One97 Communications Limited is an Indian multinational technology company started in the year 2000 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma. Paytm, a subsidiary of One97, is an Indian financial services and digital payments company founded in the year 2010.
This case study of Paytm highlights its evolution from a prepaid mobile and DTH recharge platform to a mainstream player with the launch of wallet services in 2014, marking a key moment in enabling cashless transactions for users.”

Today, Paytm stands as a one-stop-shop for consumers, offering a plethora of financial and other services that include e-commerce, banking, investments, loans, bus tickets, money transfers, etc.
The business model of Paytm has driven its total revenue growth from ₹2,802 Cr in FY 2021 to ₹7,990 Cr in FY 2023, achieving a CAGR of 69%.
In 2017, Paytm piloted bill payment services in Canada and in the year 2018, Paytm partnered with Softbank and Yahoo Japan Corporation to launch PayPay, a leading digital payments and financial services company in Japan.
Paytm went public with its IPO on NSE & BSE in November 2021 and raised INR 18,300 crs via IPO. The IPO was one of the largest in India, although Paytm’s debut in the stock market faced mixed reactions.
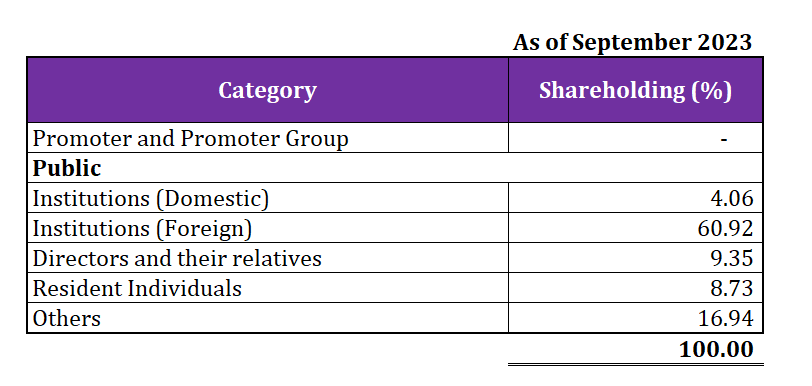
As of September 2023, there is no identifiable Promoter of Paytm. Have a look at the shareholding pattern of Paytm:
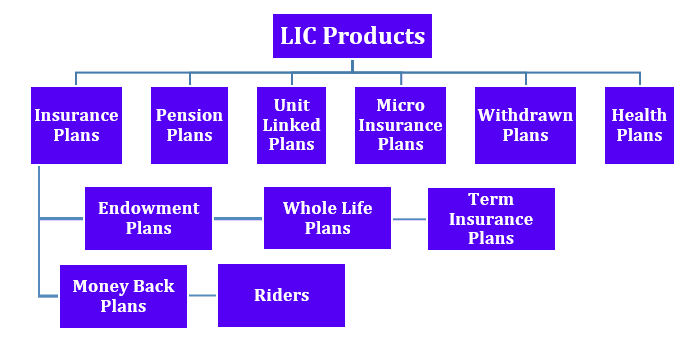
Products and Services of Paytm
Paytm offers a variety of products and services, such as payment services, financial services, cloud, etc.
Payment Services
Payment Services are meant for both consumers and merchants and enable them to make and receive payments seamlessly both online and in-store. Paytm has an overall market share of 40% in payment transactions. Paytm also launched the Paytm Wallet in 2014 and QR code services in 2015. QR Code was later upgraded to an All-in-One QR code in 2020 so that consumers and merchants can have a seamless payment experience while accepting payments from third-party UPI platforms.
Further, in 2020, Paytm launched soundbox service that gives real-time payment audio confirmation for payment completion. With Paytm’s payment services, consumers can make online bill payments, recharge, and transfer money through the app.
Commerce & Cloud Services
Paytm allow consumers to avail of lifestyle commerce services that include booking online tickets, entertainment, gaming, and food delivery within the Paytm app. Merchants can also connect with consumers to improve their business operations. Paytm provides merchants with services such as billing, ledger, vendor management, inventory management, catalogues, etc.
Paytm also provides software and cloud services to enterprises, telecom companies, digital and fintech platforms.
Financial Services
Paytm provide the following financial services to consumers and merchants:
Mobile Banking Services – Paytm provides mobile banking services through Paytm Payments Bank that includes digital banking products such as current accounts, savings accounts, salary accounts, fixed deposit accounts, and debit cards for individuals, SMEs and corporates.
Lending – Paytm collaborates with financial institutions to improve distribution, underwriting and collections and provide seamless access to loans to consumers and merchants. Paytm also launched the Paytm Postpaid, which is a buy now pay later (BNPL) product.
Insurance and Attachment Products – Paytm in collaboration with its insurance partners, provides attachment products like movie and travel ticket cancellations protection. Paytm’s subsidiary company, Paytm Insurance Broking Private Limited provides insurance services that include auto insurance, life insurance and health insurance.
Wealth Management – Paytm provides wealth management services to consumers through the Paytm app and Paytm Money App. It also launched Paytm Gold, which allows customers to buy digital gold on their platform. Paytm Money app offers investment in mutual funds, equities, and derivatives trading.
Read Also: What exactly happened to Paytm Payments Bank & why has the RBI banned it?
Awards & Recognitions of Paytm

Paytm has received multiple awards and recognitions. Some of the major recognitions are:
- BrandWagon Ace Award for best social media campaign in 2020.
- ET BFSI Excellence Award for Best Digital Bank of the Year in 2020.
- India Digital Award by IAMAI for Best Fintech Growth Story and Best Data-Driven Marketing Strategy in 2021.
- FinTech India Innovation Awards 2023 for Best Fintech Company of the Year in 2022.
- 8th CFO Vision and Innovation Summit & Awards 2023 for Best Fintech Company of the Year.
- Quantic 4th Annual BFSI Excellence Awards 2023 for best Wealth Management Company of India.
Advertising Campaigns
- “Kar De Paytm” in the year 2010.
- “Zindagi jeene ka naya tarika shuru karo – Paytm Karo” in the year 2015.
- “ATM nahi, Paytm Karo” in the year 2016.
- “Dimag Khul ke Jee” in the year 2017.
- “India Kahe Paytm Karo” in the year 2022.
Competitive Advantages of Paytm
- Paytm was an early entrant into the digital payments landscape and had a first-mover advantage.
- Paytm has a wide market of payment services across India with a brand value of US $6.3 billion.
- Paytm builds and innovates its technology which helps it to launch products and services rapidly with a high success rate. Paytm has a technology team of over 2,500 members that continuously works to improve the user experience.
- Paytm tries to understand the needs of its users and innovates products accordingly.
- To engage with customers, Paytm invests in marketing campaigns and other promotional offers.
Growth Trajectory of Paytm

Paytm has shown an impressive growth and expansion journey over the years. It has evolved from a mobile recharge platform to a financial services powerhouse. It claims to have more than 300 million active users. Paytm’s strategic partnerships with HDFC Bank, Uber, Indian Railways, and major E-commerce platforms have helped the company to grow over the years. Cashback and Promotional offers still attract new customers and hold the existing ones. Paytm has moved beyond payment services and has ventured into travel, wealth, credit cards, loans, etc.
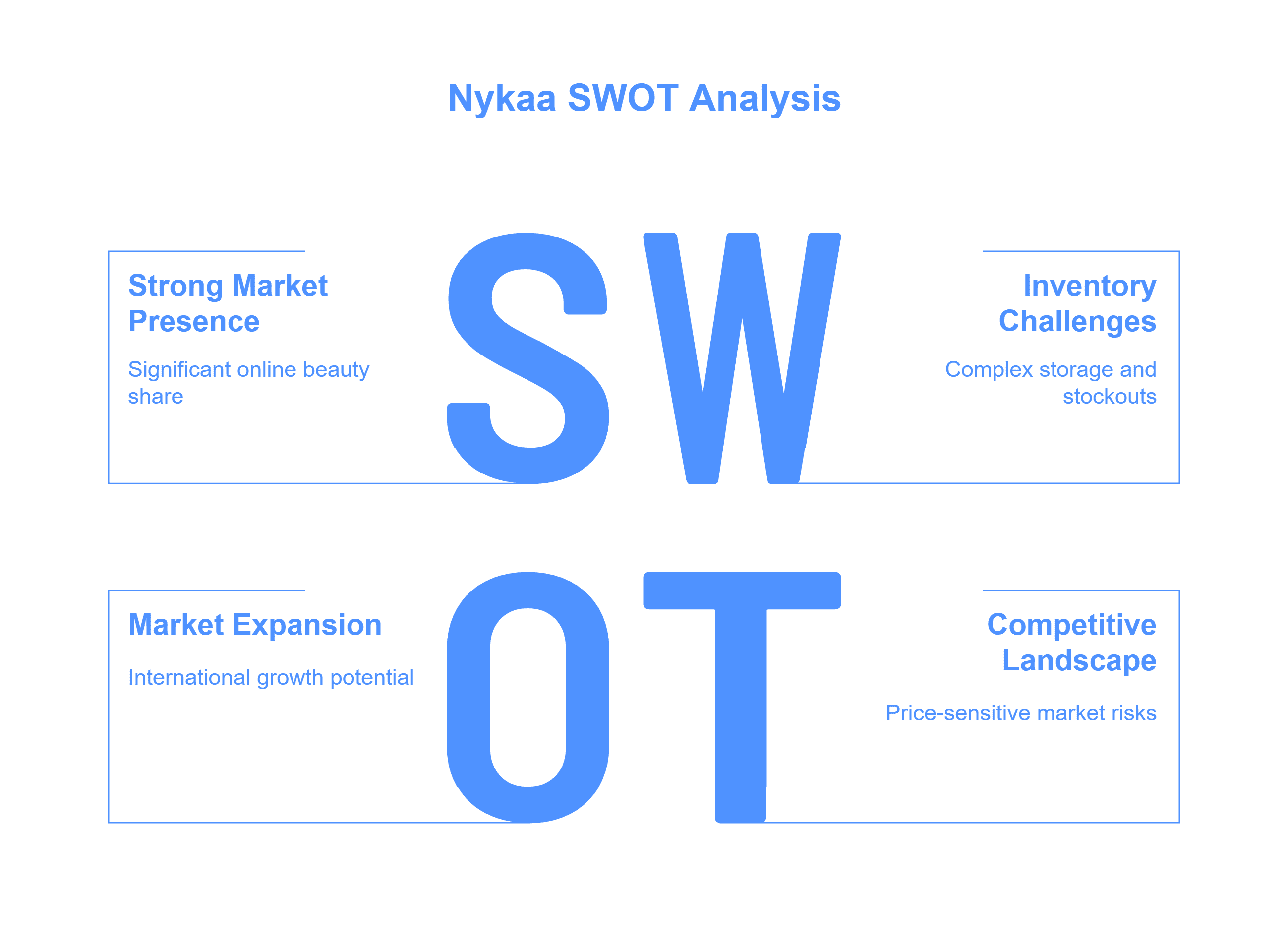
SWOT Analysis of Paytm
The Paytm SWOT Analysis highlights its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, showcasing its market position and growth potential.

Strengths
- Paytm is a leading player in the payment sector and enjoys a large user base.
- Paytm has strong brand recognition in the fintech sector of India.
- Paytm has a diversified product portfolio such as financial services, loans, broking, credit cards, travel, etc.
Weakness
- The lack of profits in the company has raised financial sustainability issues for the company.
- Paytm heavily depends on the Indian market for its revenue and any kind of regulatory changes can impact the company’s business operations.
- The company faces tough competition from other fintech startups like PhonePe, Google Pay, etc.
Opportunities
- Penetration in the rural area to provide digital payment services can help Paytm grow its business further.
- A comprehensive app for seamless user experience can drive the revenue growth of the company.
- Tapping into the International markets can help Paytm provide services outside of India, which boosts the company’s revenue growth.
Threats
- Digital payment systems like Paytm are often prone to cyber security risks. Such risks have the potential to significantly alter the user base of Paytm.
- Economic downturns can affect consumer spending. This will eventually reduce the user base and revenue growth of the company.
- Innovative Competitors and Big Giants like Google Pay and PhonePe could challenge Paytm’s growth.
Read Also: One MobiKwik Systems Case Study: Business Model, Financials & SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Paytm’s case study provides useful insights into the dynamics of the fintech landscape and cashless economy in India. Paytm’s diversification of services and first-mover advantage have allowed it to create a strong and loyal user base in India. The company should continue to innovate and explore the emerging digital landscape of India for better market positioning and customer engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who founded Paytm?
Vijay Shekhar Sharma founded Paytm in 2010.
What is the shareholding percentage of promoters in Paytm?
As of September 2023, holding of promoters is nil.
Paytm faces tough competition from which companies?
PhonePe, Google Pay, etc..
When was Paytm listed on NSE & BSE?
November, 2021.
What financial services are offered by Paytm?
Mobile Banking Services, Loans, Mutual funds, Equity Investments, Credit Cards, etc.
What is the UPI transaction limit through Paytm per day
Paytm UPI allows you to transfer the maximum amount of Rs 1 lakh in a day.