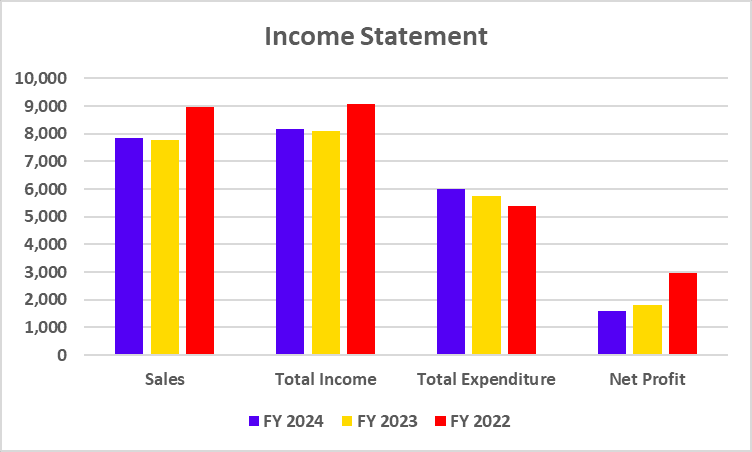
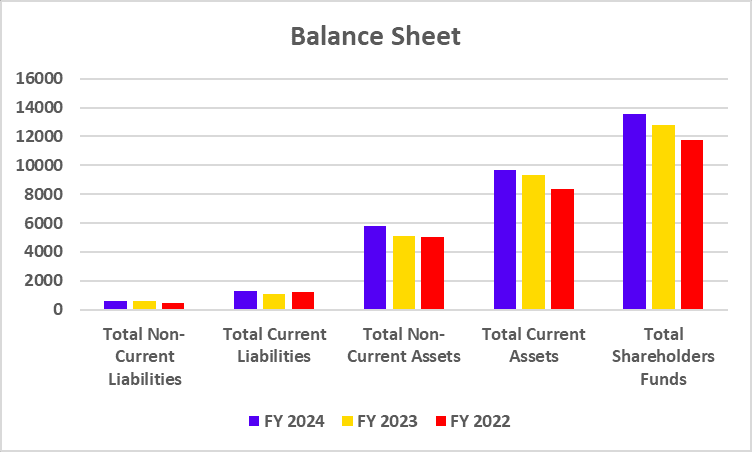
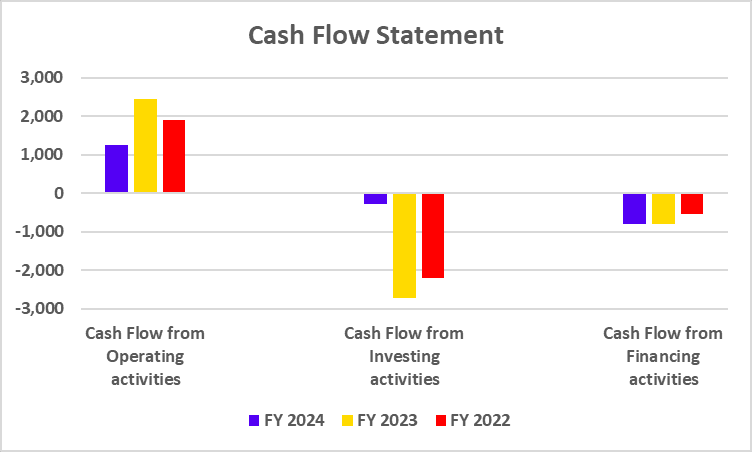
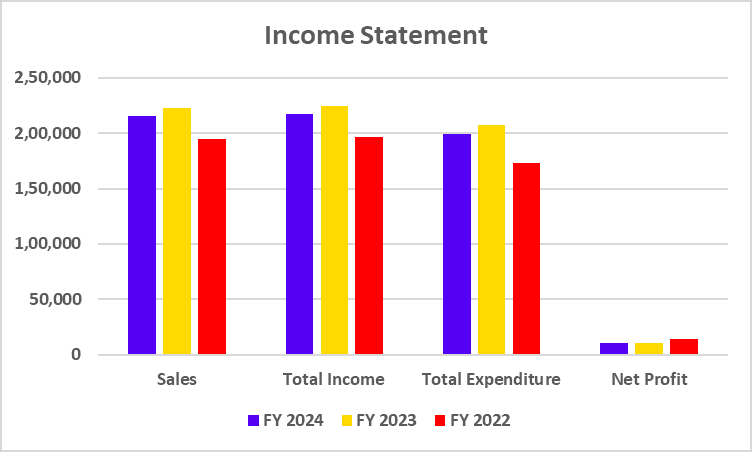
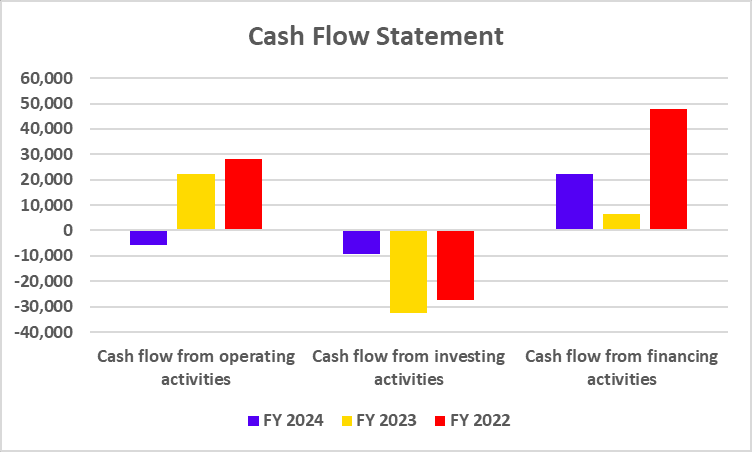
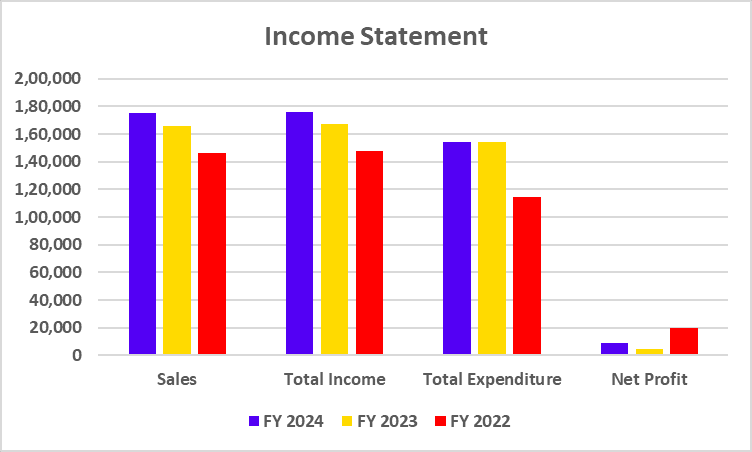
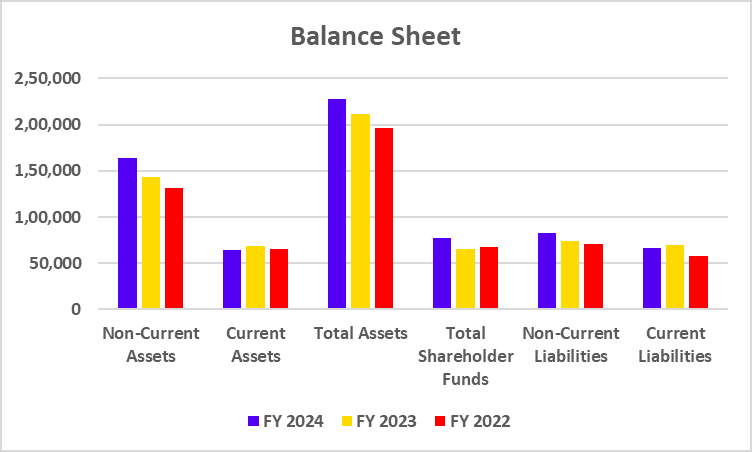
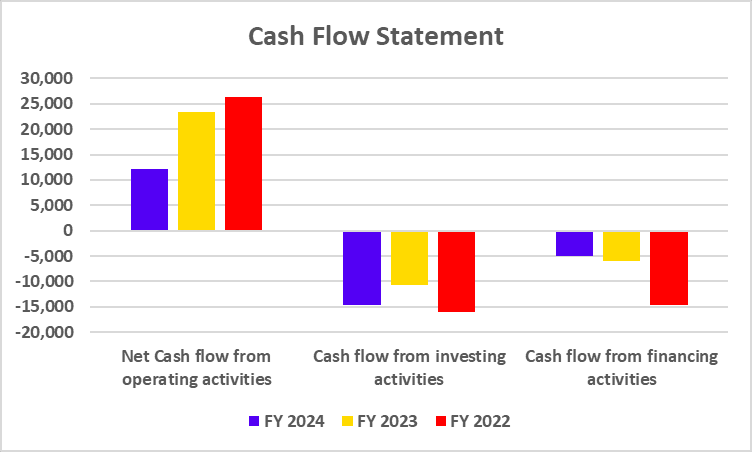
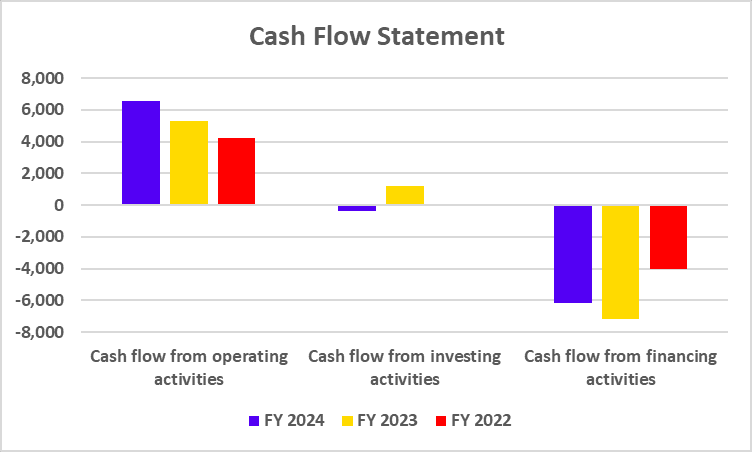
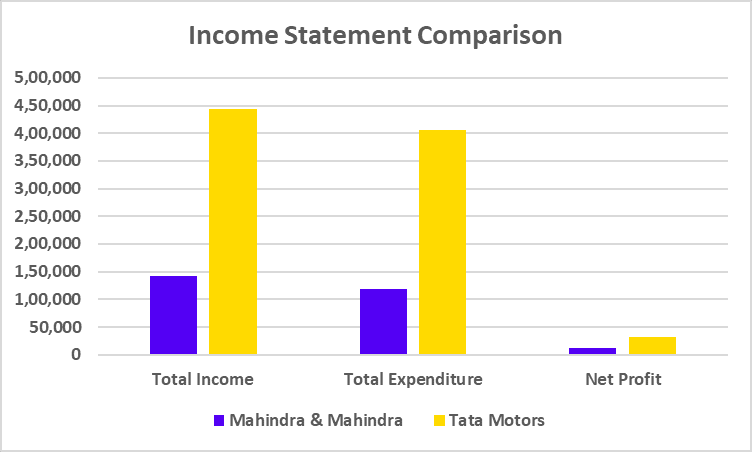
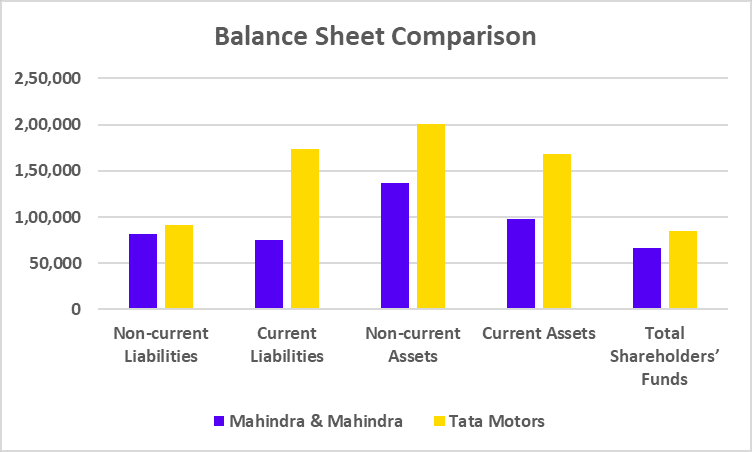
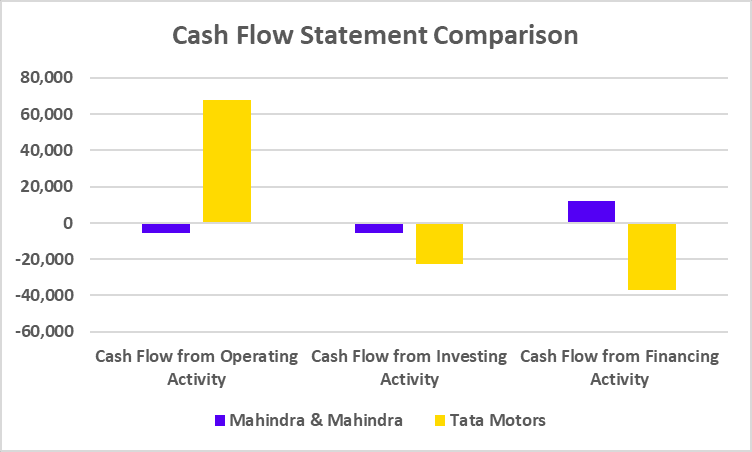
Tata Motors has recently undertaken a strategic move to convert its Differential Voting Rights shares (Tata Motors DVR) into Ordinary shares (Tata Motors). This move is a part of Tata Motors’ strategy to simplify its capital structure, enhance market transparency, and provide equal voting rights to all shareholders.
The decision, which converts DVR shares into ordinary shares at a predetermined ratio, was unanimously approved by shareholders and is expected to improve the share’s trading volume and boost shareholder value. In today’s blog, we will discuss Tata Motors’ recent announcement of converting its DVR shares into ordinary shares in detail.
Overview of Tata Motors
Tata Motors Limited is a leading global automobile manufacturer of cars, utility vehicles, buses, trucks, and defense vehicles. It was incorporated in 1945 and was formerly known as Tata Engineering and Locomotive Company Ltd. The company designs, manufactures, and sells a wide range of automotive vehicles. It also manufactures engines for industrial and marine applications. As India’s largest automobile company and part of the Tata Group, Tata Motors has operations in the UK, South Korea, Thailand, South Africa, and Indonesia through a strong global network of 86 subsidiary and associate companies, including Jaguar Land Rover in the UK and Tata Daewoo in South Korea.

The company is ramping up its electric vehicle offerings, with plans to launch more models in the coming years. Tata Motors aims to be a leader in the Indian EV market, which is expected to grow rapidly in the near future.
Difference Between Tata Motors Ordinary Shares and DVR Shares
In 2008, Tata Motors introduced Differential Voting Rights (DVR) shares to raise capital without diluting existing shareholders’ voting power. DVR shares have fewer voting rights than ordinary shares but typically offer higher dividends to compensate for the same. Here’s a detailed comparison:
- Voting rights: DVR shares typically have one-tenth the voting power of ordinary shares. Tata Motors DVR shares have 10% of the voting rights compared to ordinary shares.
- Dividends: DVR shares generally offer higher dividends than ordinary shares. In 2024, Tata Motors DVR declared a 300% equity dividend, amounting to Rs 6 per share.
- Pricing: DVR shares are often sold at discounts compared to ordinary shares due to their lower voting power.
- Market Impact: DVR shares may be attractive for investors seeking income rather than control over the company. They can also appeal to small investors and other retail shareholders who don’t vote.
However, DVR shares have certain drawbacks, including limited or no voting rights, low liquidity, and no guarantee of higher dividends.
Recent Update to Cancel Tata Motors DVR shares
Tata Motors recently announced the conversion of Tata Motors DVR shares into ordinary shares. The company will cancel its listed DVR shares and issue ordinary shares as compensation. For every 10 DVR shares, investors will receive 7 ordinary shares. This swap aims to simplify the company’s capital structure and improve liquidity, shareholder value, and market transparency.
The primary objectives behind this decision are:
- Simplifying the Capital Structure: Conversion of DVR shares into ordinary shares will make Tata Motors’ capital structure less complex. This simplification is expected to enhance market transparency and improve the overall efficiency of trading in Tata Motors’ shares.
- Enhancing Shareholder Value: The conversion ratio (7 ordinary shares for every 10 DVR shares) gives DVR shareholders a significant premium. This move is valuable for shareholders and makes it an attractive deal.
- Improving Market Perception: With this move, Tata Motors eliminates the differential voting rights shares, which can be seen as a point of debate in corporate governance. This unification is likely to enhance the company’s image in the eyes of investors and could lead to a more favorable market perception.
Details Of Share Swap
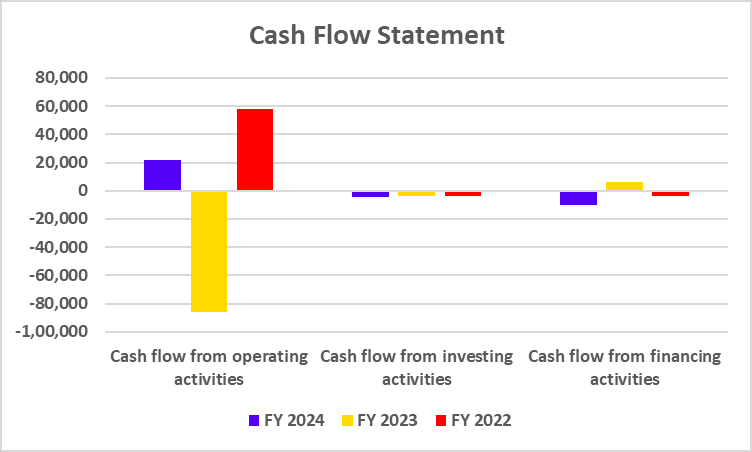
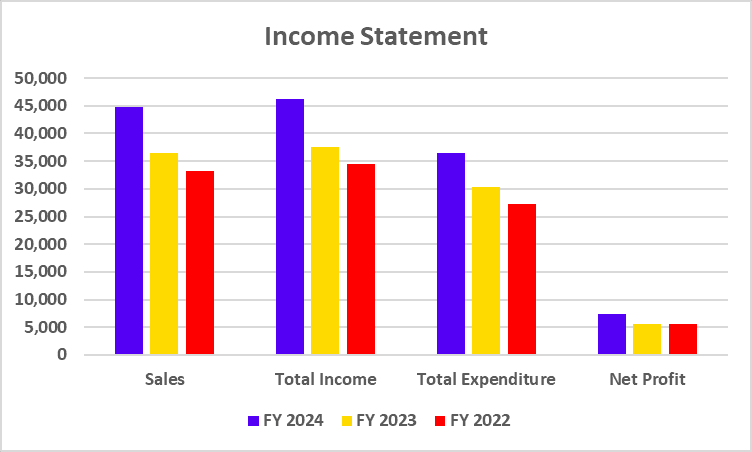
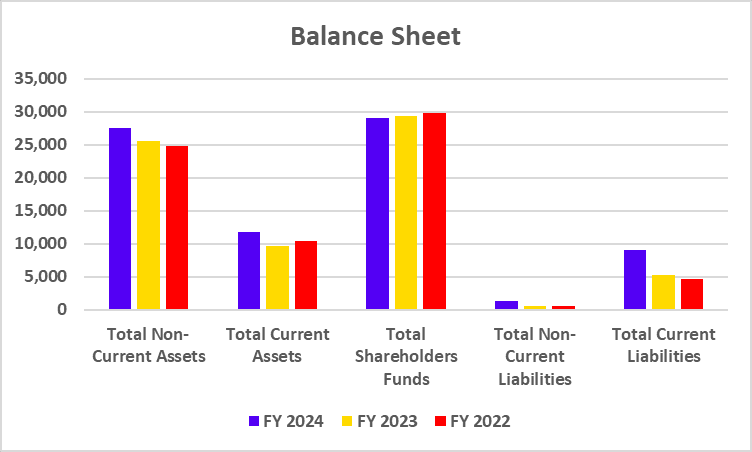
The DVR shares, which have been trading since 2008, will be swapped for ordinary shares at a predetermined ratio of 7 ordinary shares for every 10 DVR shares. The swap will be done on September 1, 2024, with the listing and trading approval of the new ordinary shares starting on September 11, 2024. The shares will be credited to accounts on September 18, and the remittance of cash entitlements will happen on September 21. Consequent to the aforesaid allotment, the paid-up ordinary share capital of the company will increase from Rs 664.97 crore divided into 332.46 crore ordinary shares of Rs 2 each to Rs 736.17 Crore divided into 368.06 Crore ordinary shares of Rs 2 each (considering the amount of subscribed share capital plus shares forfeited less calls in arrears).
Tax Implications for Shareholders
Delisting of DVR shares will reduce capital and have the same implications as witnessed in a liquidation. When the shares are delisted in 12–15 months, all accumulated profits on the balance sheet will be considered dividends to current DVR shareholders. As a result, it will have tax consequences (withholding tax). Long-term capital gains from these transactions will be taxed, and any short-term capital gains earned during the period will also be taxed.
Read Also: Tata Steel Case Study: Business Model, Financial Statements, SWOT Analysis
Performance of Tata Motors And Tata Motors DVR
| Company | 6 Months Return | 1 Year Return |
|---|---|---|
| Tata Motors | 2.39% | 63.94% |
| Tata Motors DVR | 11.5% | 81.03% |
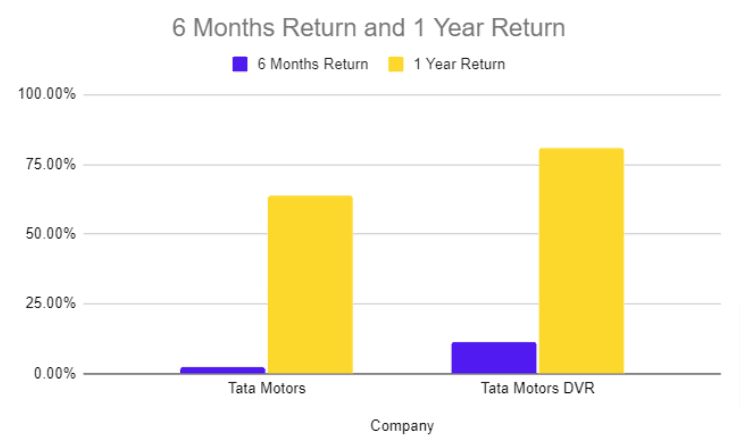
During the past year, Tata Motors DVR shares have given superior returns compared to Tata Motors shares. Due to the premium paid to the DVR shareholders according to the conversion ratio, the Tata Motors DVR shares have outperformed Tata Motors ordinary shares.
Read Also: Tata Motors Case Study: Business Model, Financials, and SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
The recent announcement of the cancellation of DVR shares and their conversion into ordinary shares is expected to simplify Tata Motors’ capital structure, increase liquidity, and enhance shareholder value. For investors, this will eliminate the discount associated with DVR shares, bringing their value closer to that of ordinary shares. Overall, it is a strategic move and will be positive for the shareholders as it will simplify the company’s shareholding structure and potentially boost market confidence in Tata Motors. Understanding this development is important for anyone looking to trade or invest in Tata Motors stock. However, it is advised to consult a financial advisor before investing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the meaning of Tata Motors DVR shares conversion into ordinary shares?
The conversion of Tata Motors’ Differential Voting Rights (DVR) shares into ordinary equity shares means that shareholders of Tata Motors DVR will receive 7 ordinary shares for every 10 DVR shares held.
Why did Tata Motors decide to convert DVR shares with ordinary shares?
Tata Motors decided to convert DVR shares with ordinary shares to simplify its capital structure, increase market transparency, and enhance shareholder value.
What is the conversion ratio for Tata Motors DVR to ordinary shares?
The conversion ratio is 7 ordinary shares for every 10 DVR shares. If you hold 10 DVR shares, you will receive 7 ordinary shares of Tata Motors post-conversion.
What is the record date for the DVR conversion?
The record date for the conversion was set for September 1, 2024. Shareholders must hold DVR shares by this date to be eligible for conversion.
How does this conversion benefit shareholders?
Shareholders will benefit from a 23% premium on the DVR share price, improved liquidity, and a simplified capital structure.