Whenever we go to buy gold, our attention is mostly focused on its shine, design, and price. But the real question is is the gold truly pure? People, in particular, lack accurate information about 20-karat gold. Some mistake it for 22K, while others think it’s 24K. This blog has been written to clear up this confusion, so you can understand the purity of 20-karat gold, how to identify hallmarks, and what to keep in mind when buying it.
What is 20-Carat gold?
20-karat gold means that the gold is not entirely pure. It contains approximately 83.33% pure gold, while the remaining portion consists of other metals. These metals are added to make the jewelry more durable and less prone to damage. In simple terms, 100 grams of 20-karat gold contains approximately 83 grams of pure gold.
Easy Methods to Check 20-Carat Gold Purity at Home
1. Magnet Test
Real gold does not stick to a magnet. If your jewelry is attracted to a magnet, it may be impure.Some fake metals also do not stick to magnets, so this test is not entirely conclusive.
2. Water Test (Float Test)
Gold is heavy, so it sinks immediately when placed in water.
How to do it?: Take a bowl of water and drop the jewelry in. If it floats, you should be suspicious.
3. Vinegar Test
Put a little vinegar on the gold. If the color changes, it is not pure.
Wash the jewelry with clean water afterward. This is not a reliable purity test.
4. Skin Reaction Test
Many people say that wearing fake gold causes skin discoloration, but this method is not reliable. Skin reactions can also be caused by sweat and other chemicals.
Professional Methods for Accurate Purity Testing
1. XRF Machine Test
This is the most reliable and non-destructive method available today. Jewelers can check the complete composition of gold in just a few seconds using this machine. Since it doesn’t require cutting or damaging the jewelry, it is considered the safest method.
2. Acid Test
In this method, a special acid is applied to the gold, and its reaction is used to determine the purity. If done incorrectly, the jewelry can be damaged, so always have this test performed by an expert.
Testing at a BIS Assaying Center:
If you want 100% guaranteed results, get your jewelry tested at a nearby BIS-accredited laboratory.
Read Also: Gold Investment: How to Invest in Gold in India?
The difference between 18K, 20K, 22K and 24K.
| Carat | Accuracy (%) | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 18K | 75% | Fashion Jewelry |
| 20K | 83.33% | Limited Jewelery |
| 22K | 91.67% | Indian jewelry |
| 24K | 99.9% | Investments, coins |
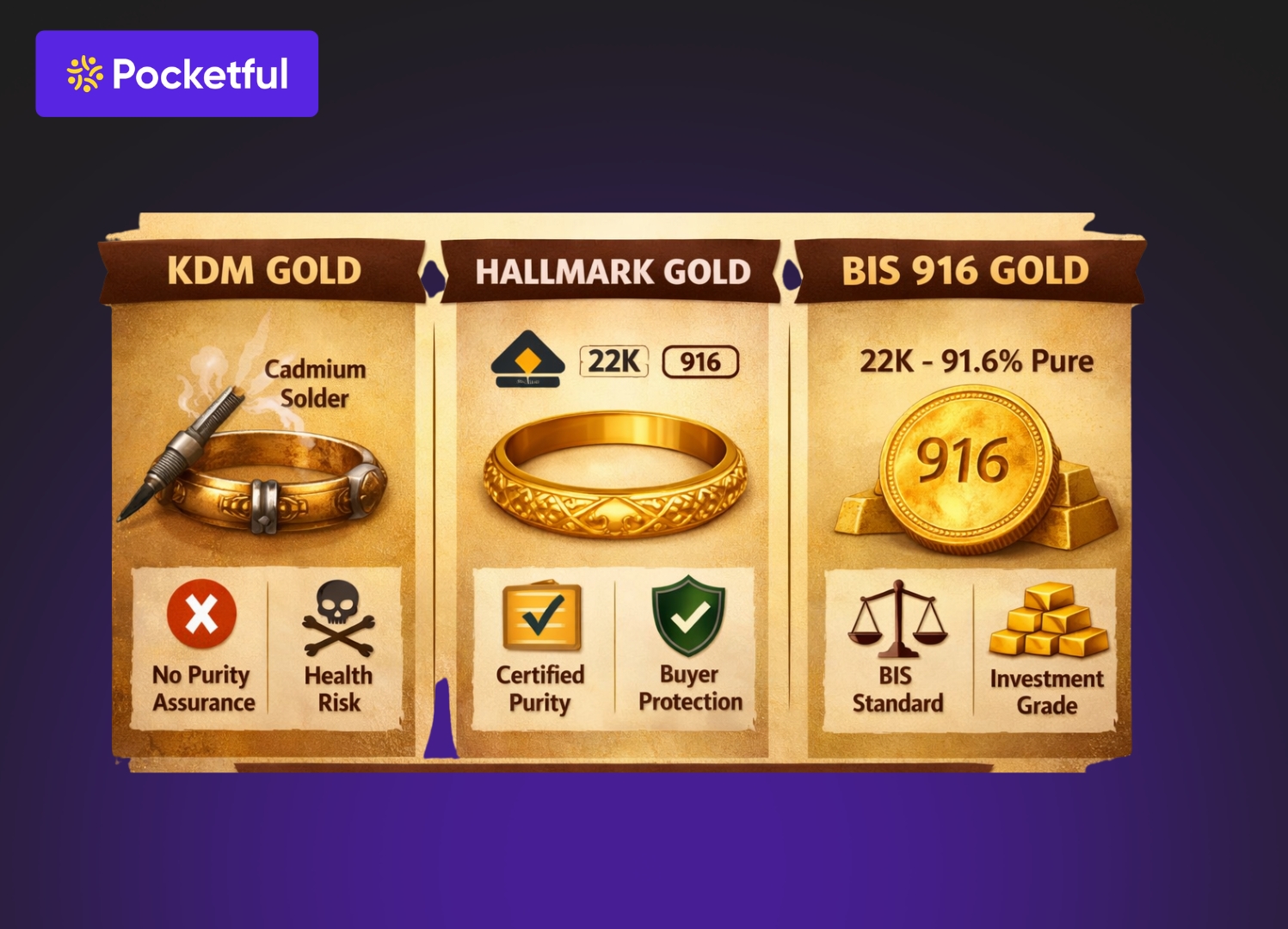
What is a 20 Carat Gold Hallmark?
A hallmark is an official mark that proves the purity of gold has been tested according to government standards. A 20-carat gold hallmark means that the purity of the jewelry has been tested in a laboratory.
Role of BIS
In India, the responsibility for hallmarking lies with the BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards). Gold is tested in BIS-accredited laboratories to ensure that customers receive the correct quality.
Why is Hallmarking Now Mandatory ?
The government has made hallmarking mandatory to protect customers from fraud. This ensures that the gold you are buying is of the correct purity.
Difference Between Hallmark and Purity Certificate
- Hallmark: An official mark stamped on the gold.
- Purity Certificate: A document provided by the shop.
A hallmark is more reliable because it is based on government standards.
How to identify the 20-karat gold hallmark sign?
- First, look for the BIS mark: Hold the jewelry in your hand and examine it carefully. There should be a small BIS logo on it. This indicates that the gold has been tested in a government-approved laboratory.
- Always check the purity number: 20-karat gold is usually marked with 20K or 833. This is its true identifier. If this number is missing, you should be suspicious.
- Look for the testing lab’s mark: Every hallmarked piece of jewelry has the mark of the center where it was tested. It’s small, but very important.
- There should also be a jeweler’s code: The shop from which you are buying the gold will also have a unique code in the hallmark. This identifies the seller of the jewelry.
- The markings should be clearly visible: If the markings are blurry, worn, or difficult to read, be cautious.
Smarter Gold Investment Options
Investing in Gold Mutual Funds
Gold mutual funds are funds that invest in gold ETFs or companies related to gold. You don’t need to buy physical gold with this option.
Advantages
- You can start investing with a small amount
- No worries about storage or theft
- Professional fund managers manage the money
Risks
- Returns depend on market performance
- Expense ratio is applicable
List of Top 5 Gold Mutual Funds available to invest
| Mutual Fund | NAV ( in INR ) | AUM ( in INR Cr.) | Expense Ratio | 1-year Return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBI Gold Fund | 43.68 | 10,770 | 0.23% | 79.13% |
| HDFC Gold ETF FoF | 44.66 | 8,500 | 0.18% | 79.23% |
| ICICI Prudential Regular Gold Savings Fund (FOF) | 45.65 | 4,480 | 0.09% | 79.10% |
| Nippon India Gold Savings Fund | 56.92 | 5,300 | 0.13% | 78.42% |
| Kotak Gold Fund | 57.37 | 5,210 | 0.16% | 78.19% |
Investing in Gold ETFs
Gold ETFs are traded on the stock exchange, just like shares. Their price is based on the price of gold.
Liquidity Advantage You can buy or sell it whenever you want, meaning you can access your money quickly.
Taxation
- Short-term tax if sold before 1 years
- Long-term capital gains tax after 1 years
Physical Gold vs. ETF
- No making charges in ETFs
- No concerns about purity
- Safe and transparent investment
| ETFs | NAV ( in INR ) | AUM ( in INR Cr.) | Expense Ratio | 1-year Return |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nippon India ETF Gold BeES | 118.01 | 39,900 | 0.8% | 73.54% |
| ICICI Prudential Gold ETF | 122.28 | 17,750 | 0.5% | 74.44% |
| SBI Gold ETF | 122.01 | 17,400 | 0.7% | 74.05% |
| HDFC Gold ETF | 122.19 | 18,500 | 0.59% | 78.93% |
| Kotak Gold ETF | 118.51 | 12,150 | 0.55% | 78.21% |
For investors who prefer a simple and cost-efficient way to invest, platforms like Pocketful allow you to invest in Gold ETFs with free account opening and zero brokerage on delivery trades, making long-term gold investing more convenient and transparent.
Read Also: What is Gold ETF? Meaning & How to Invest Guide
Common Mistakes Buyers Make
- Confusion between 20K and 22K: Many people confuse 20-karat and 22-karat gold, even though they have different levels of purity. This mistake can affect the price and resale value.
- Ignoring the Hallmark: Some buyers simply trust the jeweler’s word and don’t check the hallmark. Buying gold without a hallmark can be risky.
- Not checking the purity on the bill: Often, people receive a bill but don’t carefully read the karat details mentioned on it. This small mistake can lead to big problems later.
- Buying based solely on design: It’s common to be swayed by a beautiful design and forget to check the purity and weight, which is not the right approach.
- Relying on verbal promises: Avoid trusting statements like, “This is absolutely pure.” Always look for written proof and the hallmark.
Conclusion
Checking the purity of 20-karat gold isn’t difficult; you just need to know the right method. Recognizing hallmarks, performing basic tests at home, and getting a professional assessment when needed these three things can protect you from making a bad purchase. If you take a few precautions yourself, you won’t have to blindly trust the jeweler’s word. Making an informed choice is true wisdom.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is 20-carat gold considered pure gold?
No. 20-carat gold contains 83.33% pure gold, with the remaining portion made of other metals like copper or silver. It is purer than 18K but less pure than 22K or 24K.
Is 20K gold hallmarked in India?
Yes. Under BIS rules, 20-carat gold can be hallmarked, provided it is tested at a BIS-accredited assaying center and carries all required marks such as BIS logo, purity mark (20K or 833), jeweler code, and lab mark.
Is 20-carat gold good for investment purposes?
Not really. For investment, 24K gold (coins, bars, ETFs) is preferred due to higher purity and better resale value. 20K gold is more suitable for limited jewelry use rather than long-term investment.
How can I differentiate 20K gold from 22K gold easily?
Check the purity mark on the jewelry.20K gold is marked 20K or 833 22K gold is marked 22K or 916Never rely on appearance alone, as both can look similar.
Does 20-carat gold have good resale value?
Yes, but it is lower than 22K and 24K gold. During resale, the value is calculated based on the actual gold content (83.33%) and prevailing gold rates, after deducting making charges if applicable.