quick-commerce start-up that brings groceries and essentials to customers’ doorsteps in under 10 minutes. Customers place orders through the Zepto app and the nearest dark store processes the order and hands it over to a delivery partner, achieving ultra-short delivery times.
How does Zepto manage to deliver groceries in just 10 minutes?
Ultra-fast delivery is possible for Zepto due to a combination of tech-enabled logistics, micro-warehousing, and sophisticated route planning algorithms. Zepto’s use of dark stores along with predictive systems to forecast demand, enables it to fulfill orders at record speeds.
Who are Zepto’s target customers?
Zepto target customers are urban millennials and Gen Z that require quick delivery and convenience. Typically, these are working professionals, students, or young families residing in metropolitan areas who would want quick fixes to their grocery shopping problems.
Which features are unique to Zepto as compared to grocery delivery applications like BigBasket and Swiggy Instamart?
The 10-minute delivery guarantee is what sets Zepto apart from the rest within the online grocery space. Zepto’s speed, unparalleled user experience, and targeted advertising at specific regions puts it ahead of competitors in the quick commerce industry.
How does Zepto make money?
Zepto makes money through a combination of product markups, delivery fee, and brand partnerships. They buy the products at whole prices and sell them for higher than the cost. Furthermore, Zepto makes additional revenue by advertising with FMCG brands, and D2C companies through sponsored listings, featured placements, and co-branding advertising.