As an investor, various brokers must have approached you to open a Demat account with them. Some will offer you lower brokerage charges, and some will provide additional benefits. Suppose you compare the services of your current brokers with those of others and decide to shift to another broker. Then a second thought comes to your mind: Do I need to sell my current holdings before shifting to another broker? The answer is no; you do not need to sell your holdings to shift to another broker. You can simply transfer them without worrying about selling them.
In this blog, we will walk you through the steps involved in moving your holdings from one Demat account to another.
What is the Transfer of Shares?
Securities such as shares, ETFs, Bonds, etc., are held electronically in the demat account of the investor. Transferring shares from one demat account to another demat is known as the transfer of shares. This is generally done in situations when the investor decides to switch to another broker offering better services at a lower rate than the current broker.
For example – Mr. A wants to move his holdings to the demat account with Broker Y from the demat account with Broker X without selling any securities because Broker Y offers superior services at a cheaper cost. He can accomplish this by transferring the securities.
Types of Share Transfer
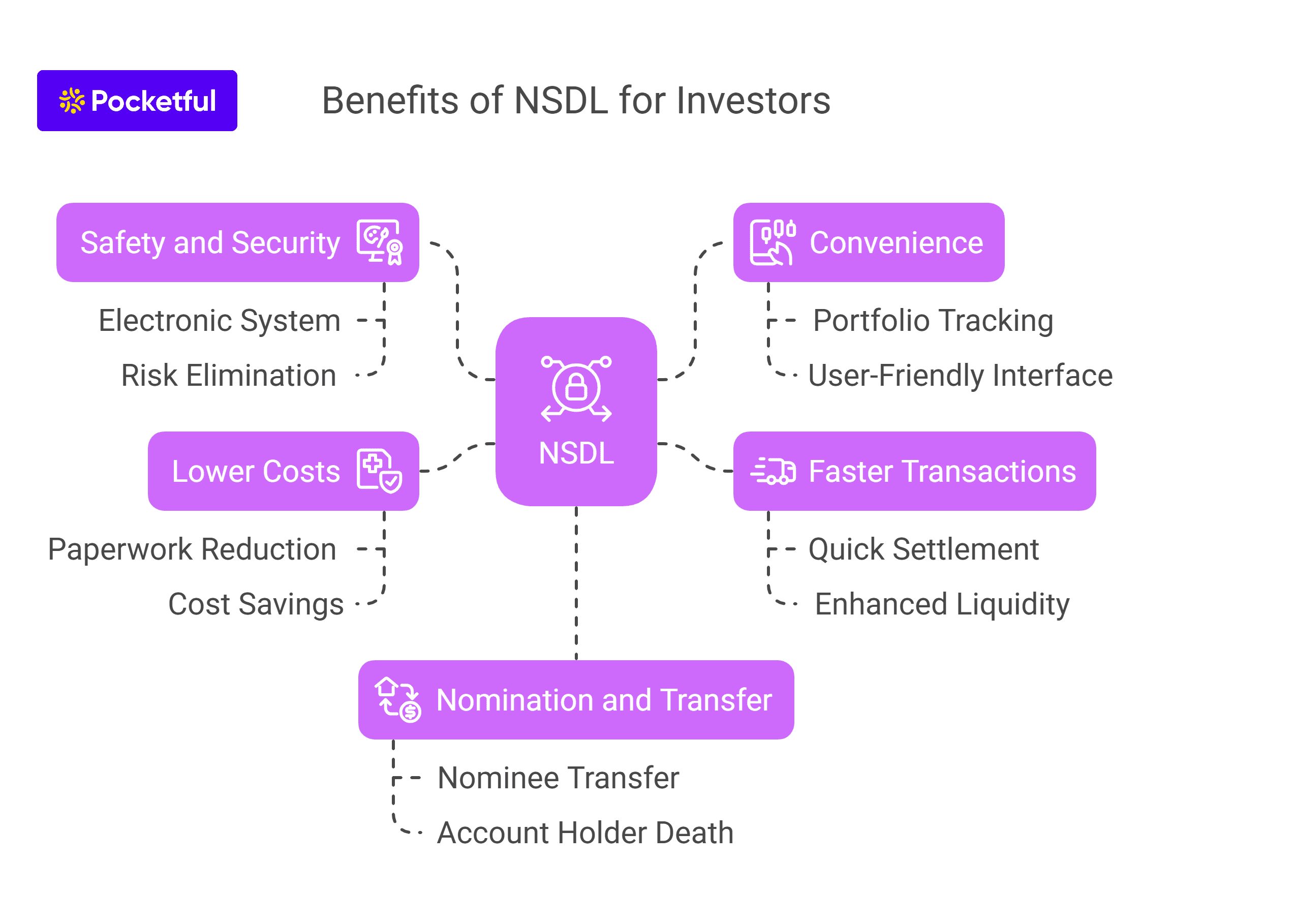
CDSL and NSDL are the two depositories in India, and there are two types of share transfer-
1. Intra-Depository Transfer – In case of an Intra-Depository transfer, shares are transferred between demat accounts registered with the same depository.
2. Inter-Depository Transfer – In an Inter-Depository transfer, the shares are transferred between Demat accounts registered with different depositories.
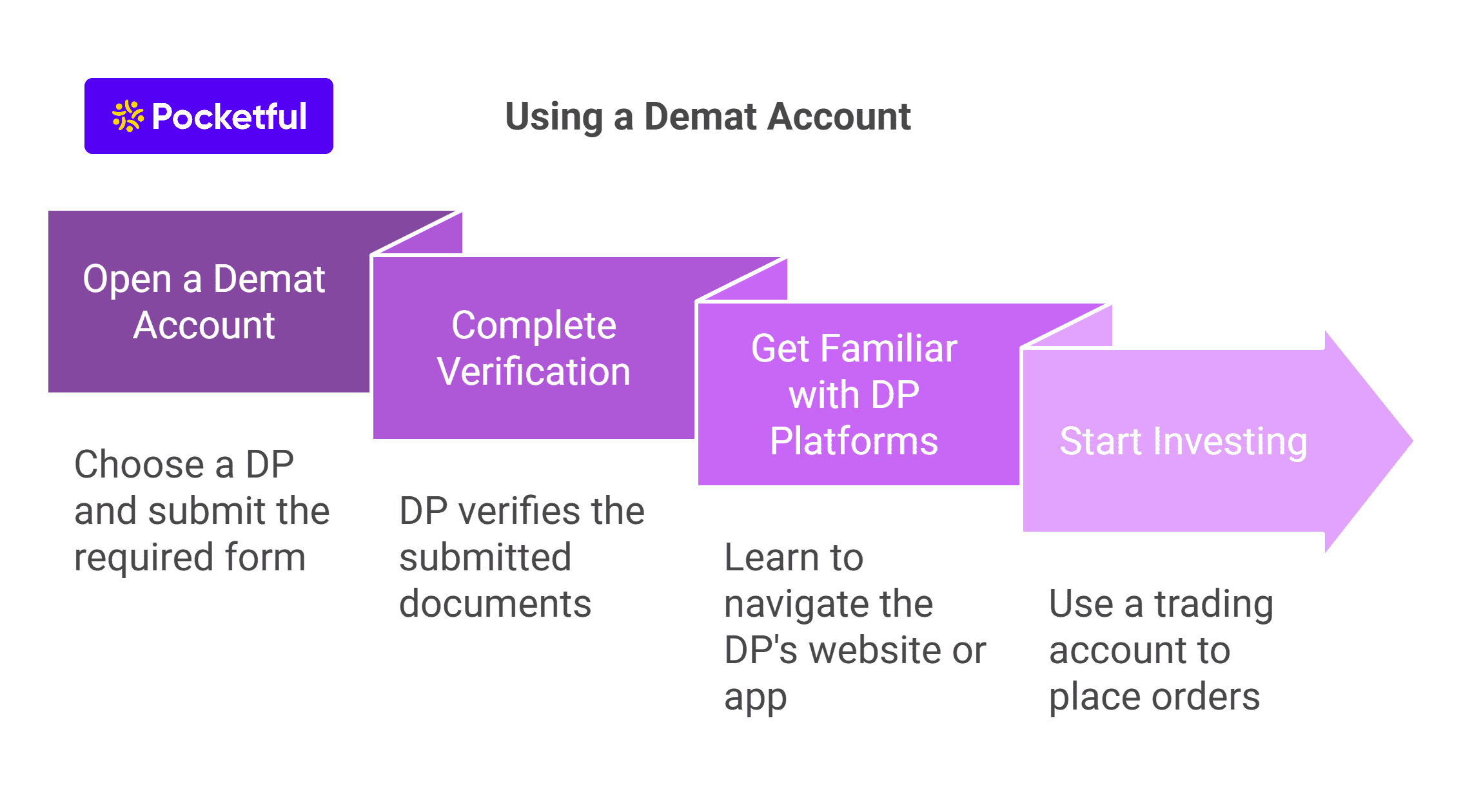
Different Ways to Transfer Shares from One Demat Account to Another
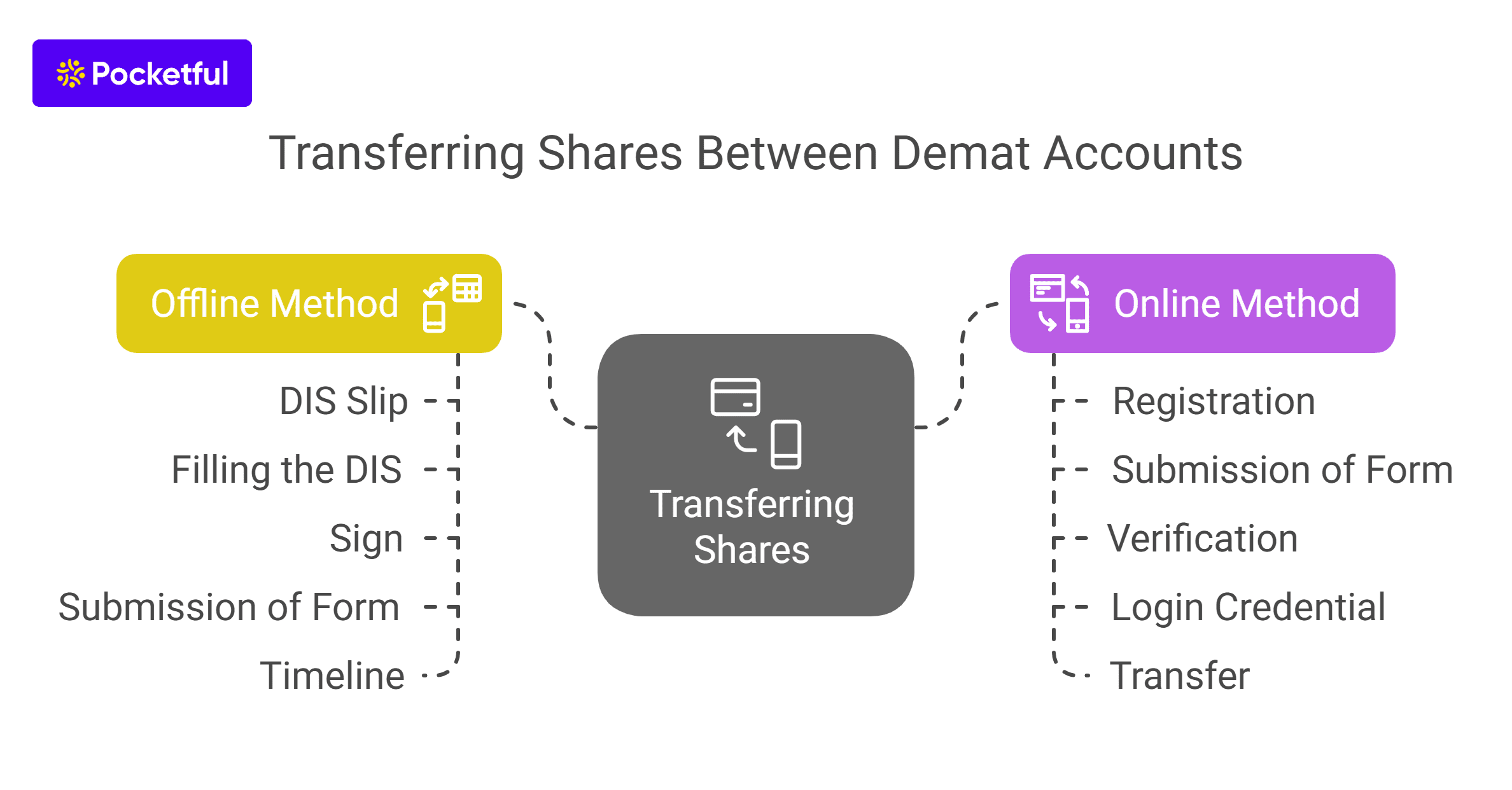
You can transfer shares from one demat account to another in two ways, i.e., online and offline.
Offline Method
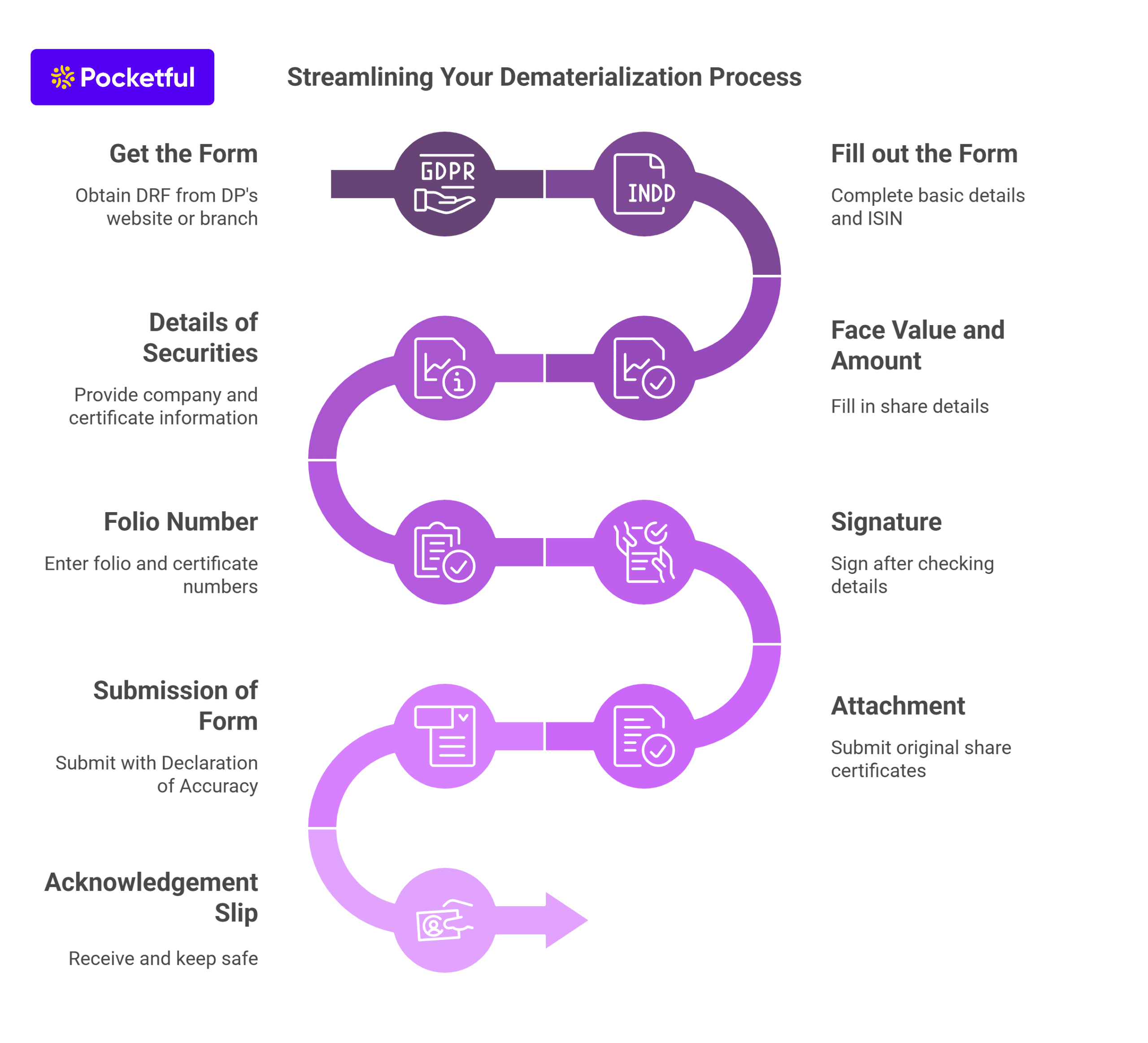
One of the methods to transfer shares is the offline method or manual method. The steps involved are mentioned below-
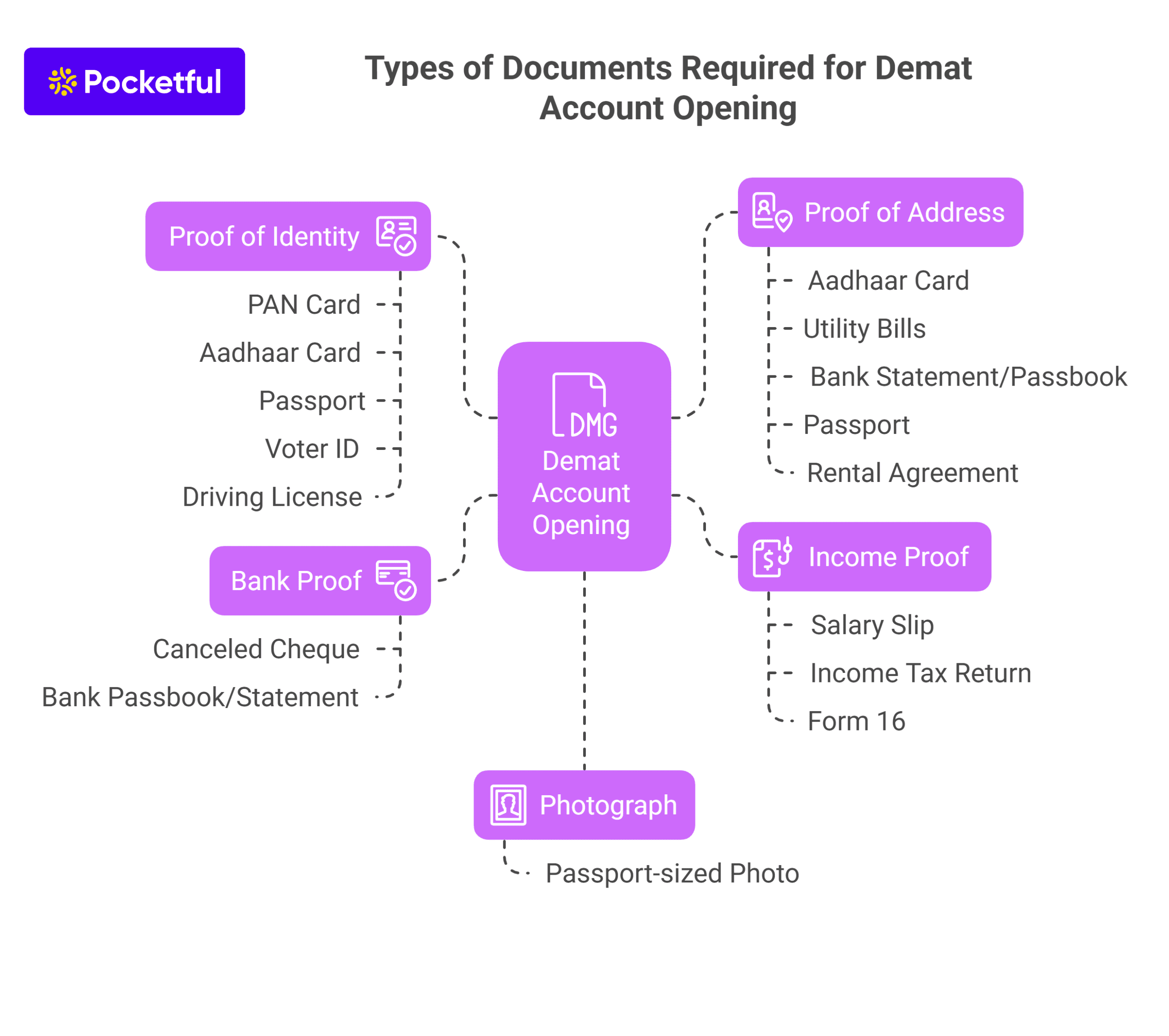
1. DIS Slip – Get the Delivery Instruction Slip or DIS slip from your broker.
2. Filling the DIS – Various details needed to fill out the DIS (Delivery Instruction Slip) are:
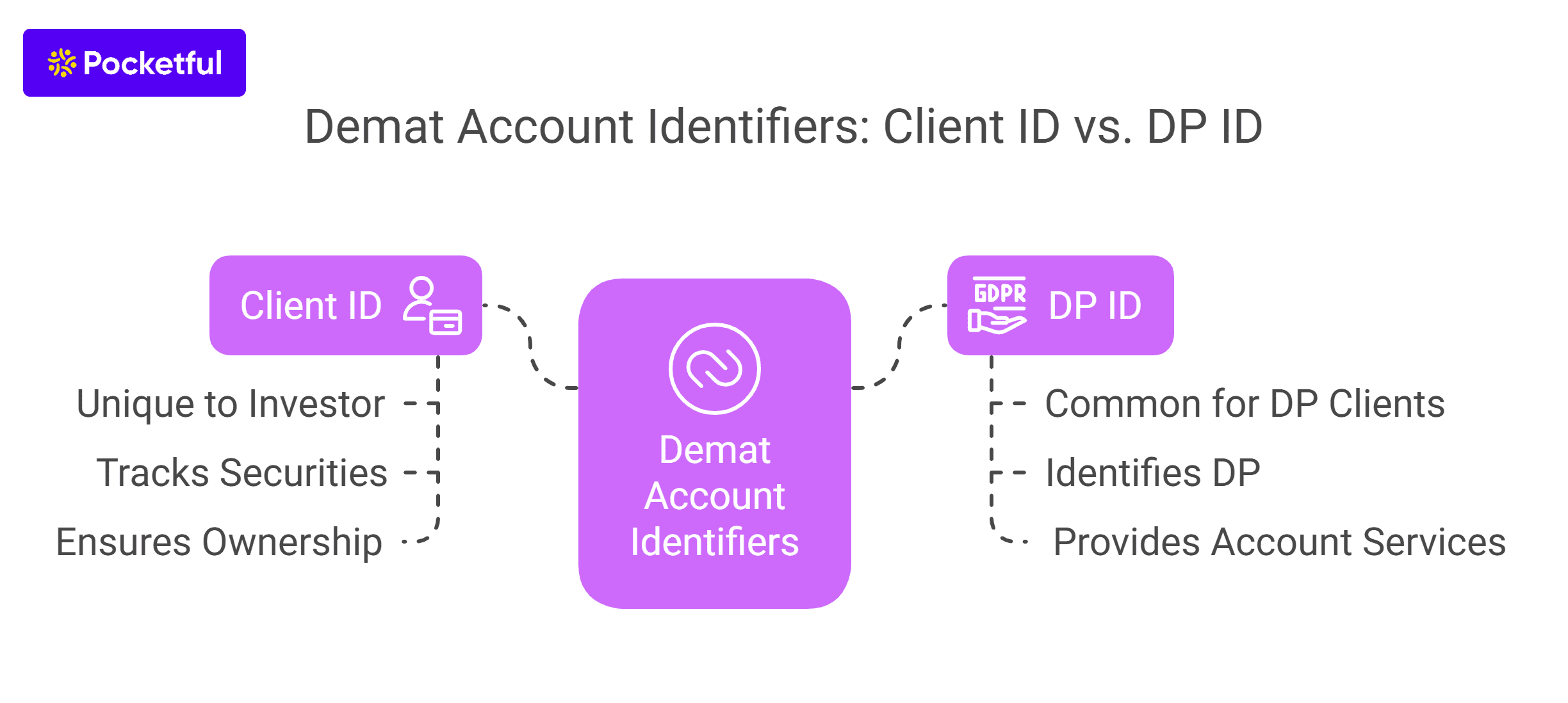
- ISIN – ISIN or International Security Identification Number, a 16-digit code, must be filled in to authenticate the shares.
- BO ID – Beneficiary Owner ID or Target Client ID needs to be filled out. This 16-digit ID is a combination of both DP ID and Client ID.
- Mode – You must select the transfer type, whether inter-depository or intra-depository transfer.
3. Sign – After filling in all the relevant details, you must sign the DIS (Delivery Instruction Slip).
4. Submission of Form – Submit the signed DIS to your broker, who will issue you an acknowledgment slip.
5. Timeline – The transfer of shares will take 3-5 working days.
Online Method
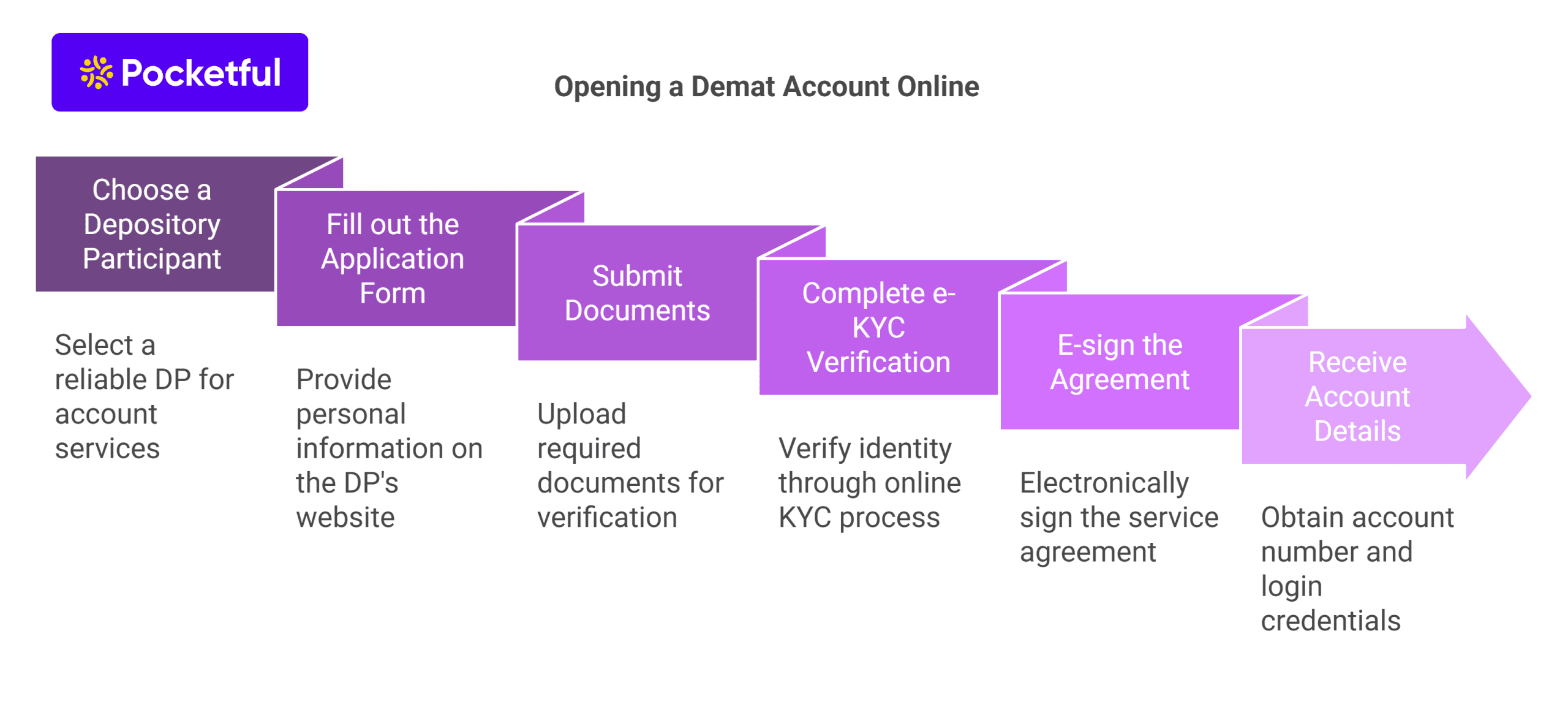
Other than the offline method, there is also an online mode of transfer, the steps of which are as follows –
A. Registration – You must register on the official website of CDSL (Central Depository Services Limited) or NSDL (National Securities and Depository Limited). CDSL offers the “Easiest,” and NSDL offers the “Speed-e” facility to the investors. Register for these facilities.
B. Submission of Form – Once you fill out the form and submit it, you must send a copy of it to your DP.
C. Verification – Your broker will verify the form and submit it to the depository to verify your details.
D. Login Credential – Once your details are verified, your account will be activated, and you will receive your login credentials on your registered mail ID.
E. Transfer – In the last step, you will have to log in to your account and transfer the share from one demat account to another.
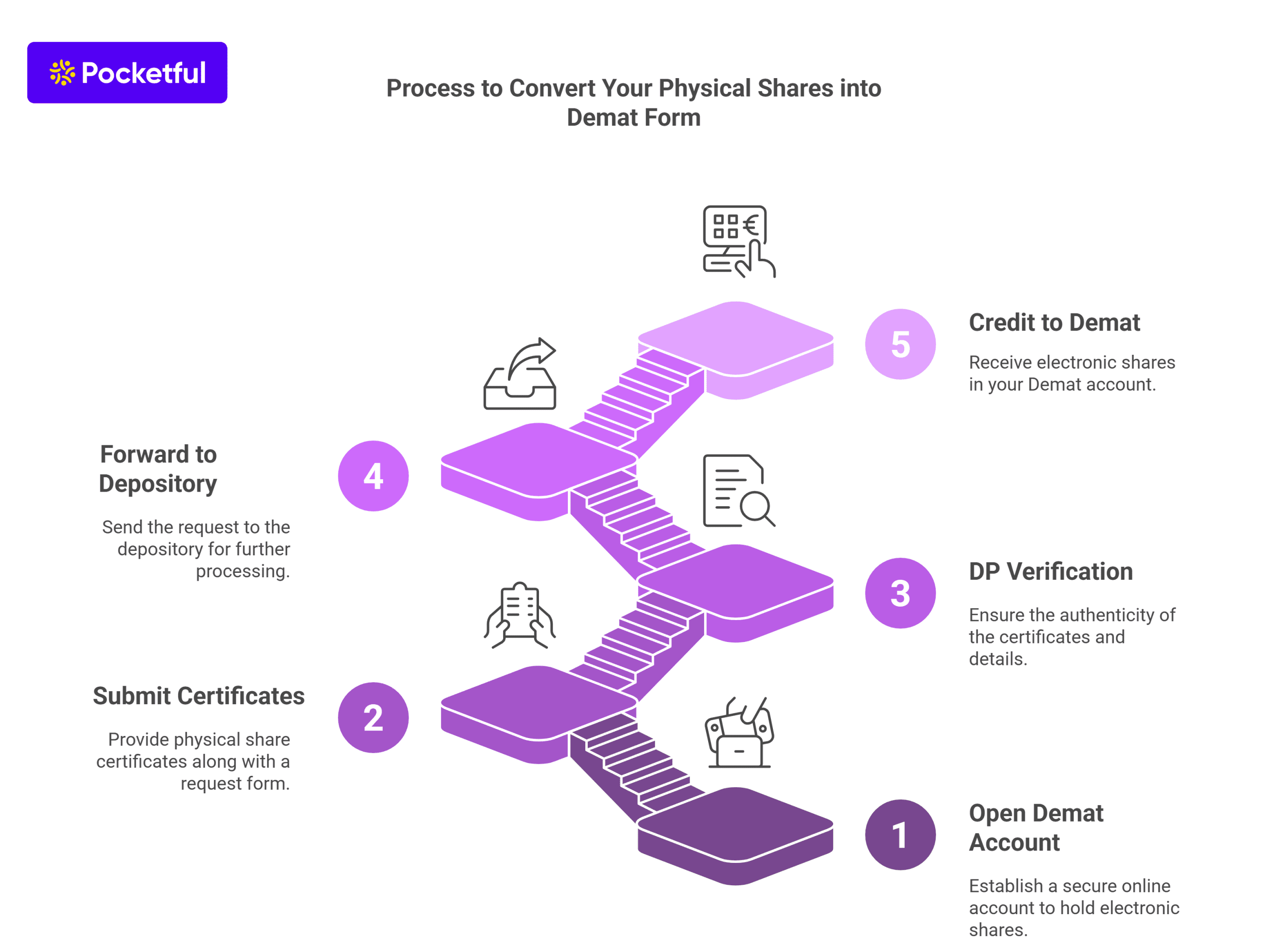
Read Also: How to Convert Physical Shares into Demat Form?
Who are the Participants in the Transfer of Shares?
The list of parties who are engaged in this transfer process is mentioned below-
1. Transferor – It is the person who currently holds the shares and will initiate the transfer process.
2. Transferee – This is the person or entity who will receive the shares and become the new owner of the securities.
3. Depositories – Depositories such as NSDL and CDSL are responsible for transferring the shares and updating the owner’s record.
4. Depository Participants– These refer to the entities authorized by the depositories to offer Demat account services.
How to Ensure That the Transfer of Shares is Successful?
Check your Demat account holding statement to ensure that the shares were successfully transferred from one Demat account to another. The holdings appear in your designated demat account after the procedure is finished. However, your DP will notify you that the share transfer process was completed successfully.
Time Required for Transfer of Shares
Whether shares are transferred online or offline, the process usually takes three to five business days. You must periodically monitor the holdings, regardless of whether shares were moved or not. If there has been any delay in the process, you will need to get in touch with the broker or DP right away.
Things to Keep in Mind Before Transferring the Shares
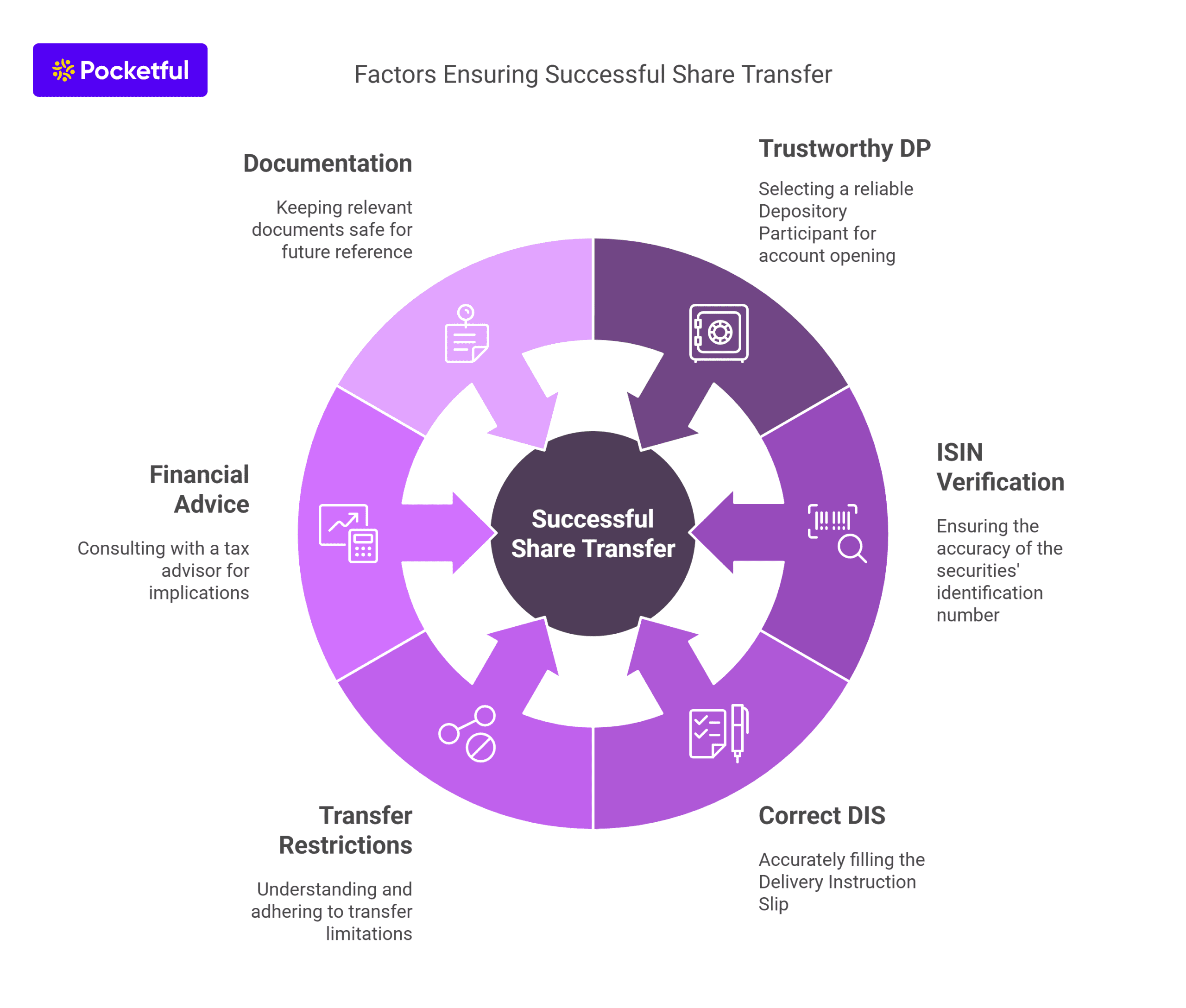
Once you decide to transfer shares from one DP to another, there are various points one should keep in mind. A few points are mentioned below-
- Selecting a DP – Before initiating the process of share transfer, ensure you select a trustworthy Depository Participant for opening a new Demat account.
- ISIN Code – The International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) of the securities should be checked and verified because if it is incorrect, the share transfer will be unsuccessful .
- Delivery Instruction Slip – Make sure the Delivery Instruction Slip is correctly filled to avoid any rejection or delay in the process.
- Restrictions on Transfers – The DP can restrict the transfer of shares due to specific reasons, such as regulatory guidelines and the types of shares being transferred.
- Consult your Financial Advisor – There might be specific tax implications while transferring the shares. One needs to consult with their tax advisor before initiating the process.
- Documentation – All relevant documents, such as DIS (Delivery Instruction Slip) and acknowledgment form must be kept safe for future references.
Read Also: How to Transfer Money from a Trading Account to a Bank Account?
Conclusion
In conclusion, moving shares across demat accounts has become much simpler nowadays. The shares can be transferred either online or offline. However, before beginning the procedure, be sure the DP to whom you plan to transfer your shares provides superior services at a reasonable price. It is advised to speak with an investment advisor before beginning any transfer procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I transfer my stocks from one demat account to another without selling them?
You can transfer your holdings from one demat account to another without selling them by initiating a transfer request with your current DP.
How long will it take to transfer shares from one broker to another?
It generally takes 3 to 5 business days once you submit the relevant documents to transfer shares from one demat account to another.
Can I transfer my shares online from one demat account to another?
Depending on your depository, you can visit the NSDL or CDSL website and complete the process online.
Can shares be gifted to a family member?
You can easily gift shares by transferring the shares directly to the family member’s Demat account of the.
How many depositories are there in India?
NSDL (National Securities Depository Limited) and CDSL (Central Depository Services Limited) are the two depositories in India.