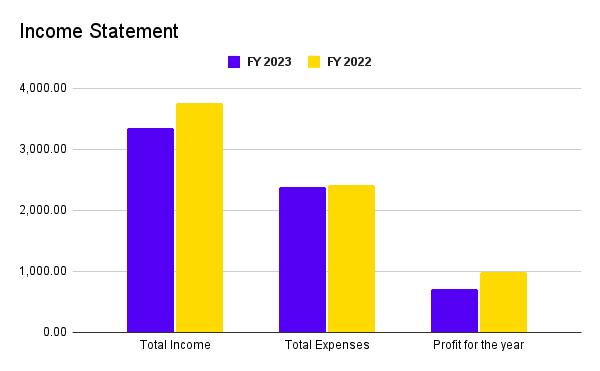
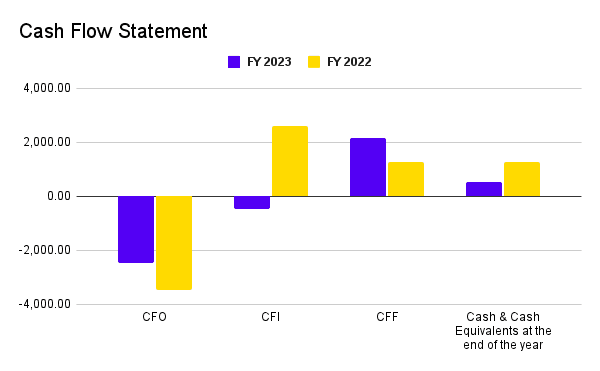
Have you ever heard of a city specifically created to function as a financial tech city? Yes, you read correctly; a city in India is known as Gujarat International Financial Tech City or Gift City. The world’s financial, tech and other businesses will establish offices in this city.
So, let’s explore Gift City in more detail and save you time.
Gift City Overview
Gujarat International Financial Tech City, commonly referred to as Gift City, is established as a special economic zone. The city aims to give corporate houses access to top-notch infrastructure and amenities. With these, they hope to draw domestic and foreign businesses, particularly those in the financial industry.
A joint venture between the Gujarat state government and Infrastructure Leasing and Financial Services Ltd (IL&FS) created Gift City.
To foster a positive atmosphere for technology companies, the city offers tax breaks and simplified regulatory procedures as unique incentives for businesses relocating to Gift City.
Did you know?
Special Economic Zones are areas designated by the government where business establishments are granted certain privileges, such as single-window clearance, tax rebates, and other concessions, intending to promote development in the area and its nearby area.
Timeline
2007 – The Indian government announced the establishment of The International Financial Service Center (IFSC) in Gujarat.
2010 – Then, Gujarat International Financial Tech City Company Limited (GIFTCL) was incorporated to oversee the establishment of Gift City.
2015 – The inauguration of this city was done this year.
2017 – The International Financial Service Center Authority (IFSCA) was founded to control financial activity in the city.
2023 – The SGX Nifty is now called Gift Nifty and has moved from Singapore to Gift City.
2024 – A metro station connecting Ahmedabad to Gift City was completed in March.
Current Status
There are a lot of high-rise apartments in the city, as well as a lot of schools and hospitals, to supply all kinds of infrastructure facilities. The 78,000 crore plan is regarded as the prime minister’s pet project. Over 26,000 people work in this high-rise tower, which houses about 400 workplaces.
Management
Mr. Tapan Ray, IAS, is the managing director and group CEO of Gift City, whereas Mr. Hasmukh Adhia is the chairman of the city.
Area Covered
Spread across 359 hectares or 886 acres; the gift city has two sections in the area:
- Special Economic Zone – The region primarily draws in foreign financial institutions and corporate houses.
- Domestic Tariff Area – The area of this section is spread over the remaining area and focuses on domestic companies that function in the Indian regulatory framework.
Did you know?
The tallest building in the Gift City is called “The Gift One Tower” and is 122 meters tall and has 29 floors.
Developers
Hiranandani Group, Mumbai, is developing Signature Tower.
Brigade Group, Bangalore, is developing BIFC Tower.
Savvy Group, Ahmedabad, is developing Pragya Tower.
Advantages
1. It is estimated to create 5,00,000 direct jobs and a much higher number of indirect jobs.
2. The city will provide infrastructure facilities and connectivity across the globe.
3. There is a strong dedication to environmental preservation and integrated technology that safeguards the ecosystem.
4. It offers financial incentives and regulatory independence to companies.
Stakeholders
In Gift City, there are three primary stakeholders.
- Gujarat Urban Development Company Limited (GUDCL) – It helps the government create policies and secure funding from international organizations.
- Gujarat Maritime Board (GMB) – It was founded to develop India’s ports, privatize them, and provide specialized cargo handling.
- Gujarat Industrial Development Corporation (GIDC) – The government of Gujarat founded this organization to supply industrial infrastructure at a reasonable cost with a prompt and transparent delivery system.
Read Also: Case Study of Petrol & Diesel Price History in India
Highlights
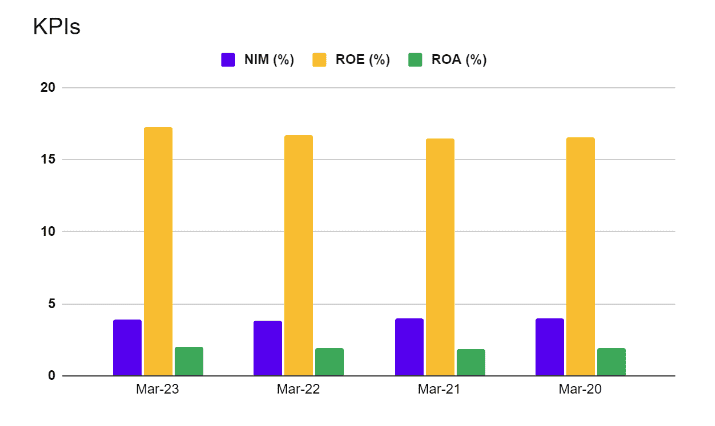
1. On average, over 20 billion dollars are exchanged daily in foreign currency.
2. More than 360+ units licensed.
3. As of now, more than 16000+ employment generated in Gift City.
4. Around 33 billion dollars of total assets are held by the IFSC banking unit in Gift City.
5. Reinsurance premiums worth over 297 million dollars were reserved in the Gift City.

Companies Operating
The companies operating in the gift city can be divided into different sector
1. Banking Sector – The leading businesses in this industry that have set up their offices in the Gift City include Standard Charter, Citibank, JP Morgan, Yes Bank, Indian Bank, Federal Bank, RBL Bank, ICICI Bank, SBI, and HSBC.
2. Insurance Sector – Life Insurance Corporation of India, The New India Assurance Company Limited, HDFC Life Insurance, etc. are operating from the insurance sector in the city.
3. Financial Services – The companies operating in Gift City from the financial services sector are National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL), BSE, India International Exchange (IFSC) Ltd., Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL), etc.
4. IT and Technology – TCS, Infosys, Accenture, Wipro, etc. are the companies operating in Gift City.
5. Other – Adani group, reliance industries, etc.
Read Also: Yes Bank Case Study: Business Model, Financial Statement, SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
The Gujarat government decided to establish Gift City, which will encourage foreign companies to enter the Indian market and ultimately boost the country’s GDP and per capita income. This would enhance India’s reputation around the world.
Things are moving forward rather nicely in Gift City, and eventually, we will be able to compete with the global financial hubs in places like London and New York.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Gift City tax-free?
Companies in Gift City will enjoy tax exemption benefits for 10 years out of a total of 15 consecutive years.
Is Gift City also known as a smart city?
Yes, Gift City is India’s first operational smart city, spread across 886 acres and has world-class infrastructure.
Did the government establish Gift City?
The government of Gujarat is developing Gift City through various undertakings.
Is Gift City operational?
Yes, Gift City is operational now, but the project’s first phase is expected to be completed in 2025.
What is an IFSC?
IFSC stands for International Financial Services Center (IFSC), which caters to customers outside of India’s jurisdiction. Its major objective is to provide financial services to residents and non-residents in foreign currencies.