Healthcare is one of the key and growing sectors of the Indian economy, as it significantly contributes to the country’s GDP. The diagnostic industry plays an important role in shaping this sector. With the rise of chronic disease and increasing health awareness, the diagnostic sector has witnessed a significant growth in the past few years.
In today’s blog post, we will give you an overview of the top diagnostic companies in India, along with the benefits and factors to be considered before investing in them.
What are Diagnostic Stocks?
Diagnostics stocks are the shares of companies that operate diagnostics and medical testing centers. They generally provide services such as preventive healthcare checkups, pathology, radiology, genetic testing, etc. These medical tests play a major role in diagnosing and monitoring diseases.
Top Diagnostic Stocks Based on Market Capitalization
- Global Health Limited
- Dr. Lal Path Labs Limited
- Rainbow Children Medicare Limited
- Vijaya Diagnostic Center Limited
- Metropolis Healthcare Limited
- Thyrocare Technologies Limited
- Krsnaa Diagnostics Limited
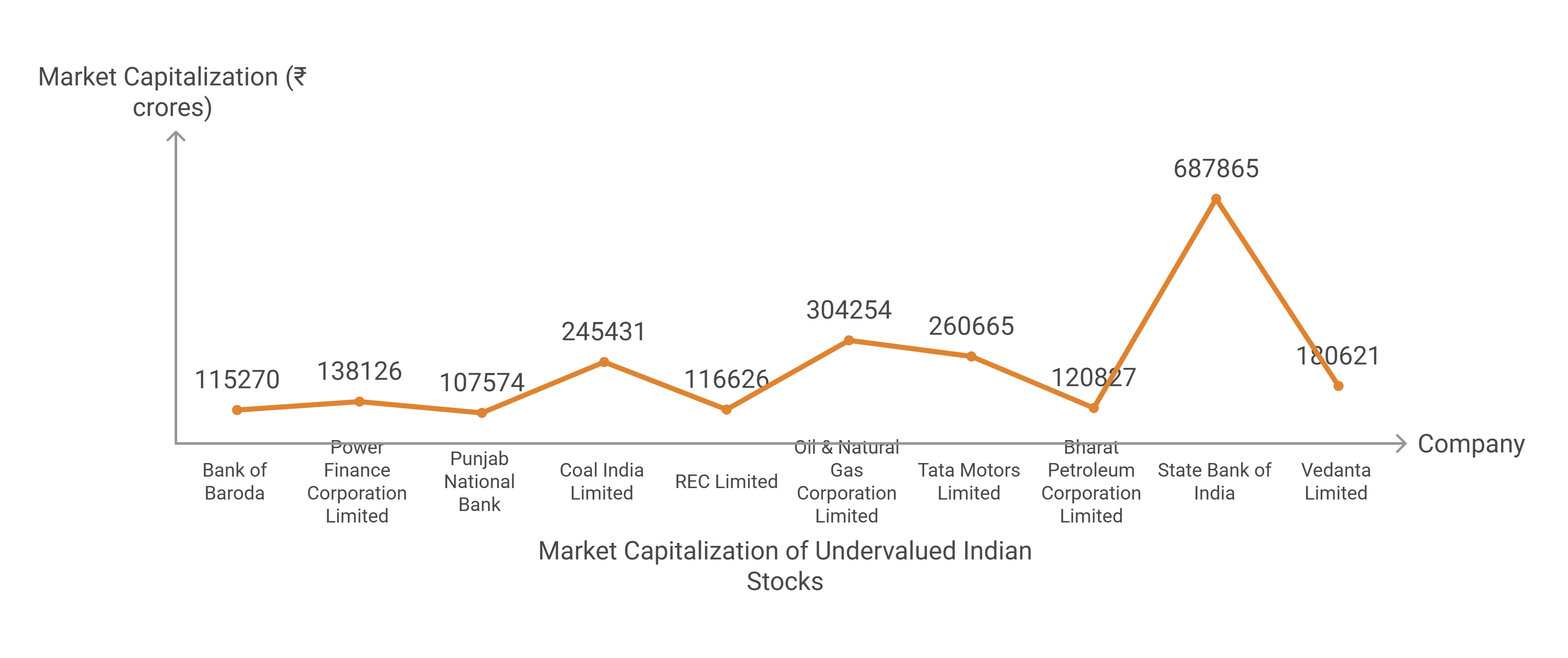
Market Information of Top Diagnostic Stocks in India
| Company | Current Market Price (₹) | Market Capitalisation (in ₹ Crores) | 52-Week High (₹) | 52-Week Low (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Health Limited | 1,174 | 31,547 | 1,456 | 995 |
| Dr. Lal Path Labs Limited | 1,424 | 23,851 | 1,771 | 1,147 |
| Rainbow Childrens Medicare Limited | 1,265 | 12,846 | 1,646 | 1,206 |
| Vijaya Diagnostic Center Limited | 996 | 10,248 | 1,192 | 740 |
| Metropolis Healthcare Limited | 1,908 | 9,889 | 2,263 | 1,315 |
| Thyrocare Technologies Limited | 467 | 7,433 | 538 | 219 |
| Krsnaa Diagnostics Limited | 717 | 2,326 | 915 | 626 |
Read Also: Best Healthcare Stocks in India
Best Diagnostics Stocks in India Based on Market Capitalization – An Overview
A brief overview of the best diagnostic stocks in India is given below:
1. Global Health Limited
Global Health Limited operates a private multi-specialty hospital in India under the brand Medanta. The company was incorporated in 2004 and was initially named Global Health Pvt Ltd. It was founded by Dr Naresh Trehan, a renowned cardiovascular surgeon. In 2022, the company converted itself into a public limited company and changed its name to Global Health Limited. The company’s headquarters is located in New Delhi.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 12.79% | 160.34% | 192.99% |
2. Dr. Lal Pathlabs Limited
Dr. Lal Pathlabs is a leader in diagnostic services in India. The company was founded in 1949 by Dr Major S.K. Lal. The company began its journey as a pathology service provider and a blood bank. In 1995, the company was incorporated as Dr Lal PathLabs Pvt Ltd. The company started expanding rapidly in the early 2000s. To expand operations, it raised capital through an initial public offering in 2015 and got itself listed on the Indian Stock Exchange. The company’s headquarters is situated in Gurgaon.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| -0.72% | 30.88% | 18.39% |
3. Rainbow Children Medicare Limited
Rainbow Children Medicare Limited was founded in 1999 by Dr Ramesh Kancharla. Earlier, the company established a pediatric specialty hospital in Hyderabad that focused on providing maternal and pediatric services. To establish more hospitals across the country, the company raised capital and launched its IPO in 2022. The company’s headquarters is situated in Telangana.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| -16.29% | 69.74% | 148.10% |
4. Vijaya Diagnostic Center Limited
Vijaya Diagnostics is a leading diagnostic service provider in India. It was established in 1981 by Dr Surendranath Reddy in Hyderabad. The company focuses on establishing diagnostic centres, especially in South India. The company issued an offer for sale in 2021 and got itself listed on the Indian stock exchange. The headquarters of the company is situated in Telangana Hyderabad.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 16.91% | 144.85% | 85.43% |
5. Metropolis Healthcare Limited
Metropolis Healthcare Limited was founded by Dr Sushil Kanubhai Shah in 1980. The company established its first pathology in Mumbai and with time it has expanded globally. From 2001 onwards, Amira Shah, daughter of the founder Sushil Kanubhai Shah, played a major role in the expansion of the company. It launched its IPO in 2019 and became a publicly listed company. The company’s headquarters is situated in Mumbai.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.88% | 37.88% | 12.70% |
6. Thyrocare Technologies Limited
Thyrocare Technologies was founded by Dr. A. Velumani in 1996 to provide affordable diagnostic services. As the name suggests, the company initially focuses on providing thyroid testing services. In 2014, in collaboration with Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, it established the world’s largest laboratory automation track in Mumbai. The company launched its IPO in 2016 and got itself listed on the Indian Stock Exchange. In 2021, API Holding acquired a controlling stake in Thyrocare. The company’s headquarters is situated in Mumbai.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 65.91% | -144.04% | 44.00% |
7. Krsnaa Diagnostics Limited
Krsnaa Diagnostics was established in 2010 and offers various diagnostic services such as radiology, pathology, and tele-radiology. The company has a presence across India and has collaborated with various private hospitals to provide its services. The company launched its IPO in 2021, which was an offer for sale. The company’s headquarters is situated in Pune.
Know the Returns:
| 1Y Return (%) | 3Y Return (%) | 5Y Return (%) |
|---|---|---|
| -19.71% | 67.04% | -28.48% |
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The key performance metrics of diagnostics companies are mentioned below:
| Company | Operating Margin (%) | Net Profit Margin (%) | ROE (%) | ROCE (%) | Debt to Equity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Health Limited | 21.40 | 14.59 | 16.45 | 19.01 | 0.14 |
| Dr. Lal Path Labs Limited | 24.01 | 16.27 | 19.34 | 26.86 | 0.05 |
| Rainbow Childrens Medicare Limited | 27.28 | 16.83 | 17.23 | 17.50 | 0 |
| Vijaya Diagnostic Center Limited | 33.72 | 21.83 | 18.08 | 20.30 | 0 |
| Metropolis Healthcare Limited | 16.33 | 10.63 | 11.66 | 15.06 | 0 |
| Thyrocare Technologies Limited | 17.44 | 12.08 | 13.43 | 18.03 | 0.04 |
| Krsnaa Diagnostics Limited | 13.95 | 9.17 | 7.01 | 9.71 | 0.13 |
Read Also: Most Undervalued Stocks in India
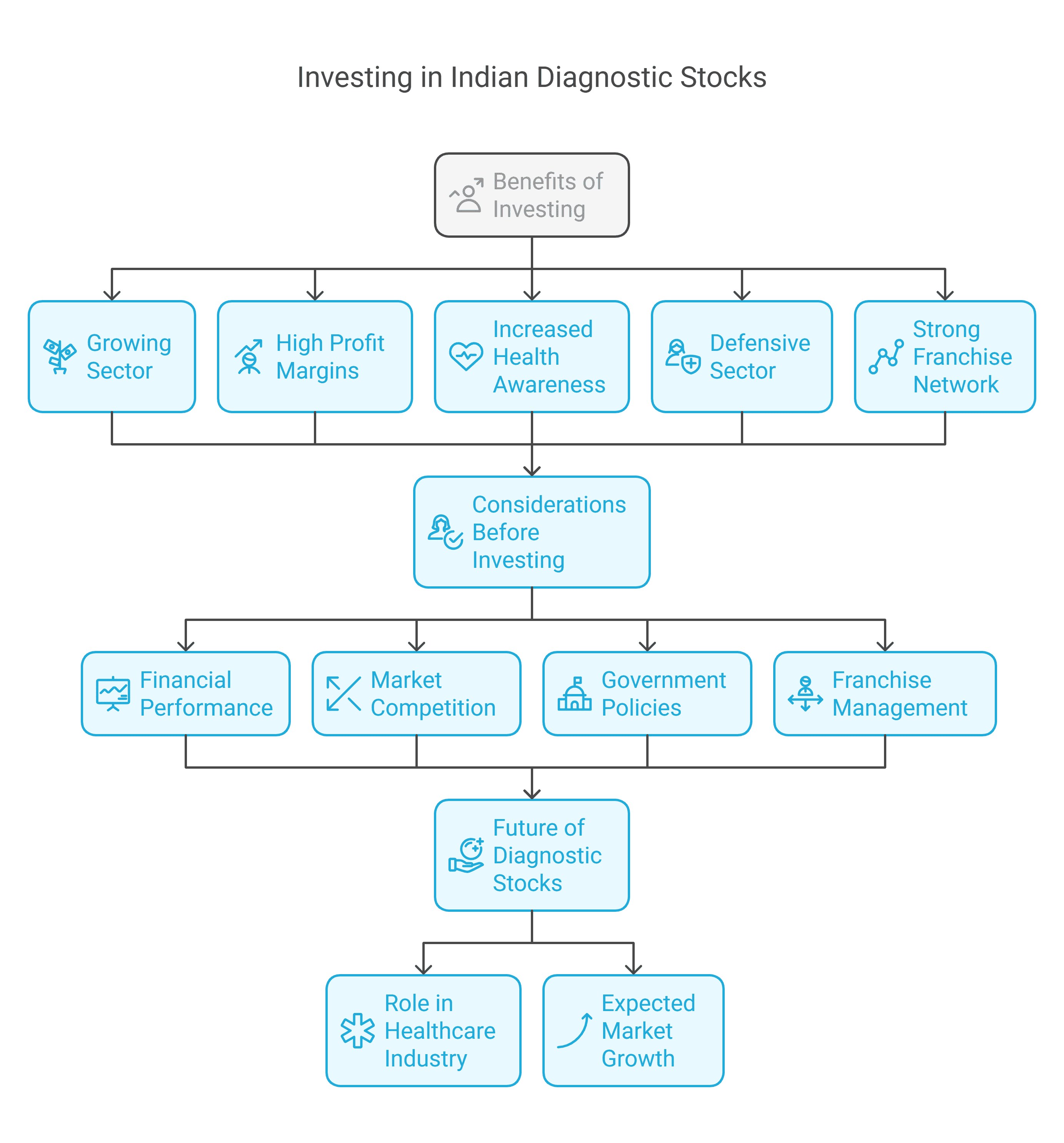
Benefits of Investing in Diagnostic Stocks
The major benefits of investing in Diagnostic stocks are as follows:
- Growing Sector: The Indian healthcare sector is growing at an annualized growth rate of 15-17%. Hence, this growth will also benefit the diagnostics companies.
- Profit Margins: Companies operating in the diagnostic sector generally have high profit margins because of low operating costs.
- Health Awareness: People are becoming more and more health-conscious; hence, they opt for regular preventive checkups, which could increase the revenue of diagnostic companies.
- Defensive Sector: Investment in diagnostic companies is considered a defensive bet, as the demand for health checkups will increase with time, and it will not be impacted by any economic downturn.
- Business Model: Diagnostic companies operate in various cities through their strong franchisee network, helping the company earn stable revenues.
Factors to be Considered Before Investing in Diagnostic Stocks
The key factors that one should consider before investing in diagnostic stocks are as follows:
- Financial Performance: Before choosing any diagnostic company for investment, one should check the financial performance of the companies, which includes revenue, profit margins, etc.
- Market Competition: The new companies are competing with the established companies like Dr. Lal Pathlabs, Thyrocare, etc. Hence, one should opt for a company that has a competitive advantage over others.
- Government Policies: There are various initiatives taken by the government or healthcare policies such as Ayushman Bharat, etc., as well as public-private partnerships that can help diagnostics companies get consistent revenue.
- Franchisees: The company’s ability to manage its franchise network and sample collection centres will impact the company’s performance.
Future of Diagnostic Stocks In India
The Indian Diagnostic sector plays an important role in shaping the Indian healthcare industry. Various government initiatives, such as the National Health Mission (NHM), have allocated a budget of approximately ₹290 billion, which will be used to improve the infrastructure and services of the healthcare industry. The Indian diagnostic industry consists of 60% pathology and 40% radiology, and this industry is expected to reach a total market value of ₹1,360 billion by the end of FY 2026 and will have an expected CAGR of 14%. Hence, the diagnostic sector will have a bright and promising future.
Conclusion
On a concluding note, the Indian diagnostic industry is on a growth trajectory. The increasing cases of chronic diseases require continuous monitoring, which can be done through regular health checkups. This trend can support revenue growth for diagnostic sector stocks. However, there are certain factors that need to be considered by the investor before investing in diagnostic stocks, such as market competition, regulatory changes, etc. Therefore, it is advisable to consult your investment advisor before making any investment decision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which companies are associated with the diagnostics sector in India?
Some of the major companies in India’s diagnostic sector are Thyrocare Technologies Limited, Metropolis Healthcare Limited, Dr Lal Pathlabs Limited, Rainbow Children Medicare Limited, etc.
Is it a good time to invest in the stocks of diagnostics companies?
Yes, it is a good time to invest in the stocks of diagnostics companies because the rise in chronic diseases and awareness about preventive health checkups will drive the growth of this sector. However, one should consider their risk profile and consult their financial advisor before investing in these stocks.
What are the major factors that need to be considered before investing in diagnostic companies?
The key factors that one should consider before investing in the diagnostic sector are competition, market trends, technologies used by diagnostic companies, etc.
How to select the best diagnostic company for investment?
One can select the best diagnostic company by analyzing its financial performance and key metrics, its business model, regulatory risks, competition in the industry, promoter holdings, etc.