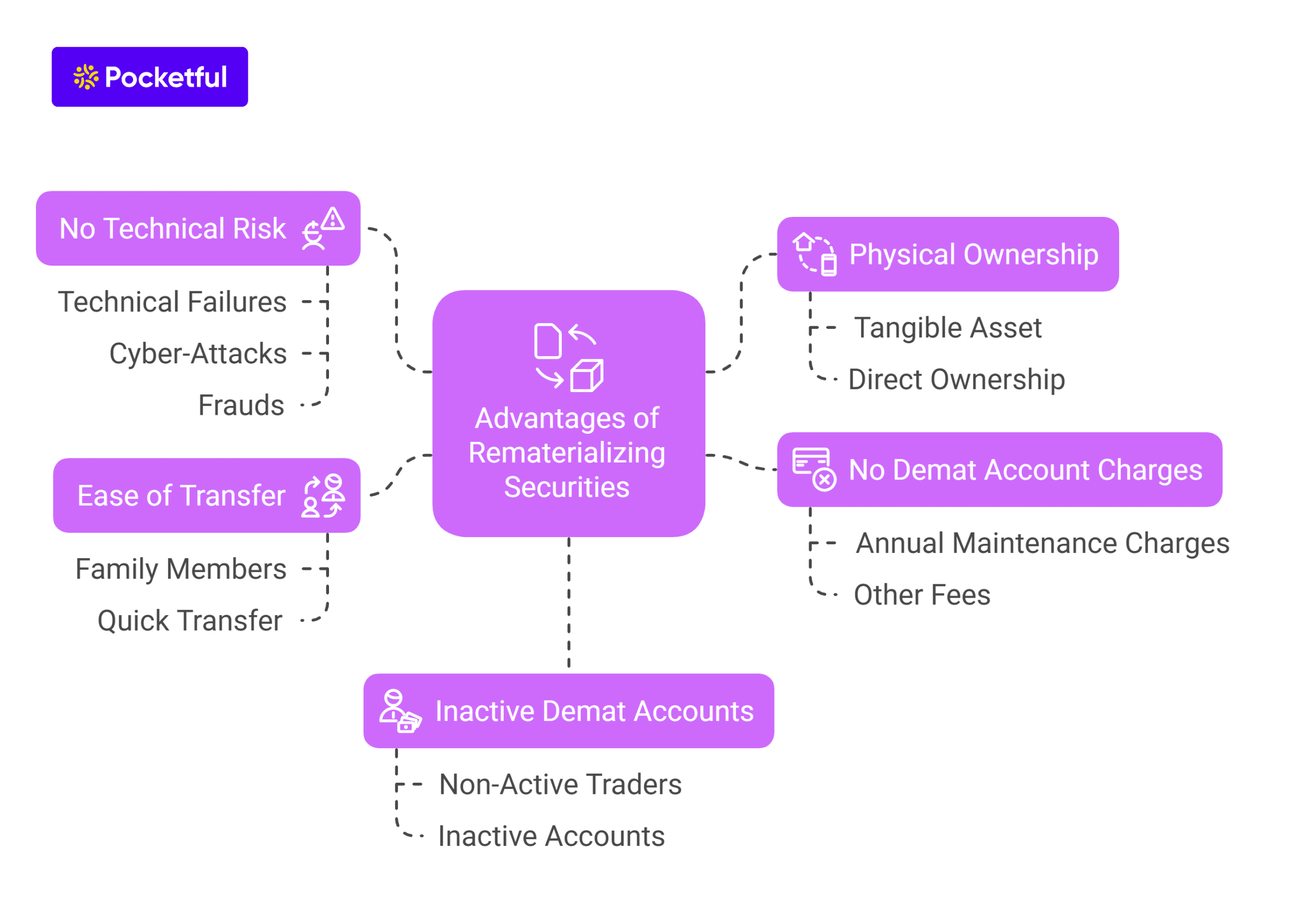
Since the introduction of Demat Accounts, investors have been enjoying its various benefits, such as protection against theft, reduced paperwork and easy settlement of transactions. However, there are several tax implications of holding securities in a Demat account.
Understanding the tax implications of demat accounts in India is crucial for identifying the tax liabilities and remaining tax-compliant when holding securities in demat accounts. Knowledge about how the investments will be taxed helps investors make better investment decisions. In this blog, we will discuss the tax implications of holding securities in a Demat account in detail.
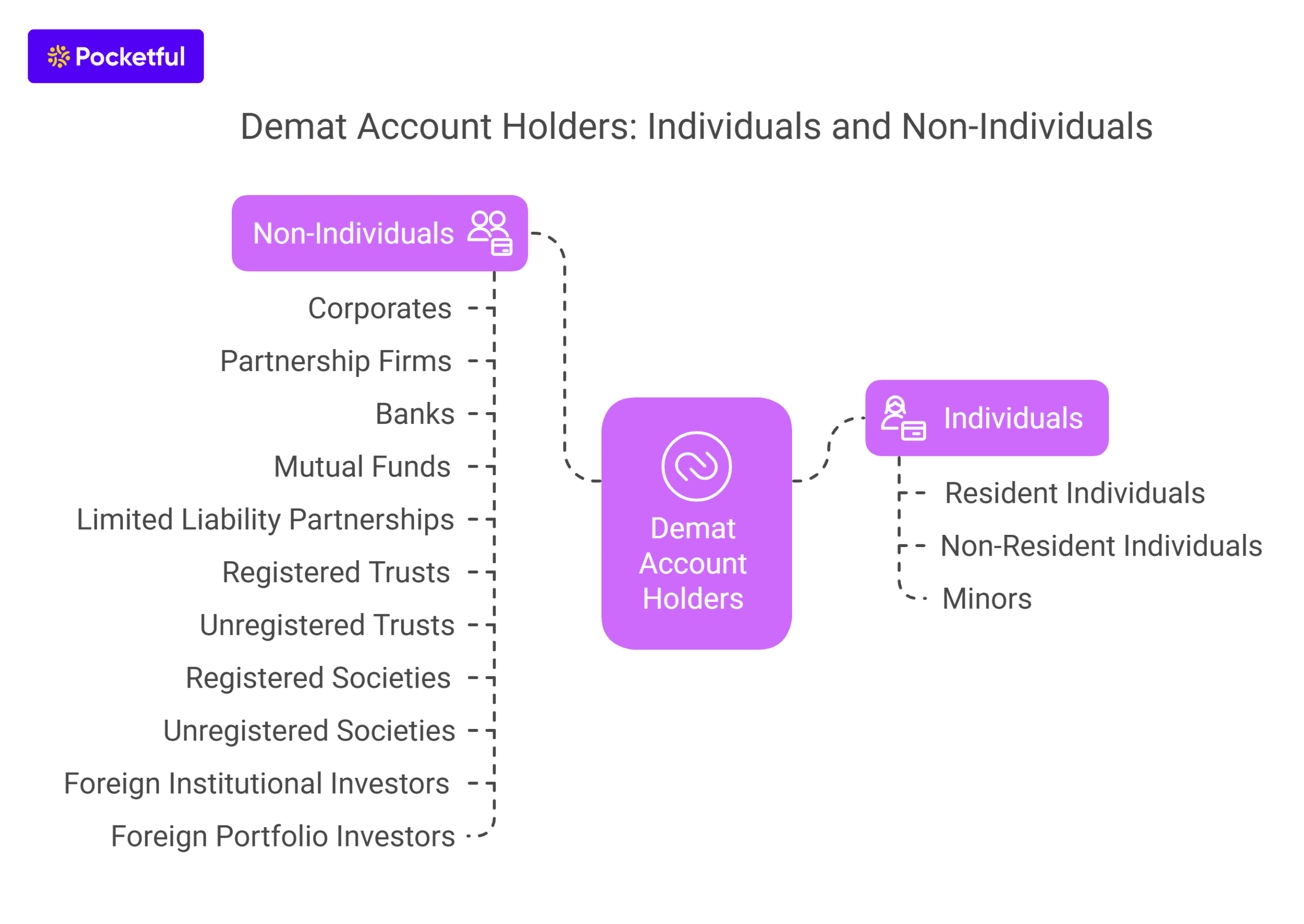
What are the Tax Implications on a Demat Account?
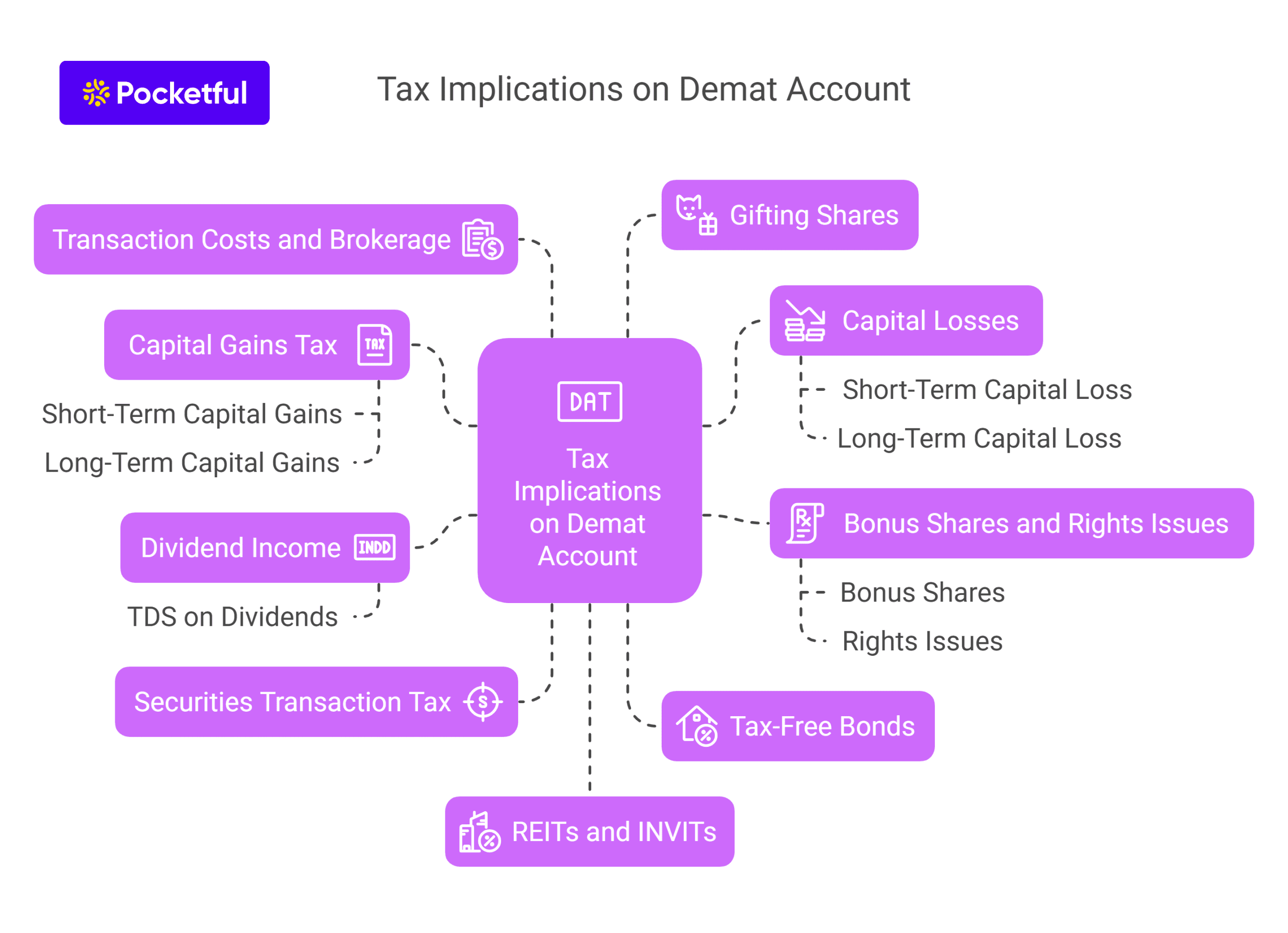
The tax implications of a demat account are the applicable taxes on short and long-term capital gains, dividend income, and other transaction costs related to securities held in a Demat account. These are applicable when you buy or sell equities, mutual funds, bonds, or other financial instruments kept in your Demat account. Here’s a detailed overview of the tax implications:
1. Capital Gains Tax
Capital gains are classified as either short-term or long-term, depending on the holding period. According to the Budget 2024, there will be only two holding periods: 12 months for listed securities and 24 months for unlisted securities
A. Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG)
- Listed Equity Shares & Equity-Oriented Mutual Funds: The gains are considered short-term if security is sold within 12 months of the purchase. STCG is taxed at a flat rate of 20%, regardless of your income tax slab.
- Other Assets: For other assets such as real estate, unlisted equity shares, specified mutual funds, etc., the gains are taxed at your income tax slab rate. Specified mutual funds are more than 65% of assets invested in debt and money market securities, and the gains realized are categorized as STCG.
B. Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG)
- Listed Equity Shares & Equity-Oriented Mutual Funds: Gains from shares or equity mutual funds held for more than 12 months are classified as long-term. LTCG is exempt from taxes up to 1.25 lakh per financial year. Gains exceeding 1.25 lakh are taxed at 12.5%.
- Other Assets: For other assets, LTCG is taxed at 12.5% without indexation benefit for transfers made on or after 23 July 2024.
2. Dividend Income
- From FY 2020-21 onwards, dividends received from shares and mutual funds are added to your total income and taxed according to your income tax slab.
- TDS on Dividends: A 10% TDS is deducted if the dividend income exceeds ₹5,000 in a financial year. For NRIs, the TDS on dividends is 20%.
3. Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
- STT is a tax levied on the purchase and sale of securities. On the sale and purchase of equity shares, STT is 0.1% of the transaction value, and on the purchases or sale of equity-oriented mutual funds, STT is 0.001%.
- STT is not deductible from the sale price.
4. Tax-Free Bonds
- The interest earned from these bonds is fully exempt from tax, making them a good option for tax-saving investments.
5. Capital Losses
- Short-Term Capital Loss (STCL): These can be set off against both short-term and long-term capital gains in the same year.
- Long-Term Capital Loss (LTCL): These can only be set off against long-term capital gains.
- Carry Forward: If capital losses cannot be fully utilized in the current year, they can be carried forward for up to 8 years to offset future gains.
6. Transaction Costs and Brokerage
- Brokerage fees and other transaction costs incurred while buying or selling shares can be deducted from the sale price when calculating capital gains. However, annual Demat account maintenance fees are not deductible.
7. Bonus Shares and Rights Issues
- Bonus Shares: When bonus shares are sold, their cost of acquisition is considered zero, and the sale proceeds are fully taxed as capital gains (either short-term or long-term, based on the holding period).
- Rights Issues: When shares are purchased through a rights issue and sold within 1 year, the gains are subject to short-term capital gains tax (15%).
8. Gifting Shares
- Gifting shares or securities is not taxed. However, if the recipient sells the shares, they will be liable to pay tax on the capital gains. For capital gains calculation, the original purchase price and holding period of the person who gifted the shares are considered.
9. REITs and INVITs
- If you hold Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) or Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) in your Demat account, dividends may be tax-exempt under certain conditions.
- Capital gains from the sale of REIT or InvIT units are taxed just like shares: short-term gains at 20% and long-term gains at 12.5% after holding for over 1 year.
Understanding these tax implications is important to plan your investments more effectively and minimize tax liability when using a Demat account.
Tax on Gains Made over a Longer Term
| Type of Investment | HoldingPeriod (Long-Term) | Tax on Long-Term Gains |
|---|---|---|
| Equity Shares & Equity Mutual Funds | More than 1 year | 12.5% on gains exceeding ₹1.25 lakh (₹1.25 lakh exemption per year) |
| Debt Mutual Funds | More than 3 years | Income Tax slab rate |
| Non-Equity Assets | More than 3 years | 12.5% |
| Dividends | N/A | Taxed at applicable income slab rate; TDS of 10% on dividend income > ₹5,000 |
In summary, long-term holding of investments through a Demat account can provide substantial tax benefits, especially when taking advantage of LTCG exemptions and indexation benefits for non-equity investments. One can Plan and time the investments to maximize exemptions and offset capital losses, further minimizing your tax liability.
Summary of Short-Term Tax Implications
| Type of Investment | Holding Period (Short-Term) | Tax on Short-Term Gains |
|---|---|---|
| Equity Shares & Equity Mutual Funds | Less than 1 year | 20% flat tax rate, irrespective of income tax slab. |
| Non-Equity (Debt Funds, Gold ETFs, etc.) | Less than 3 years | Taxed at your income tax slab rate |
| Dividends | N/A | Taxed at your applicable income tax slab rate; TDS of 10% on dividend income > ₹5,000/year. |
| Bonus Shares (sold within 1 year) | Less than 1 year | Entire sale proceeds taxed as STCG at 20% (since the acquisition cost is zero). |
| Rights Issues (sold within 1 year) | Less than 1 year | Gains taxed as STCG at 20%. |
| Offset Short-Term Losses | N/A | Can be set off against both STCG and LTCG; carried forward for up to 8 years. |
Read Also: How to Download Your Demat Holding Statement?
How to Save Tax using a Demat account?
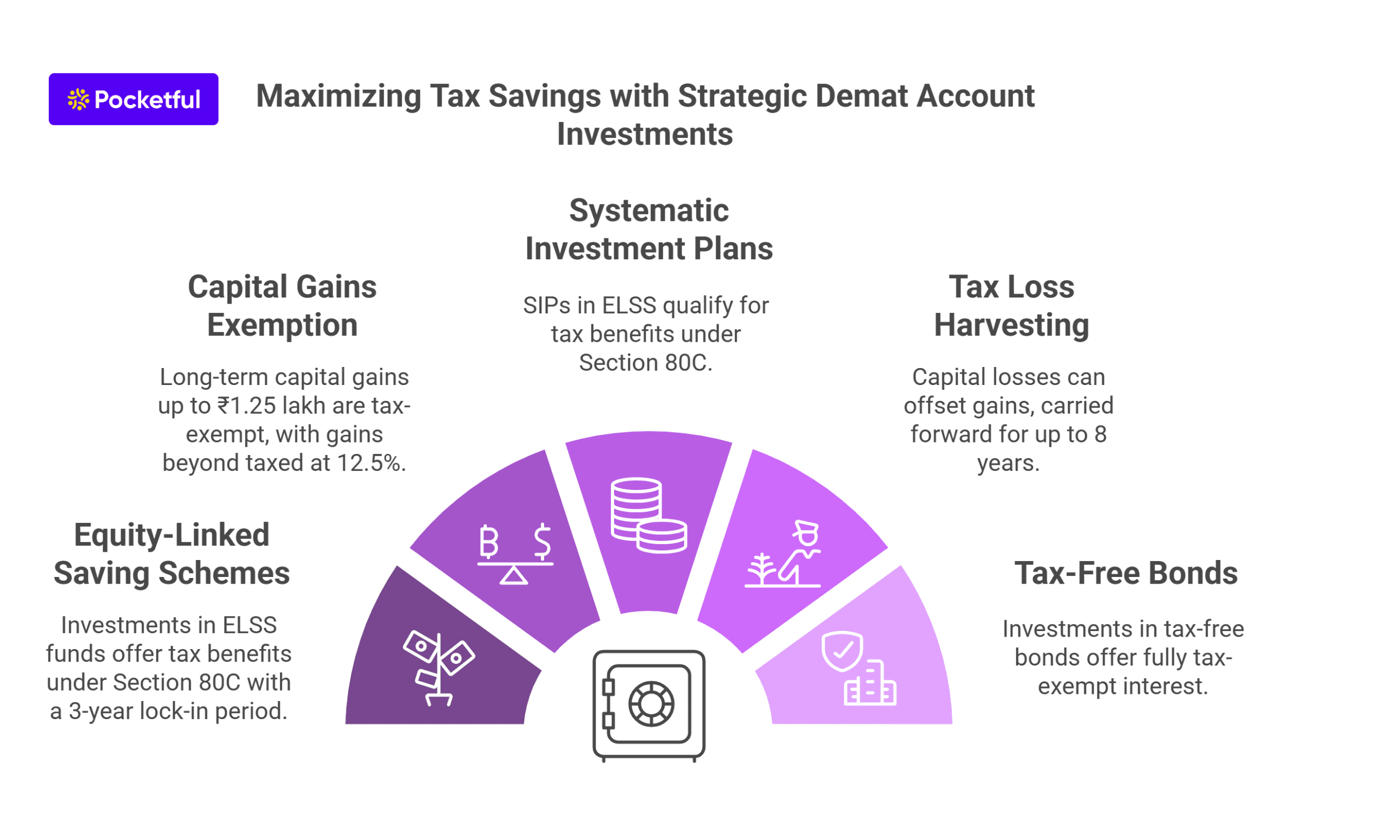
Using a Demat account in India can indirectly help save taxes by facilitating investments in tax-saving instruments. Here’s how you can leverage a Demat account to reduce your tax liability:
1. Investing in Equity-Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS)
- ELSS funds are mutual funds that invest in equities and offer tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Investments up to ₹1.5 lakh per financial year are eligible for deduction, but ELSS has a lock-in period of 3 years, which is the shortest among all tax-saving instruments under Section 80C.
2. Capital Gains Exemption
- Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG) on equities and equity mutual funds (held for more than 1 year) are exempt from tax up to ₹1.25 lakh per year. Any gain beyond ₹1.25 lakh is taxed at 12.5%.
- Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG) on equities are taxed at 20% if the holding period is less than 1 year.
3. Tax Benefits through Systematic Investment Plans (SIP)
- One can enjoy tax benefits under section 80 C on SIPs in ELSS.
4. Dividend Income
- Earlier, it was tax-free, but since FY 2020-21, dividends have been taxable as per the investor’s income tax slab.
5. Tax Loss Harvesting
- Short-term capital losses can be set off against both short-term and long-term capital gains, whereas long-term capital losses can be set off only against long-term capital gains. These losses can be carried forward for up to 8 years to offset future gains.
6. Investing in Tax-Free Bonds
- You can use your Demat account to invest in tax-free bonds issued by government entities. The interest earned on these bonds is fully exempt from tax.
7. Avoid Frequent Trading
- Avoid frequent trading, as short-term capital gains are taxed at 20%. By holding investments for the long term (more than 1 year), you can qualify for lower tax rates on long-term capital gains.
8. Tax Deductions on Brokerage and Transaction Costs
- Brokerage fees and other transaction costs can be used to reduce the overall capital gains liability.
You can optimize your tax savings by strategically using your Demat account for tax-saving investments and planning capital gains.
Tax Planning and Strategies for Demat Account Holders
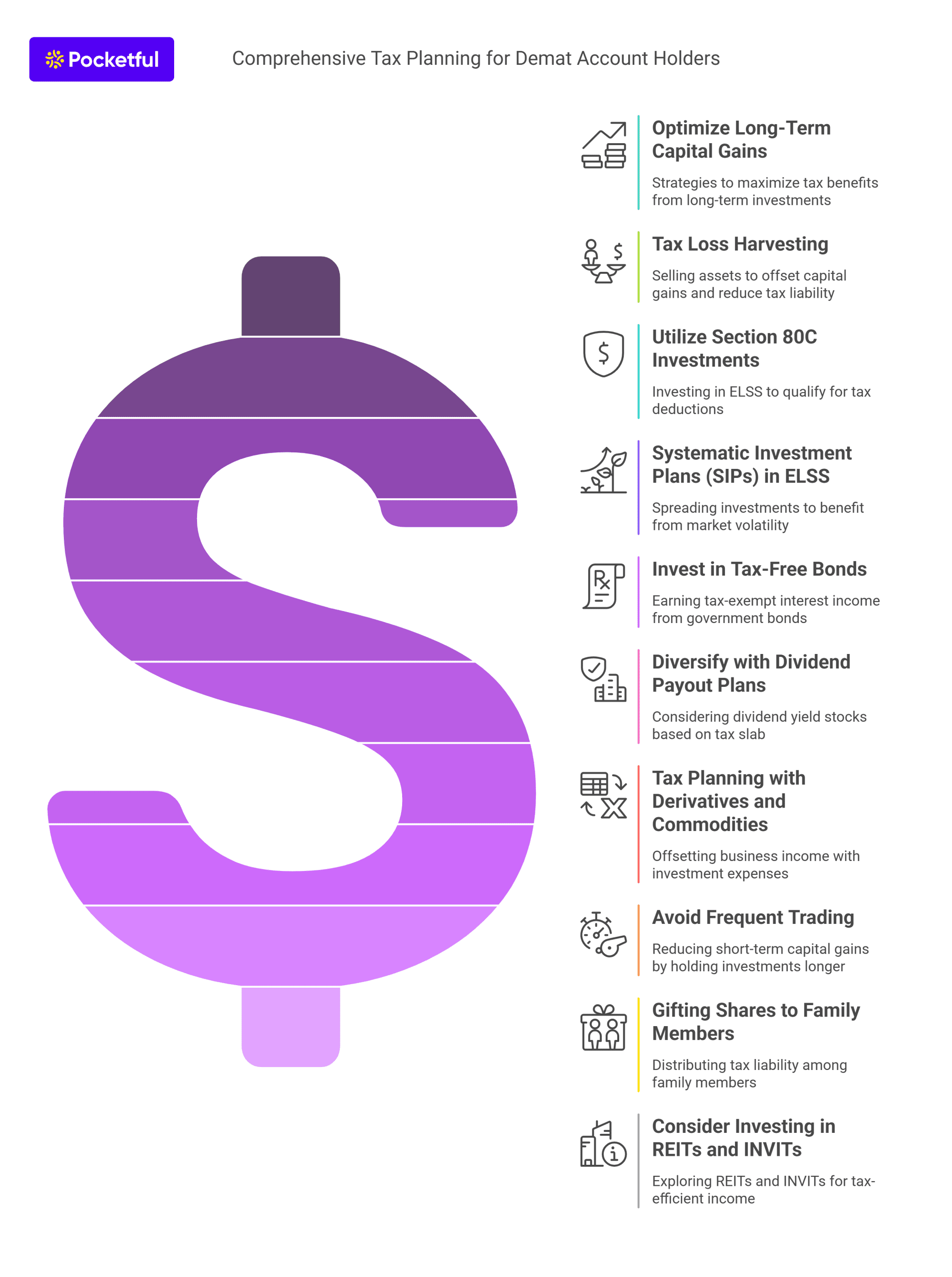
Tax planning for Demat account holders in India involves utilizing available exemptions and deductions to minimize tax liabilities. Here’s a breakdown of effective tax planning and strategies for Demat account holders:
1. Optimize Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG)
- LTCG on Equity: When you sell shares or equity / mutual funds after holding them for more than 1 year, you qualify for long-term capital gains (LTCG). LTCG up to ₹1.25 lakh is exempt from tax in a financial year. Beyond that, LTCG is taxed at 12.5%. Avoid short-term trading (holding for less than 1 year) as short-term capital gains (STCG) are taxed at 20%.
2. Tax Loss Harvesting
- Tax loss harvesting is the strategy of selling assets in your Demat account that have incurred losses. These losses can be used to offset capital gains, reducing your taxable gains; they can also be carried forward for up to 8 years to offset future capital gains.
- Set-off rules:
- Short-term capital losses (STCL) can be set off against both short-term and long-term capital gains.
- Long-term capital losses (LTCL) can only be set off against long-term capital gains.
3. Utilize Section 80C Investments
- Invest in Equity-Linked Saving Schemes (ELSS) to qualify for a deduction of up to ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
- ELSS funds have a lock-in period of 3 years but provide both tax benefits and potential equity market returns.
4. Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) in ELSS
- Spread your investment in ELSS funds throughout the year by using a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP). This allows you to take advantage of market volatility and gain Section 80C benefits while accumulating wealth over time.
5. Invest in Tax-Free Bonds
- You can buy tax-free bonds (issued by government-backed entities) through your Demat account. The interest income earned from these bonds is fully exempt from tax.
6. Diversify with Dividend Payout Plans
- Dividend income is taxable as per the individual’s tax slab. One should consider dividend yield stocks if your tax slab is lower.
7. Tax Planning with Derivatives and Commodities
- If you invest in derivatives (futures and options) or commodities, the gains are considered business income rather than capital gains. This can provide tax benefits as you have expenses (such as brokerage fees, Demat charges, etc.) to offset against the income.
8. Avoid Frequent Trading (Minimize STCG)
- Engaging in frequent buying and selling of shares leads to short-term capital gains (STCG), taxed at 20%, which is higher than the 12.5% on LTCG.
- Strategy:
- Hold your investments for the long term to reduce tax liability.
- If frequent trading is your strategy, plan your trades carefully with a higher risk-reward ratio to offset the higher tax rate for the short term.
9. Gifting Shares to Family Members
- Gifting shares to family members (e.g., spouse/ and children) can help distribute tax liability, especially if they fall in lower tax brackets or have no other significant income.
10. Consider Investing in REITs and INVITs
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (INVITs) can provide income in the form of interest, dividends, and capital gains. Dividends from REITs and INVITs are exempt from tax in certain cases, while interest income is taxed as per the individual’s tax slab.
Reporting Demat Account in ITR
Here is a table format outlining how to report a Demat account in ITR in India, the applicable forms, exemptions, credits, and other related details:
| Type of Income/Transaction | Where to Report in ITR | Applicable ITR Form | Exemptions Available | Credits/Deductions Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG) | Schedule CG (Capital Gains) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | No exemptions | Set off short-term capital losses (STCL) |
| Long-Term Capital Gains (LTCG) | Schedule CG (Capital Gains) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | ₹1.25 lakh LTCG exemption (on equity shares & mutual funds) | Set off long-term capital losses (LTCL) |
| Dividend Income | Schedule OS (Other Sources) | ITR-1 / ITR-2 / ITR-3 | No exemption; fully taxable at slab rate | TDS credit if 10% TDS deducted for dividends |
| Interest from Tax-Free Bonds | Schedule EI (Exempt Income) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | Fully exempt | Not applicable |
| Bonus Shares | Schedule CG (Capital Gains) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | No exemptions | Not applicable (Zero acquisition cost) |
| Rights Issues | Schedule CG (Capital Gains) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | No exemptions | Deduct the cost of purchase of rights shares |
| Capital Losses | Schedule CFL (Carry Forward Losses) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | Not applicable | Carry forward losses up to 8 years |
| REIT/InvIT Dividends | Schedule OS (Other Sources) or EI (Exempt Income) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | Exempt if eligible | Not applicable |
| Securities Transaction Tax (STT) | Not Reported Separately (Impacts CG) | ITR-2 / ITR-3 | Not applicable | Not deductible, but required for claiming concessional rates (20% STCG, 12.5% LTCG) |
| Demat Account Maintenance Fees | Not applicable | All Forms | Not exempt | No deduction allowed. |
By reporting capital gains, dividends, and other related incomes accurately in the relevant schedules and forms, you ensure compliance and can claim appropriate exemptions and deductions.
Conclusion
In summary, long-term holding of investments through a Demat account can provide substantial tax benefits, especially when taking advantage of LTCG exemptions and tax-free bond income. One can plan and time the investments to maximize exemptions and offset capital losses, which can further minimize your tax liability. In conclusion, short-term investments through a Demat account are subject to a higher tax rate, and careful planning around capital gains, dividends, and transaction costs can help minimize tax liabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the tax implications of bonus shares or rights issues?
For bonus shares, the cost of acquisition is considered zero. When it is sold, all proceeds are taxed as capital gains. For rights issues, the cost of acquisition is the amount paid to purchase the shares. The tax treatment depends on the holding period (short-term or long-term capital gains).
Can capital losses be adjusted or carried forward to reduce tax liability?
Yes, capital losses can be used to offset gains. Short-term losses can be set off against both short-term and long-term capital gains. On the other hand, long-term losses can only be set off against long-term capital gains. Unadjusted losses can be carried forward for up to 8 years.
Are the annual maintenance charges of a Demat account tax-deductible?
No, these charges are not tax-deductible.
What are the changes introduced in Budget 2024 related to LTCG?
According to Budget 2024, long-term capital gains will be taxed at 12.5%, and the exemption limit has been increased to INR 1.25 lakhs.
What are the changes introduced in Budget 2024 related to STCG?
According to Budget 2024, the tax rate on short-term capital gains has been increased from 15% to 20%.