Retirement planning has always been a key financial goal for an individual. For Central Government Employees, there are various retirement schemes such as PPF, NPS, etc. But recently, the Government has introduced another scheme commonly known as “UPS” or “Unified Pension Scheme”, this scheme offers a minimum guaranteed Pension.
In this blog post, let’s understand about the Unified Pension Scheme, its eligibility criteria, the process to apply and the key difference between NPS and UPS.
What is the Unified Pension Scheme?
The Unified Pension Scheme was introduced by the Government of India on 24th August 2024, and it became effective from 1st April 2025 for Central Government Employees. This scheme does not include armed- force personnel. The central Government employees can continue with the National Pension Scheme or switch to UPS. If the employee opts for UPS, they cannot be changed back to NPS.
Eligibility Criteria for Unified Pension Scheme
The following are the eligibility criteria for an individual to become eligible for the Unified Pension Scheme:
- Only central Government employees who are serving on 1st April 2025 and are covered under NPS can invest in UPS.
- Any new employee joining after 1st April 2025 is eligible for UPS.
- Any central Government employee covered under NPS who has taken voluntary retirement on or before 31st March 2025.
- The spouse of a Central Government employee, who was an NPS subscriber and passed away before exercising the option to opt for the OPS.
Who is Not Eligible for the Unified Pension Scheme
The following persons are not eligible for the Unified Pension Scheme:
- Employees retiring from their service before the period of 10 years.
- Employees who have been removed from the service.
- The Central Government of an employee who has been dismissed from the service.
UPS Scheme Minimum Pension Amount
The minimum Pension amount guaranteed under the Unified Pension Scheme will be 10,000 per month only for employees who have completed 10 years of service.
Benefits of Unified Pension Scheme
The key benefits of the Unified Pension Scheme are as follows:
- Fixed Pension: An individual will receive a fixed sum of amount after their retirement, which is equal to 50% of their average basic pay over the previous 12 months of retirement.
- Contribution: The employee will contribute only 10% of their basic salary, whereas the Government contributes 18.5% of the employee’s basic salary.
- Family Pension: In case of the demise of the account holder before retirement, 60% of the Pension will be given immediately to the spouse of the Pensioner.
- Minimum Amount of Pension: An employee who has completed only 10 years of service and retires is eligible for 10,000 INR of monthly Pension.
- Inflation Benefit: The individual will get the benefit of inflation adjustment based on the dearness allowance.
Read Also: National Pension System (NPS): Should You Invest?
Process to Apply For the Unified Pension Scheme
One can apply for the Unified Pension Scheme either online or offline:
1. Online Process:
To apply for UPS through online mode, one can follow the steps mentioned below:
- First, an employee needs to visit the Protean Website.
- On the home page of the website, there is an option for the Unified Pension Scheme. Click on it.
- There you will find Register for UPS; however, if you want to migrate NPS to UPS, you can also select the same on this page.
- You can fill out the form and submit the details.
2. Offline Process:
For the offline process, one can follow the steps mentioned below:
- The first step is to visit the Protean website.
- You will find a ‘Forms’ section under the Unified Pension Scheme. Download the relevant form depending on your service status.
- You need to fill in the form and submit it to the drawing and disbursing officer.
- The DDO will check the form and send it to the Pay and Accounts Officer for approval.
UPS Withdrawal Rule and Conditions
The conditions related to the withdrawal are based on two rules, namely complete withdrawal or partial withdrawal, the details of which are as follows:
- Complete Withdrawal: An employee can withdraw a maximum of 60% of their corpus under the Unified Pension Plan. The remaining amount of the corpus will be utilised towards the regular monthly Pension. However, if the withdrawal is made, the monthly Pension can be reduced proportionately. In case of the death of an employee, their spouse receives 60% of the last Pension for their lifetime.
- Partial Withdrawal: An employee can make a partial withdrawal a maximum of three times during their service period. The provision of partial withdrawal is applicable only after a period of three years. Only 25% withdrawal is allowed each time for specific circumstances, such as children’s higher education, medical expenses, etc.
Read Also: NEFT vs RTGS vs UPI vs IMPS: A Comparative Study
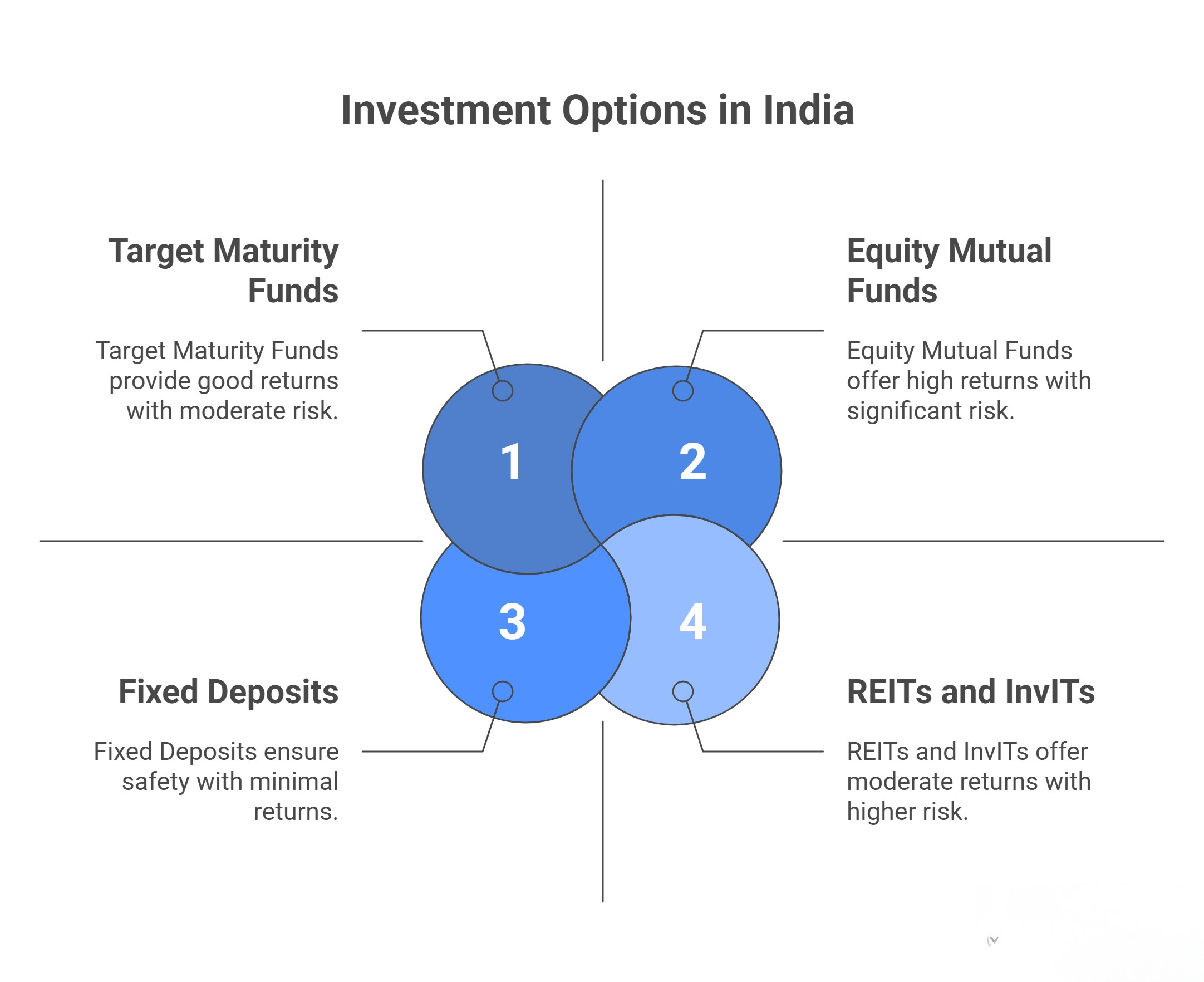
Difference Between UPS vs NPS
The key difference between the Unified Pension Scheme and the National Pension Scheme is as follows:
| Particular | UPS | NPS |
|---|---|---|
| Pension Amount | UPS offers a fixed Pension amount. | The Pension through NPS depends on the corpus accumulated. |
| Minimum Pension | A minimum guaranteed Pension of INR 10,000 is provided in this scheme. | There is no provision for a minimum Pension. |
| Eligibility | This scheme applies only to central Government employees. | Both central and state Government employees, along with private individuals, are eligible for NPS. |
| Market Risk | There is no market risk in it. | As the amount under this scheme is invested in market-linked instruments. Hence, it carries a high risk. |
| Inflation | The amount of the Pension is adjusted for inflation. | There are no provisions for inflation adjustment. |
| Portability | Central Government employees opting for UPS can port their investment. | Portability across sectors applies to it. |
Conclusion
The recent introduction of the Unified Pension Scheme by the Government of India is a major reform by the Indian Government in providing benefits to Central Government Employees. It offers an assured Pension without any market risk. However, the Pension amount depends on the corpus accumulated by the employee during their service period. However, it is advisable to consult your investment advisor for your comprehensive retirement planning, as it can help you in managing your expenses post-retirement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the minimum Pension amount under the Unified Pension Scheme?
If an employee has served a minimum period of 10 years, they will get a minimum Pension of 10,000 INR per month.
Can a private sector employee get a Pension under the Unified Pension Scheme?
No, a private sector employee cannot invest in the Unified Pension Scheme; therefore, they are not eligible to get a Pension under UPS.
Will UPS provide a Pension to the employee’s family after their death?
Yes, UPS provides a family Pension scheme, which means that in case of the death of an employee, their spouse or an eligible family member will get 60% of the Pension that the employee would have received.
Can an existing employee opt for the Unified Pension Scheme?
Yes, an existing central Government employee can opt for the Unified Pension Scheme once in their service tenure. However, once they opt for UPS, they cannot switch back to NPS.
When will the Unified Pension Scheme come into effect?
The Unified Pension Scheme came into effect from 1st April 2025.