When planning to invest, you need to compare the options before you. This comparison should be based on your goals, risk appetite, and return expectations. Doing this helps you choose the right asset, instead of following market noise.
But here is a question many investors miss. Do you know which assets stand out at a global level? Many of them fall under stocks, but not all stocks carry the same weight. This is where understanding the top assets by market cap becomes important. It shows which assets dominate globally and why investors continue to trust them.
So, if you are looking to start your investment journey with the right information, read this guide. Find the assets that are at the top of the charts and have been heavily invested in the market for years. So, let us explore the details now.
Top 10 Assets by Market Cap Worldwide
When you start comparing investment options, numbers bring clarity. Market cap is one such number that tells you how big an asset truly is in the global market. It reflects total value, investor confidence, and long-term demand.
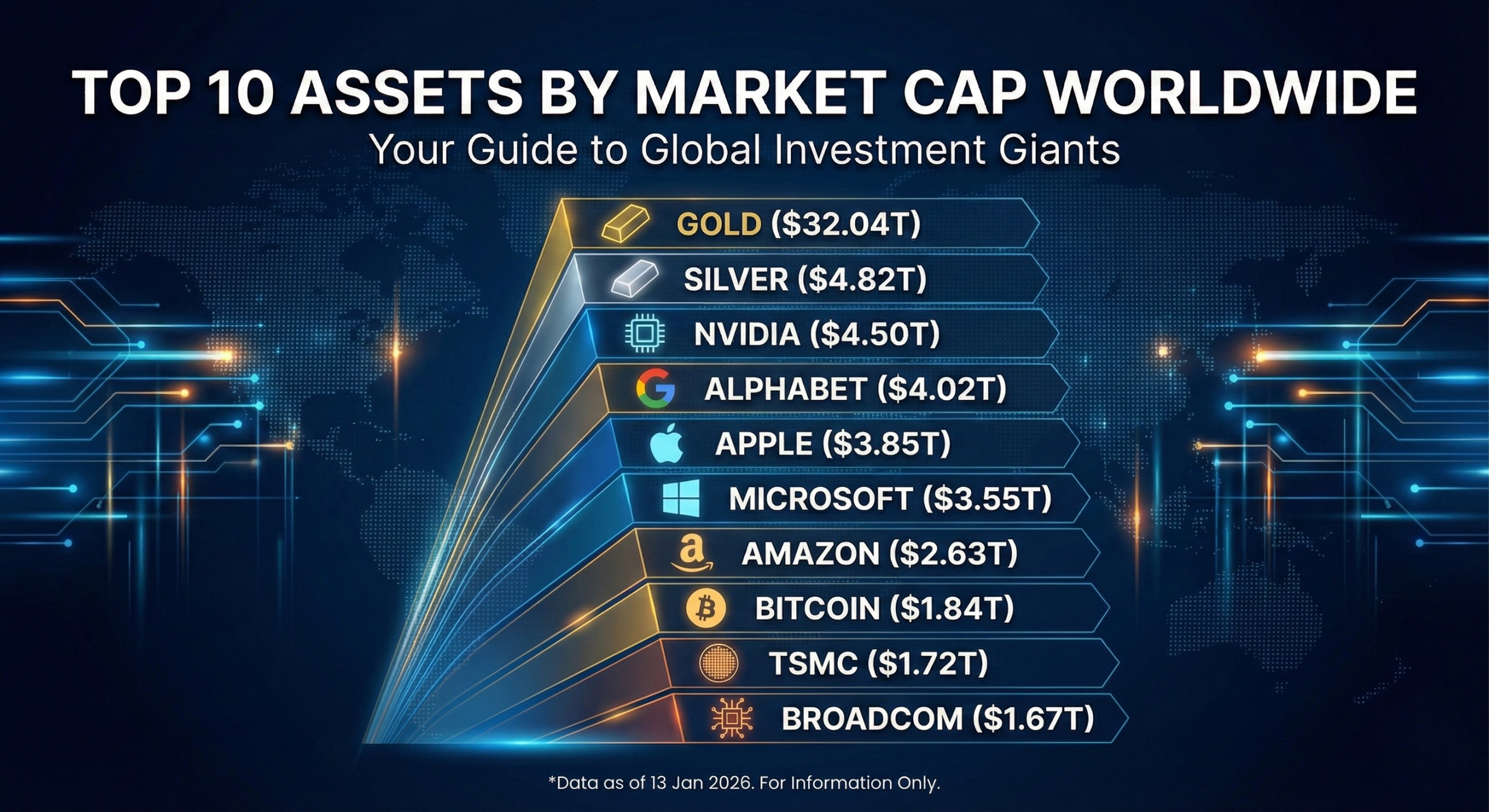
Looking at the top assets by market cap helps you understand which assets dominate globally and why they continue to attract large pools of capital. This view puts stocks, commodities, and digital assets on the same scale for easy comparison.
| Asset Name | Asset Price (USD) | Market Cap (USD Trillion) |
|---|---|---|
| Gold | $4,608 per oz | 32.04 |
| Silver | $85.58 per oz | 4.82 |
| NVIDIA | 185.00 | 4.50 |
| Alphabet | 333.00 | 4.02 |
| Apple | 260.00 | 3.85 |
| Microsoft | 477.00 | 3.55 |
| Amazon | 246.00 | 2.63 |
| Bitcoin | 91,768.00 | 1.84 |
| TSMC | 332.00 | 1.72 |
| Broadcom | 352.00 | 1.67 |
Note: The data shared above is as of 13 January 2026. This is for information only. Market prices and market capitalisation change frequently. It is important to check all the details well before investing.
1. Gold
Gold sits at the top of the global asset list for a reason. It is widely used as a hedge during inflation, currency stress, and geopolitical uncertainty. Central banks continue to increase their gold reserves to reduce reliance on paper currencies. It is one with a long history, limited supply, and universal acceptance. This makes it a core anchor asset in global portfolios.
2. Silver
Silver is not just a precious metal to invest in. It is also one of the major raw materials for industries. It is a metal whose demand is generated from sectors like renewable energy, electronics, and electric vehicles. This dual role makes silver more precious in nature. This also makes it more sensitive to economic cycles than gold. At the same time, limited supply and rising industrial use have helped silver maintain a strong position among the top global assets.
3. NVIDIA
NVIDIA has become one of the most influential companies in the world due to its role in artificial intelligence infrastructure. It manufactures chips that power data centres, AI models, and high-performance computing systems. Investors view NVIDIA as a long-term beneficiary. This is one of the companies that is seen to stay agile during the rapid global shift. Its contribution towards automation, AI-driven services, and advanced computing across industries makes it a leader.
4. Alphabet (Google)
Alphabet controls platforms that billions of users rely on every day. Search, video, and digital advertising form the backbone of its business. Its ability to monetise user intent at scale gives it a strong competitive edge. It is a company that has a great investment in artificial intelligence and cloud services. All these support its position as one of the most valuable global assets.
5. Apple
Apple is known for its innovation. It is a trendsetter in the market. It is one of the brands whose products and services are known for quality. This creates stable revenue and high margins. Beyond hardware, services like subscriptions and payments add predictable income. Investors value Apple for its consistency and brand trust. At the same time, its ability to generate cash even in slower economic phases makes it a great choice for investors.
6. Microsoft
Microsoft plays a critical role in both personal and enterprise computing. Its software products are deeply embedded in workplaces worldwide. Cloud services have become a major growth driver for the company. This is mainly because all the companies are now moving workloads online. Strategic focus on artificial intelligence has further strengthened its relevance. This makes it a key pillar of the global technology landscape.
7. Amazon
Amazon operates at the intersection of retail, logistics, and cloud computing. While online shopping built its brand, cloud services drive much of its profitability. Many businesses rely on Amazon’s Cloud infrastructure. This is one of the reasons why Amazon’s cloud platform is becoming more central. Its scale, efficiency, and ability to reinvest profits support its long-term global valuation.
8. Bitcoin
Bitcoin has moved beyond being a niche digital asset. It is now tracked and held by institutions as an alternative store of value. Its fixed supply and decentralised nature attract investors looking for protection against currency dilution. Though volatile, Bitcoin’s growing acceptance has secured its place among the world’s top assets.
9. TSMC
TSMC sits at the core of the global semiconductor supply chain. Many leading technology companies depend on it. This is mainly because of its advanced chip manufacturing. So, as the demand for AI, smartphones, and data centres increases, there will be more demand for this company. Hence, TSMC’s importance continues to grow. Its technical expertise and scale make it one of the most critical companies in modern technology.
10. Broadcom
Broadcom focuses on the infrastructure that is the base for many businesses. It is a company that connects and powers data centres. Its products enable high-speed communication between servers and networks. As cloud computing and AI workloads expand, this connectivity becomes essential. Broadcom’s valuation reflects its behind-the-scenes role in supporting the digital systems that global businesses rely on every day.
Read Also: What is an Underlying Asset?
Why Market Cap Matters When Choosing an Asset
Market cap is more than a ranking metric. It helps you understand how an asset behaves, how much confidence it commands, and where it fits in your portfolio. When you look at market cap alongside risk and return, decision-making becomes more grounded.
1. Shows the True Size of an Asset
Market cap tells you the total value of an asset in the market. This prevents confusion caused by high or low unit prices and gives a realistic view of scale.
2. Reflects Long-Term Investor Confidence
Assets with larger market caps usually attract institutional money. This indicates sustained trust rather than short-term speculation.
3. Helps Assess Volatility and Risk
Larger market cap assets tend to move more steadily. Smaller ones may offer higher returns but usually come with sharper price swings.
4. Enables Fair Comparison Across Asset Classes
Market cap places stocks, metals, and digital assets on one scale. This makes cross-asset comparison simpler and more meaningful.
5. Supports Smarter Portfolio Allocation
Understanding market cap helps balance stability and growth. It allows you to combine safer assets with selective risk based on your goals.
How to Select Assets While Investing
Choosing the right asset is not about following what is popular. But it is about making a choice that is better for you and your portfolio. So, here are some of the steps that you should consider when you select an asset for your portfolio:
1. Define Your Investment Goal
Find and understand what your investment goal is. Know whether it is a short-term or long-term goal that you are trying to meet. It can be wealth creation or meeting some expenses in short run.
2. Understand Your Risk Tolerance
Every asset carries risk. Assess the amount of fluctuation and volatility. Once you know this, you will be able to understand the risk you are taking. Match it with your capacity, and you can find the right asset.
3. Evaluate Return Expectations
Set realistic return expectations. It will ensure that you plan as per the returns you expect. Also, setting the right expectations will avoid any kind of speculation, which is all you need for better planning.
4. Consider Time Horizon
Short-term and long-term investing need different assets. Longer horizons allow you to absorb market swings more easily.
5. Use Market Cap as a Filter
Market cap helps you judge stability and scale. Combine it with other factors to build a well-balanced portfolio.
Conclusion
Understanding the top assets by market cap helps you see where global capital is concentrated and why certain assets hold long-term importance. But it is important to note that rankings alone are not enough. You must consider various other aspects as well. This will help you to create the right portfolio.
And if you are looking for some support and guidance, register on Pocketful. It is the perfect platform to compare assets, track market data, and build a portfolio that fits your risk and return expectations before committing your capital.
| S.NO. | Check Out These Interesting Posts You Might Enjoy! |
|---|---|
| 1 | What Is the National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange (NCDEX)? |
| 2 | MCX Trading: What is it? MCX Meaning, Features & More |
| 3 | Top Tips for Successful Margin Trading in India |
| 4 | What is Commodity Market in India? |
| 5 | What is Intraday Trading? |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the top assets by market cap worldwide?
The top assets by market cap include a mix of commodities, large global companies, and digital assets. These assets stand out due to their size, long-term demand, and strong investor participation across global markets.
Why is market cap important while comparing assets?
Market cap shows the overall value and scale of an asset. It helps investors judge stability, market acceptance, and relative importance beyond just the asset price.
Do high market cap assets always give better returns?
Not always. High market cap assets are usually more stable, but returns depend on timing, market conditions, and investment horizon.
Can beginners use market cap to select investments?
Yes. Market cap is a useful starting point for beginners as it provides clarity on asset size and risk. It should be used along with goals and risk assessment.
How can Pocketful help while analysing assets?
Pocketful helps you compare assets, track market movements, and review key metrics in one place. This makes it easier to evaluate options before investing.