The stock market in India has witnessed a record number of new investors in the past year. It’s crucial to develop a solid understanding of the bid-ask spread.
In this blog, we will explore the concept of bid-ask spread, the factors that influence it and its significance.
What is Bid and Ask?

Bid and ask can be defined as:
- Bid Price: The bid price is the price a buyer is willing to pay for a security. It’s the amount a seller can receive if they sell their security at that moment.
- Ask Price: The asking price, also known as the offer price, is the price at which a seller is willing to sell a security. It’s the amount a buyer must pay to buy the security.
What is Bid-Ask Spread?
The difference between the bid and ask prices is known as the “Bid-Ask Spread.” This spread indicates the liquidity and volatility of security. A narrow spread typically suggests a highly liquid market with low volatility, while wider spreads indicate lower liquidity with higher volatility.
Calculation of Bid-Ask Spread
The bid-ask spread can be calculated using the following formula:
Bid-Ask Spread = Lowest Ask Price – Highest Bid Price
Example: Suppose a stock is trading with low liquidity and is currently trading at INR 107. A trader wishes to purchase a stock and sees the following information:
| Number of Buyers | Bid Prices | Ask Prices | Number of Sellers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7,000 | 105 | 110 | 8,000 |
| 5,000 | 104 | 112 | 5,000 |
| 3,000 | 102 | 114 | 4,000 |
| 2,000 | 101 | 115 | 2,000 |
Lowest Ask Price = INR 110
Highest Bid Price = INR 105
In order to purchase the stock immediately, the trader must pay the ask price, which is the price a seller is willing to accept to sell the security. Bid-Ask spread, in this case, is INR 5. Now, let’s see what narrow and wide bid-ask spreads signify.
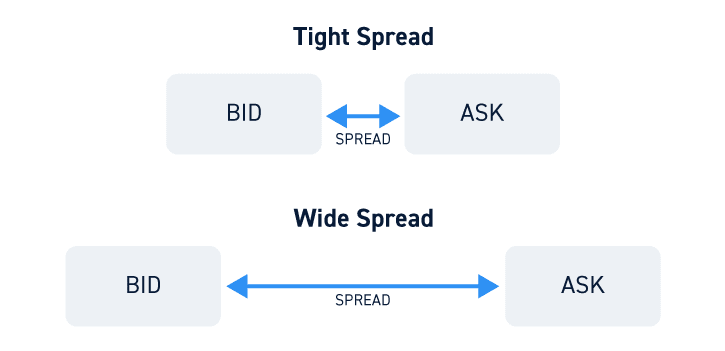
Narrow Bid-Ask Spread
In a narrow bid-ask spread, the gap between bid and ask prices is tiny. It’s generally a sign of high liquidity, a condition where lots of potential buyers and sellers are present. This makes trading the stock simpler and doesn’t drastically swing its price.
Wide Bid-Ask Spread
In a wide bid-ask spread, the bid and ask prices are far apart. That’s a sign of low liquidity. Selling or buying a stock can be a tough task without causing a lot of change in the price. The execution cost per share increases, and you may have to pay more for purchasing a share or accept a lower price when selling a share.
Significance of Bid-Ask Spread
The bid-ask spread can be used in the following ways:
- Liquidity Indicator: A narrow bid-ask spread indicates high liquidity, while a wide bid-ask spread indicates lower liquidity.
- Transaction costs: A wide bid-ask spread indicates that the transaction costs would be higher. On the other hand, a narrow bid-ask spread indicates lower transaction costs.
- Volatility Indicator: A wide bid-ask spread means the participants in the market are cautious of high volatility. Meanwhile, markets with a narrow bid-ask spread indicate low volatility.
- Market efficiency: In efficient markets, the market information flows freely, and due to the low probability of volatile movements, the bid-ask spreads are generally narrow. On the other hand, inefficient markets often have a wide bid-ask spread.
Factors that Influence BID-ASK Spread
Various factors that affect the bid-ask spread are given below:
- Liquidity: Highly liquid stocks, such as those of large, well-known companies, generally have narrower spreads because there are many buyers and sellers. Whereas less liquid stocks often have wider spreads due to fewer market participants.
- Market Conditions: During periods of high volatility or market uncertainty, spreads can widen as market participants become less willing to transact at the current prices.
- Stock Price: Higher-priced stocks have larger absolute spreads, although the percentage spread may remain small. Lower-priced stocks can have relatively smaller absolute spreads.
- Trading Volume: Stocks with higher trading volumes have narrower spreads due to the high competition among buyers and sellers.
- Time of Day: Usually, spreads are wider at the market open and close due to increased volatility and lower liquidity during these times.
Read Also: What is Spread Trading?
Conclusion
The gap between bid and ask is key to trade execution. A trader should trade in markets with a narrow bid-ask spread as a wider bid-ask spread increases the transaction costs and, thus, reduces the profit of the trader. However, it is advised to consult a financial advisor before making any investment decision.
Frequently Answered Questions (FAQs)
How does the bid-ask spread affect day traders differently from long-term investors?
Day traders often experience higher costs due to frequent trading, as the bid-ask spread can accumulate quickly. Long-term investors are less affected because they trade less frequently.
Is it possible for the bid-ask spread to be zero?
While rare, a zero spread occurs in extremely liquid markets or during certain market-making activities where bid and ask prices converge.
How do electronic trading platforms impact the bid-ask spread?
Electronic trading platforms reduce the spread by increasing market efficiency and the number of market participants.
How can retail investors leverage bid-ask spreads to identify trading opportunities?
Retail investors can use the spread to gauge market liquidity and execute trades when spreads are narrower to reduce costs.
How does high-frequency trading (HFT) influence the bid-ask spread?
HFT can narrow spreads by providing liquidity and increasing trading volume.

