Whenever you decide to invest in the stock market, the first thing that comes to your mind is whether to invest for the short term or for the long term. Both of them require different strategies and mindsets.
In today’s blog post, we will give you an overview of short-term and long-term trading, along with the different strategies used in it.
Meaning of Short-Term Trading
Buying and selling various kinds of financial instruments, including stocks, commodities, currencies, etc., within a short time—generally between a few minutes to a few days—is known as short-term trading. Making quick profit from quick fluctuations in prices is the primary objective of short-term trading. The short-term trades primarily depend on technical analysis.
Types of Short-Term Trading
There are generally four types of short-term trading as follows:
- Intraday Trade: It is the most common form of trading, where the trader squares off their position before the market closes. This was done to avoid the risk of a change in the price of securities overnight.
- Scalping: This is the fastest trading style among all short-term trading styles. In this, the trader executes numerous trades during a particular trading session and tries to earn profit from the smallest price change.
- Swing Trade: In this short-term trade, the trader holds their position for a few days, with the objective of earning a profit from the short-term price movement that occurs over time.
- Momentum Trading: In momentum trading, one enters into a trade with the belief that the price movement (upside or downside) will continue over a period of time. The trader enters into a momentum trade for higher profit than intraday and scalping traders.
- News-Based Trading: As the name suggests, the trader tries to capitalize on the opportunity that arises due to a particular news in a stock. It generally holds its position until the impact of news on the stock price ends.
Popular Short-Term Trading Strategies
The most popular short-term trading strategies are as follows:
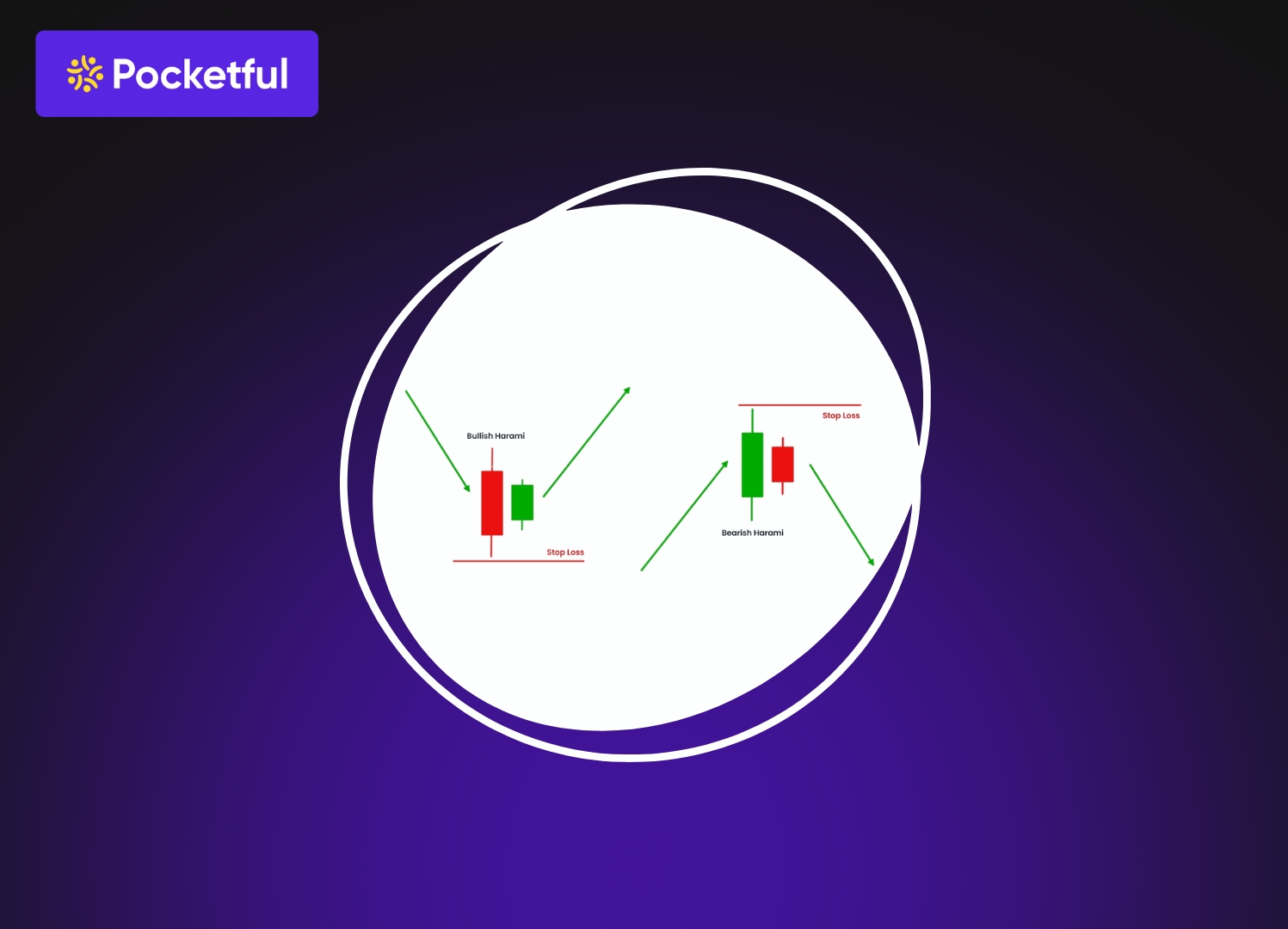
- Support and Resistance: It is the most common trading method used by a trader, as they try to identify the recent support and resistance levels in a stock. They generally buy at the support level and sell the stock at the resistance level.
- Moving Average Cross Over: In this, the traders execute trades based on the crossover of the moving averages. There are two moving averages, short-term and long-term. A combination of both moving averages indicates a buy and sell signal for a trader.
- Bollinger Band: The Bollinger Band indicates the overbought and oversold conditions in a stock. It helps a trader in identifying the selling point when the stock is in an overbought zone, and vice versa.
- Relative Strength Index: RSI is a momentum oscillator indicating the speed and change of price movement on a scale of 0-100. Generally, it is considered that 30 indicates an oversold zone, whereas 70 indicates an overbought zone. Traders execute their trades based on these parameters.
Read Also: Different Types of Trading in the Stock Market
Meaning of Long-Term Trading
Long-term trading is an investment strategy in which an investor or trader buys securities such as stocks, commodities, currencies, etc., for a period of more than one year. The primary objective of long-term investing is to create wealth, capital appreciation and regular income. The long-term trading depends on fundamental analysis.
Types of Long-Term Trading
The major types of long-term trading are as follows:
- Growth Investing: Under the growth type of long-term investing, the investor looks for stocks with high growth potential in the long run. These companies reinvest the profit earned by them in the business in order to expand further.
- Value Investing: It is a type of trading strategy in which one looks for stocks which are trading at less than their intrinsic value. It requires a deep fundamental analysis, including P/E, P/B, etc.
- Buy and Hold: In this type of strategy, the investor purchases the stock for the long term with an objective to create long-term wealth using the benefit of compounding.
- Dividend Investing: When an investor invests in a dividend-yielding company for a longer period of time to get the regular income in the form of dividends, this is known as dividend investing.
- Index Investing: Investing in index or passive funds in order to diversify their portfolio without worrying about stock picking is known as index investing. This type of investing is suitable for conservative investors.
Popular Long-Term Trading Indicator
The popular long-term trading indicators are as follows:
- EPS: Earnings per share is a key indicator used by the long-term investor, which indicates how much profit a company makes for each outstanding share. The higher the EPS the higher the profitability of the company.
- P/E Ratio: Price to Earnings Ratio of a company indicates the valuation of the stock price; it suggests whether it is fairly valued or not. An investor generally picks the stock based on valuation.
- ROE: Return on Equity indicates the company’s efficiency in generating profit using its equity. High ROE indicates the company’s efficient management. Investors look for companies with higher ROE.
- FCF: Free Cash Flow indicates what is left with the company after paying for its capital expenditure. Positive FCF indicates the company’s efficiency in generating profit.
Read Also: Difference Between Trading and Investing
Difference Between Short-Term Trading and Long-Term Trading
The key difference between short-term trading and long-term trading is as follows:
| Particular | Short-Term Trading | Long-Term Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | The primary objective of short-term trading is to earn a quick profit. | Long-term trading helps an investor create wealth in the long run. |
| Risk | Short-term trading involves higher risk. | As the investment duration is long, it carries lower risk. |
| Monitoring | Active monitoring is required in short-term trading. | As compared to short-term trading, long-term trading requires less monitoring. |
| Taxation | Equity investments, if sold before one year, are taxed at a rate of 20%. | In long-term trading, if the investments are sold after a period of one year, the gains are taxed at a rate of 12.5% over and above 125000. |
| Research | It depends on the technical analysis. | Long-term trading depends on fundamental analysis. |
Conclusion
On a concluding note, short-term and long-term trading have their own pros and cons. Choosing among them depends on the investment objective and risk profile of the investor. Traders generally give importance to technical analysis and believe in short-term profit. On the other hand, a long-term investor gives importance to the benefit of compounding and creates wealth in the long run. However, both of them carry different risks and require patience and discipline. Therefore, it is advisable to consult your investment advisor before investing in the stock market.
| S.NO. | Check Out These Interesting Posts You Might Enjoy! |
|---|---|
| 1 | Top 10 Intraday Trading Strategies & Tips for Beginners |
| 2 | Different Types of Trading in the Stock Market |
| 3 | What is Intraday Margin Trading? |
| 4 | Intraday Trading Rules and New SEBI Regulations |
| 5 | What Is Day Trading and How to Start With It? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is short-term trading?
Short-term trading means buying and selling different securities within a short period, which typically ranges from a few minutes to a few weeks.
Which carries more risk, short-term or long-term trading?
Short-term trading generally carries high risk, as short-term markets are highly volatile, but in the long run, volatility can be reduced.
Which strategy gives a high return?
A long-term trading strategy gives a steady but high return over time. However, short-term trading can give a quick return along with quick losses.
Is there any tax difference between short-term and long-term trading?
Yes, both long-term and short-term gains are taxed separately. Short-term equity gains are taxed at a rate of 20%, whereas long-term gains are taxed at a rate of 12.5% over and above 125000 INR of gains.
Which trading strategy is suitable for a beginner?
For a beginner, long-term trading is suitable as it is less volatile and more profitable. However, it totally depends on the investor’s risk profile.